 April 2023 in “Dermatologica Sinica”
April 2023 in “Dermatologica Sinica” Sex hormones affect hair growth and loss, and treatments for related hair diseases include various medications, hair transplantation, and light therapy.
 March 2022 in “Wound practice & research”
March 2022 in “Wound practice & research” New treatments for alopecia areata show promise, but standardized guidelines are needed.
 October 2021 in “Cosmoderma”
October 2021 in “Cosmoderma” Hair loss can be managed with treatments like minoxidil, finasteride, and others, but there are still gaps in effectiveness and off-label usage is increasing.
 January 2017 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology Symposium Proceedings”
January 2017 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology Symposium Proceedings” The 2015 Hair Research Congress concluded that stem cells, maraviroc, and simvastatin could potentially treat Alopecia Areata, topical minoxidil, finasteride, and steroids could treat Frontal Fibrosing Alopecia, and PTGDR2 antagonists could also treat alopecia. They also found that low-level light therapy could help with hair loss, a robotic device could assist in hair extraction, and nutrition could aid hair growth. They suggested that Alopecia Areata is an inflammatory disorder, not a single disease, indicating a need for personalized treatments.
March 2023 in “Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology” Spironolactone can effectively treat hair loss with manageable side effects.
October 2022 in “The Korean Journal of Physiology and Pharmacology” Targeting the PGD2-DP2 pathway may help treat hair loss.
October 2022 in “Cosmoderma”  January 2022 in “Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology”
January 2022 in “Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology” A mix of methotrexate, corticosteroids, and topical minoxidil effectively treated severe total body hair loss, but caused stretch marks and needs long-term monitoring.
January 2022 in “Springer eBooks” January 2020 in “Global dermatology” The growth factor cocktail significantly increased hair growth in patients with androgenetic alopecia.
 April 2017 in “Australasian Journal of Dermatology”
April 2017 in “Australasian Journal of Dermatology” Different skin conditions show distinct types of vessel inflammation, a new quality of life index for vulval disease is reliable, a certain intrauterine system might be linked to chronic vaginal yeast infections, and oral minoxidil reduces hair loss in women.
 96 citations,
October 1981 in “Drugs”
96 citations,
October 1981 in “Drugs” Minoxidil effectively treats severe hypertension but may cause side effects, so careful monitoring is needed.
 57 citations,
January 1980 in “Journal of Cardiovascular Pharmacology”
57 citations,
January 1980 in “Journal of Cardiovascular Pharmacology” Minoxidil treats high blood pressure and side effects can be managed.
 10 citations,
June 2011 in “Archives of Dermatology”
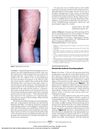
10 citations,
June 2011 in “Archives of Dermatology” Finasteride caused blisters on hands and feet.
 29 citations,
February 2017 in “International Journal of Women's Dermatology”
29 citations,
February 2017 in “International Journal of Women's Dermatology” Women with excessive male-pattern hair growth should get a full hormone check-up to find and treat any underlying issues, considering both medical and emotional aspects.
 22 citations,
August 2011 in “Endocrine Practice”
22 citations,
August 2011 in “Endocrine Practice” Most hirsutism cases are due to PCOS, and treatment focuses on lowering testosterone and blocking its effects.
 5 citations,
June 2015 in “International Journal of Women's Dermatology”
5 citations,
June 2015 in “International Journal of Women's Dermatology” Hirsutism, excessive hair growth in women, is often caused by PCOS and can be managed with medication and personalized treatment plans.
 June 2003 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology Symposium Proceedings”
June 2003 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology Symposium Proceedings” Advancements in hair biology include new treatments and tools for hair growth and alopecia.
 152 citations,
April 2012 in “Recent Patents on Inflammation & Allergy Drug Discovery”
152 citations,
April 2012 in “Recent Patents on Inflammation & Allergy Drug Discovery” Minoxidil treats hair loss, promotes growth, has side effects, and has recent patents.
 35 citations,
March 2005 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
35 citations,
March 2005 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Potassium channel openers like minoxidil help hair grow by acting on hair follicles.
 25 citations,
January 2013 in “International Journal of Trichology”
25 citations,
January 2013 in “International Journal of Trichology” Premature balding in some men may be linked to altered hormones, but it's not the male equivalent to polycystic ovary syndrome or metabolic syndrome.
 18 citations,
June 2010 in “Current medicinal chemistry”
18 citations,
June 2010 in “Current medicinal chemistry” Treating hirsutism in women often requires a mix of medications and cosmetic methods for best results.
 16 citations,
May 2011 in “Dermatologic therapy”
16 citations,
May 2011 in “Dermatologic therapy” Effective treatments for severe alopecia areata are still lacking.
 12 citations,
January 2004 in “Reproductive biomedicine online”
12 citations,
January 2004 in “Reproductive biomedicine online” Low-dose anti-androgen drugs and certain drug combinations are effective for hirsutism, and insulin sensitizers show promise, especially for those with polycystic ovarian syndrome.
 2 citations,
November 1998 in “Journal of The European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
2 citations,
November 1998 in “Journal of The European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” A patient with a severe type of hair loss experienced partial hair regrowth after treatment with a specific light therapy and a medication called interferon α2a.
 November 1998 in “Journal of The European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
November 1998 in “Journal of The European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” A man's skin cancer improved and some of his hair grew back after treatment with a special light therapy and a medication.
 232 citations,
June 1975 in “Journal of Steroid Biochemistry”
232 citations,
June 1975 in “Journal of Steroid Biochemistry” Cyproterone acetate is effective for acne but less so for hirsutism and alopecia, with some side effects and quick menstrual cycle recovery after treatment.
 101 citations,
January 1997 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology Symposium Proceedings”
101 citations,
January 1997 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology Symposium Proceedings” Nerves and chemicals in the body can affect hair growth and loss.
 86 citations,
December 2001 in “Experimental dermatology”
86 citations,
December 2001 in “Experimental dermatology” Mutant mice help researchers understand hair growth and related genetic factors.
 66 citations,
June 2010 in “Experimental Dermatology”
66 citations,
June 2010 in “Experimental Dermatology” The hair follicle is a great model for research to improve hair growth treatments.

























