 1 citations,
June 2021 in “Journal of dermatology and dermatitis”
1 citations,
June 2021 in “Journal of dermatology and dermatitis” Tyrosine kinase inhibitors show promise in treating some skin diseases but their definitive role in dermatology is still unclear.
 2 citations,
June 2005 in “Clinical Oncology”
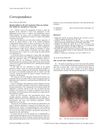
2 citations,
June 2005 in “Clinical Oncology” A man's bald spot grew hair after starting cancer treatment with gefitinib.
 April 2024 in “Journal of pharmacy & pharmacognosy research”
April 2024 in “Journal of pharmacy & pharmacognosy research” A compound from Calophyllum inophyllum L. leaf may help treat non-small cell lung cancer.

New cancer drugs can cause skin side effects like rashes, dry skin, hair changes, and nail problems.
 May 2021 in “International journal of developmental research”
May 2021 in “International journal of developmental research” Estrogens and progesterone are key in regulating melasma pigmentation.
 88 citations,
July 2014 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
88 citations,
July 2014 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Targeted cancer therapies often cause skin reactions, so dermatologists must manage these effects.
22 citations,
May 2011 in “European Journal of Cancer” The drug combination was safe and showed promise in treating advanced tumors.
508 citations,
June 2009 in “Current drug metabolism” Tyrosine kinase inhibitors effectively treat cancers but often cause skin and other side effects.
 2 citations,
January 2023 in “International journal of biological sciences”
2 citations,
January 2023 in “International journal of biological sciences” Gray hair can potentially be reversed, leading to new treatments.
 November 2023 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
November 2023 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” Blocking TYK2 might be a new way to treat hair loss from alopecia areata.
 January 2021 in “Journal of Cancer Therapy”
January 2021 in “Journal of Cancer Therapy” Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors are effective against cancer but can cause skin, digestive, and blood side effects, including hair loss.
 November 2022 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
November 2022 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” TYK2 inhibition may help treat alopecia areata by promoting hair growth and reducing immune response.
October 2021 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Blocking IL-12 can help treat alopecia areata by preventing hair follicle immune issues.
 32 citations,
September 2015 in “Dermatology”
32 citations,
September 2015 in “Dermatology” Certain leukemia drugs can cause severe skin reactions that may require stopping treatment.
July 2022 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Inhibiting TYK2 can restore hair growth in alopecia areata.
4 citations,
February 2018 in “World journal of surgical oncology” A young woman with kidney cancer experienced rare hair loss from a cancer drug and unusual cancer spread, suggesting early drug treatment might reduce spread and prolong survival.
 26 citations,
October 2018 in “Clinical & Translational Oncology”
26 citations,
October 2018 in “Clinical & Translational Oncology” Spanish experts provided guidelines for treating skin side effects in cancer patients on new therapies, stressing early action and teamwork.
December 2023 in “Journal of clinical medicine” Some leukemia treatments can cause skin reactions similar to keratosis pilaris.
 9 citations,
May 2013 in “JAMA Dermatology”
9 citations,
May 2013 in “JAMA Dermatology” A woman's hair turned white after taking a cancer drug called dasatinib.
 12 citations,
November 2006 in “Journal of thoracic oncology”
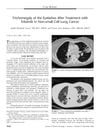
12 citations,
November 2006 in “Journal of thoracic oncology” A cancer patient's eyelashes grew excessively without other common side effects after taking the cancer drug erlotinib.
 7 citations,
May 2022 in “PLOS ONE”
7 citations,
May 2022 in “PLOS ONE” Certain genes and pathways are linked to the production of finer and denser wool in Hetian sheep.
 June 2023 in “Frontiers in Medicine”
June 2023 in “Frontiers in Medicine” Protein tyrosine kinases are key in male pattern baldness, affecting skin structure, hair growth, and immune responses.
 March 2023 in “Research Square (Research Square)”
March 2023 in “Research Square (Research Square)” Immune changes and specific genes contribute to male hair loss.
4 citations,
December 2020 in “Natural Product Sciences” The method identified and measured ten compounds from Eclipta prostrata, showing significant enzyme inhibitory effects.
 65 citations,
February 2009 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
65 citations,
February 2009 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” Anti-acne medications may work by reducing the activity of a protein involved in acne development.
65 citations,
September 2014 in “BMC genomics” Different hair types in mammals are linked to variations in specific protein genes, with changes influenced by their living environments.
 1066 citations,
March 2010 in “Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology”
1066 citations,
March 2010 in “Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology” MicroRNAs are crucial in controlling cell signaling, affecting cancer and tissue regeneration.
Hairless mammals evolved quickly in both gene and non-gene areas related to skin and hair.
 September 2023 in “Medicine”
September 2023 in “Medicine” The research suggests immune system changes and specific gene expression may contribute to male hair loss, proposing potential new treatments.
36 citations,
October 2015 in “Cell reports” Gab1 protein is crucial for hair growth and stem cell renewal, and Mapk signaling helps maintain these processes.




















