1010 citations,
August 2000 in “Cell” Hair follicle stem cells can form both hair follicles and skin.
 April 2023 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
April 2023 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Aging changes skin cells, leading to different DNA methylation and gene activity, affecting cell metabolism and aging signs.

Sensory neuron and Merkel cell changes in the skin happen independently during normal skin maintenance.
 1 citations,
April 2022 in “Regenerative Therapy”
1 citations,
April 2022 in “Regenerative Therapy” Activating the GDNF-GFRα1-RET signaling pathway could potentially promote skin and limb regeneration in humans and could be used to treat hair loss and promote wound healing.

Sensory neuron and Merkel-cell changes in the skin happen independently during normal skin maintenance.

Sensory neuron and Merkel cell changes in the skin happen independently during normal skin maintenance.

Sensory neuron changes and Merkel-cell changes in the skin happen independently during normal skin maintenance.

Sensory neuron remodeling and Merkel-cell changes in the skin happen independently.
 34 citations,
December 2012 in “Indian Journal of Dermatology, Venereology and Leprology”
34 citations,
December 2012 in “Indian Journal of Dermatology, Venereology and Leprology” Mesotherapy shows promise for cellulite and facial rejuvenation but has mixed results for body sculpting and hair loss, with more research needed for safety and effectiveness.
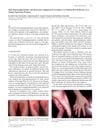 16 citations,
January 2008 in “Acta dermato-venereologica”
16 citations,
January 2008 in “Acta dermato-venereologica” Vitamin B12 deficiency can cause skin darkening and increased blood vessels, but treatment can improve symptoms.
 14 citations,
November 2013 in “PloS one”
14 citations,
November 2013 in “PloS one” HGF/SF increases skin melanocytes but doesn't change melanin type or amount.
 6 citations,
December 2016 in “Springer eBooks”
6 citations,
December 2016 in “Springer eBooks” Environmental stressors like UV radiation, pollution, and extreme temperatures can damage skin and lead to diseases and aging.
 232 citations,
October 2015 in “International journal of molecular sciences”
232 citations,
October 2015 in “International journal of molecular sciences” Stem cells are crucial for skin repair and new treatments for chronic wounds.
 96 citations,
July 2014 in “Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Medicine”
96 citations,
July 2014 in “Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Medicine” The document concludes that adult mammalian skin contains multiple stem cell populations with specific markers, important for understanding skin regeneration and related conditions.
 71 citations,
September 2006 in “Cell Transplantation”
71 citations,
September 2006 in “Cell Transplantation” Fetal skin cells from a cell bank heal wounds faster and with less scarring than adult cells.
 28 citations,
September 2015 in “Wiener Klinische Wochenschrift”
28 citations,
September 2015 in “Wiener Klinische Wochenschrift” New skin substitutes for treating severe burns and chronic wounds are being developed, but a permanent solution for deep wounds is not yet available commercially.
 27 citations,
May 2006 in “Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications”
27 citations,
May 2006 in “Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications” Wnt-10b is important for starting hair growth and developing hair follicles.
 23 citations,
May 2016 in “American Journal of Pathology”
23 citations,
May 2016 in “American Journal of Pathology” The research suggests that a specific skin gene can be controlled by signals within and between cells and is wrongly activated in certain skin diseases.
 10 citations,
November 2018 in “Genetics in medicine”
10 citations,
November 2018 in “Genetics in medicine” Lack of cystatin M/E causes thin hair and dry skin.
 9 citations,
November 2018 in “Drug Discovery Today”
9 citations,
November 2018 in “Drug Discovery Today” Using skin stem cells and certain molecules might lead to scar-free skin healing.
 2 citations,
April 2009 in “Bulletin of Experimental Biology and Medicine”
2 citations,
April 2009 in “Bulletin of Experimental Biology and Medicine” Flamena, a liposomal mix, helps skin heal better after a chemical burn.

Skin stem cells are crucial for maintaining and repairing skin, with potential for treating skin disorders and improving wound healing.
 208 citations,
January 2013 in “Lab on a Chip”
208 citations,
January 2013 in “Lab on a Chip” The Multi-Organ-Chip improves the growth and quality of skin and hair in the lab, potentially replacing animal testing.
 60 citations,
January 2004 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
60 citations,
January 2004 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” Applying a specific inhibitor lightens skin and hair color.
 56 citations,
February 2012 in “Cell Cycle”
56 citations,
February 2012 in “Cell Cycle” MicroRNAs are crucial for controlling skin development and healing by regulating genes.
 37 citations,
February 2019 in “Experimental Dermatology”
37 citations,
February 2019 in “Experimental Dermatology” Spiny mice are better at regenerating hair after injury than laboratory mice and could help us understand how to improve human skin repair.
 20 citations,
June 2016 in “Magnesium research”
20 citations,
June 2016 in “Magnesium research” Hair follicles help magnesium get through the skin more effectively.
 13 citations,
April 2022 in “Frontiers in oncology”
13 citations,
April 2022 in “Frontiers in oncology” Melanoma development can be linked to the breakdown of skin's melanin-producing units.
 6 citations,
March 1999 in “Journal of pediatric health care”
6 citations,
March 1999 in “Journal of pediatric health care” The document emphasizes the need for primary care providers to understand and care for African American children's hair and skin to boost their self-esteem.
 66 citations,
May 2021 in “Science Advances”
66 citations,
May 2021 in “Science Advances” Different scaffold patterns improve wound healing and immune response in mouse skin, with aligned patterns being particularly effective.




























