 42 citations,
December 2007 in “American Journal of Psychiatry”
42 citations,
December 2007 in “American Journal of Psychiatry” Finasteride may effectively reduce Tourette's syndrome symptoms and improve life quality.
 13 citations,
November 2013 in “Seizure: European Journal of Epilepsy”
13 citations,
November 2013 in “Seizure: European Journal of Epilepsy” Levetiracetam may cause hair loss, which can potentially reverse with lower doses or stopping the drug.
 97 citations,
July 2006 in “Dermatologic therapy”
97 citations,
July 2006 in “Dermatologic therapy” The document concludes that accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment are important for skin problems in women with PCOS.
 37 citations,
February 2014 in “Journal of Dermatology”
37 citations,
February 2014 in “Journal of Dermatology” Valproic acid increases hair count in men with hair loss.
 35 citations,
August 2004 in “Epilepsy & behavior”
35 citations,
August 2004 in “Epilepsy & behavior” Extended-release divalproex is better tolerated and more effective for seizures and psychiatric symptoms than delayed-release divalproex, but doesn't reduce hair loss.
 31 citations,
January 2016 in “Drugs - Real World Outcomes”
31 citations,
January 2016 in “Drugs - Real World Outcomes” Some new oral anticoagulants may also cause hair loss and might not be better than traditional ones for preventing hair loss.
 19 citations,
February 2007 in “International Clinical Psychopharmacology”
19 citations,
February 2007 in “International Clinical Psychopharmacology” Quetiapine may cause hair loss, a side effect not widely recognized before.
 16 citations,
March 2006 in “The American journal of psychiatry”
16 citations,
March 2006 in “The American journal of psychiatry” Lowering the dose of ziprasidone can cause sudden restlessness and urge to move in patients.
 12 citations,
February 2001 in “Annals of Pharmacotherapy”
12 citations,
February 2001 in “Annals of Pharmacotherapy” No effective treatment for hair loss after childbirth was found, but it usually gets better on its own and some cosmetic methods might help.
 9 citations,
August 2006 in “American Journal of Psychiatry”
9 citations,
August 2006 in “American Journal of Psychiatry” A woman's hair loss stopped after she stopped taking lamotrigine, suggesting it might cause hair loss.
 6 citations,
October 1997 in “CNS Drugs”
6 citations,
October 1997 in “CNS Drugs” Psychotropic drugs can cause hair loss or excessive hair growth.
 4 citations,
January 2018 in “General Physiology and Biophysics”
4 citations,
January 2018 in “General Physiology and Biophysics” The steroids allopregnanolone and allotetrahydrodeoxycorticosteron worsened absence seizures in rats.
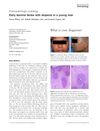 3 citations,
April 2016 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
3 citations,
April 2016 in “International Journal of Dermatology” A young man was diagnosed with trichoepitheliomas, causing thick skin and hair loss.
 2 citations,
April 2017 in “Asian Journal of Psychiatry”
2 citations,
April 2017 in “Asian Journal of Psychiatry” Valproic acid can cause hair loss when taken orally but may promote hair growth when applied topically.
 1 citations,
May 2011 in “Journal of Human Reproductive Sciences”
1 citations,
May 2011 in “Journal of Human Reproductive Sciences” Finasteride may decrease semen quality but not harm sperm production, and stopping the drug can improve semen quality; hyperprolactinemia can cause infertility but is treatable with medication.
 June 2023 in “British journal of dermatology/British journal of dermatology, Supplement”
June 2023 in “British journal of dermatology/British journal of dermatology, Supplement” Two sisters with lipoedematous scalp suggest a genetic influence in the condition.
 May 2012 in “The journal of nervous and mental disease”
May 2012 in “The journal of nervous and mental disease” The book provides comprehensive information on Impulse Control Disorders but lacks definitive evidence for effective treatments.
 August 1994 in “Drugs & Therapy Perspectives”
August 1994 in “Drugs & Therapy Perspectives” Some drugs can cause hair loss or growth, but hair usually returns to normal after stopping the drug.
 991 citations,
January 2011 in “Nature Reviews Endocrinology”
991 citations,
January 2011 in “Nature Reviews Endocrinology” The document concludes that PCOS is a complex disorder caused by both genetic and environmental factors, affecting women's health in various ways, and requires personalized treatment.
 356 citations,
September 2014 in “Journal of Clinical Research in Pediatric Endocrinology”
356 citations,
September 2014 in “Journal of Clinical Research in Pediatric Endocrinology” Childhood obesity is rising globally due to various factors, and early prevention and healthy lifestyle changes are crucial.
 320 citations,
December 2018 in “Frontiers in Immunology”
320 citations,
December 2018 in “Frontiers in Immunology” Changing how mesenchymal stromal cells are grown can improve their healing abilities.
 291 citations,
January 2014 in “The Scientific World Journal”
291 citations,
January 2014 in “The Scientific World Journal” Lichen Planus is a less common condition affecting skin and mucous membranes, with various types and associated risk factors, challenging to diagnose, significantly impacts life quality, and may have a risk of cancerous changes in oral lesions.
 179 citations,
September 1998 in “BMJ”
179 citations,
September 1998 in “BMJ” Hair loss in men is common, treatable, but not curable.
 110 citations,
August 2016 in “Drugs”
110 citations,
August 2016 in “Drugs” Minoxidil is the only FDA-approved topical drug for treating male or female pattern hair loss, and other medications like finasteride and dutasteride can also increase hair growth.
 100 citations,
September 2017 in “Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology”
100 citations,
September 2017 in “Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology” Male hormones and their receptors play a key role in hair loss and skin health, with potential new treatments being explored.
 88 citations,
April 2017 in “Journal of Pediatric and Adolescent Gynecology”
88 citations,
April 2017 in “Journal of Pediatric and Adolescent Gynecology” The document concludes that early diagnosis and treatment of Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia are crucial for preventing serious health issues and improving patient outcomes.
 86 citations,
August 2014 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
86 citations,
August 2014 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” To diagnose hair loss, use a systematic approach including history, exams, and tests.
 82 citations,
October 2019 in “Frontiers in Immunology”
82 citations,
October 2019 in “Frontiers in Immunology” Changes to the Foxp3 protein affect how well regulatory T cells can control the immune system, which could help treat immune diseases and cancer.
 80 citations,
March 2004 in “Neuropediatrics”
80 citations,
March 2004 in “Neuropediatrics” Coats' Plus is a genetic disorder with eye abnormalities, brain calcification, poor growth, bone and skin issues, and movement disorders.
 75 citations,
June 1999 in “Pediatric Clinics of North America”
75 citations,
June 1999 in “Pediatric Clinics of North America” The document concludes that early recognition and treatment of PCOS in adolescents is crucial for managing symptoms and long-term health risks.






























