 16 citations,
January 2015 in “Current problems in dermatology”
16 citations,
January 2015 in “Current problems in dermatology” Alopecia Areata is an autoimmune hair loss condition that needs more research for better treatments.
 11 citations,
September 2021 in “Anais Brasileiros de Dermatologia”
11 citations,
September 2021 in “Anais Brasileiros de Dermatologia” The conclusion is that early diagnosis of skin signs linked to diseases like Lupus, Dermatomyositis, and Rheumatoid Arthritis is crucial to prevent serious complications.
 34 citations,
June 2014 in “The BMJ”
34 citations,
June 2014 in “The BMJ” Pregnancy can change skin disease severity, with some conditions improving and others worsening, and treatment should balance benefits and fetal safety.
 December 2024 in “Journal of Population Therapeutics and Clinical Pharmacology”
December 2024 in “Journal of Population Therapeutics and Clinical Pharmacology” Psoriasis worsens in winter in India due to less sunlight and dry skin, needing personalized treatment.
 7 citations,
January 2012 in “International Journal of Trichology”
7 citations,
January 2012 in “International Journal of Trichology” Two siblings both had a rare case of alopecia areata at the same time.
 70 citations,
October 2020 in “The journal of allergy and clinical immunology/Journal of allergy and clinical immunology/The journal of allergy and clinical immunology”
70 citations,
October 2020 in “The journal of allergy and clinical immunology/Journal of allergy and clinical immunology/The journal of allergy and clinical immunology” Janus kinase inhibitors are promising drugs for treating autoimmune and inflammatory diseases.
 29 citations,
January 2007 in “American Journal of Clinical Dermatology”
29 citations,
January 2007 in “American Journal of Clinical Dermatology” Eyebrow loss has many causes and requires accurate diagnosis for proper treatment.
 114 citations,
January 2007 in “Drug Safety”
114 citations,
January 2007 in “Drug Safety” Some drugs can cause skin, nail, and hair problems, which are important for healthcare professionals to recognize and report.
 2 citations,
August 2017 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
2 citations,
August 2017 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Hair loss in Cronkhite-Canada syndrome may be due to an autoimmune response.
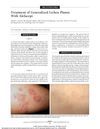 52 citations,
February 2006 in “Archives of Dermatology”
52 citations,
February 2006 in “Archives of Dermatology” Alefacept may effectively treat severe lichen planus, with patients showing significant improvement and no side effects.
15 citations,
October 2013 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Vitiligo patients should be routinely screened for thyroid disease and, if extensive or prolonged, also for RA, PA, and type 2 diabetes.
9 citations,
August 2019 in “Lupus” Poor body image from pain can lead to more depression in lupus patients.
40 citations,
July 2015 in “Kidney International” IL-3 worsens lupus nephritis and blocking it improves kidney health.

A 9-year-old girl developed type 1 diabetes and alopecia after being treated for a rare kidney disease.

COVID-19 can lead to different skin symptoms and might trigger autoimmune diseases in genetically susceptible people.
 6 citations,
February 1974 in “The BMJ”
6 citations,
February 1974 in “The BMJ” The document concludes that scalp disorders can be treated with hair washing, specific shampoos, medications, and sometimes surgery or hair transplants, but hereditary baldness is untreatable.
 2 citations,
January 2017 in “AIMS cell and tissue engineering”
2 citations,
January 2017 in “AIMS cell and tissue engineering” Mesenchymal stem cells show promise for treating various skin conditions and may help regenerate hair.
5 citations,
September 2020 in “Proceedings - Baylor University. Medical Center” Tofacitinib successfully treated a woman's severe symptoms from a rare autoimmune condition.
88 citations,
August 2019 in “Frontiers in immunology” Tyrosine kinases are important in skin autoimmune diseases and could be targets for new treatments.
 1 citations,
October 2021 in “International Journal of Research in Dermatology”
1 citations,
October 2021 in “International Journal of Research in Dermatology” Alopecia areata mainly affects men aged 21-40 and is linked to autoimmune issues, thyroid problems, and inflammation.
 23 citations,
June 2003 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology Symposium Proceedings”
23 citations,
June 2003 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology Symposium Proceedings” Alopecia Areata is an autoimmune disease affecting hair follicles, influenced by genetic and environmental factors, with rodent models being essential for research.
 2 citations,
July 2022 in “Frontiers in Medicine”
2 citations,
July 2022 in “Frontiers in Medicine” The cause of Frontal fibrosing alopecia, a type of hair loss, is complex, likely involving immune responses and genetics, but is not fully understood.
 February 2024 in “International neuropsychiatric disease journal”
February 2024 in “International neuropsychiatric disease journal” Alopecia areata severely impacts quality of life, mental health, and work productivity.
 3 citations,
June 2013 in “Turkish Journal of Rheumatology”
3 citations,
June 2013 in “Turkish Journal of Rheumatology” A 16-year-old boy with Castleman's disease and lupus was successfully treated and showed no recurrence.
 17 citations,
January 2011 in “The Korean Journal of Hepatology”
17 citations,
January 2011 in “The Korean Journal of Hepatology” Vogt-Koyanagi-Harada disease can develop during interferon therapy for chronic hepatitis C.
 January 2022 in “IntechOpen eBooks”
January 2022 in “IntechOpen eBooks” Some lesser-known causes of PCOS include autoimmune issues, genetic mutations, and changes in the body's microbiome.
 1 citations,
August 2021 in “Internal Medicine Journal”
1 citations,
August 2021 in “Internal Medicine Journal” After severe COVID-19, 71% of patients experienced excessive hair shedding and thinning within 3 months due to factors like low oxygen levels, medication, stress, and autoimmune disease.
 23 citations,
November 2018 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
23 citations,
November 2018 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” The study concluded that severity of Frontal fibrosing alopecia is not linked to how long someone has it, can start before menopause, and eyebrow loss may be an early sign.
 March 2022 in “Women's health issues”
March 2022 in “Women's health issues” The conclusion is that women are heavily affected by autoimmune skin diseases, face significant challenges, and need better research, treatments, and healthcare policies.
 80 citations,
November 1975 in “Acta dermato-venereologica”
80 citations,
November 1975 in “Acta dermato-venereologica” Large doses of glucocorticoids are not suitable for general use in treating severe alopecia areata due to inconsistent results and risks.

























