 22 citations,
June 1980 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
22 citations,
June 1980 in “International Journal of Dermatology” The document concludes that correct diagnosis of alopecia types is crucial, scalp biopsies are important, and more research is needed.
 7 citations,
January 2017 in “Clinical and medical investigations”
7 citations,
January 2017 in “Clinical and medical investigations” Suriname uses many plants for beauty, with potential for a beauty industry, but more evidence is needed for product effectiveness.
July 2022 in “Dermatologica Sinica” Many women with hair loss also have zinc deficiency, iron depletion, or thyroid issues.
 1 citations,
July 2018 in “Elsevier eBooks”
1 citations,
July 2018 in “Elsevier eBooks” Heredity and hormones cause common hair loss, and topical minoxidil is the first recommended treatment.
 18 citations,
March 2016 in “Cosmetics”
18 citations,
March 2016 in “Cosmetics” Telogen Effluvium is a condition causing excessive hair loss due to stress, illness, drugs, or hormonal changes, and can be treated with specific products or naturally resolves after 3-4 years.
 June 2023 in “Romanian Medical Journal”
June 2023 in “Romanian Medical Journal” The case shows how hard it is to tell apart Multiple Autoimmune Syndrome from other similar autoimmune conditions, but correct diagnosis is key for treatment to work.
 52 citations,
May 2017 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology”
52 citations,
May 2017 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology” PRP injections improve hair density and thickness in women with hair loss.
 1 citations,
May 2017 in “InTech eBooks”
1 citations,
May 2017 in “InTech eBooks” The document explains the causes, types, diagnosis, and treatments of hair loss, and its psychological impact, especially on women.
 29 citations,
August 2008 in “Current Opinion in Pediatrics”
29 citations,
August 2008 in “Current Opinion in Pediatrics” Hair loss in teenagers is hard to treat and lacks a cure, with some treatments available depending on the type of hair loss.
 30 citations,
November 2008 in “Facial Plastic Surgery”
30 citations,
November 2008 in “Facial Plastic Surgery” The conclusion is that the best approach for treating Female Pattern Hair Loss is a combination of different treatments.
 7 citations,
May 2022 in “The Journal of Dermatology”
7 citations,
May 2022 in “The Journal of Dermatology” Hair loss is a frequent long-term effect of COVID-19, and oral minoxidil is the most common effective treatment.
 144 citations,
July 2002 in “Clinical and Experimental Dermatology”
144 citations,
July 2002 in “Clinical and Experimental Dermatology” Telogen effluvium is a common type of hair loss that can resolve on its own or become chronic, with treatment depending on early diagnosis.
 24 citations,
January 2008 in “KARGER eBooks”
24 citations,
January 2008 in “KARGER eBooks” The document concludes that ongoing research using animal models is crucial for better understanding and treating Alopecia Areata.
 September 2024 in “Archiv Euromedica”
September 2024 in “Archiv Euromedica” Trichoscopy is a quick, accurate, and non-invasive method to diagnose and treat non-scarring hair loss.
 2 citations,
January 2023 in “Pharmaceuticals”
2 citations,
January 2023 in “Pharmaceuticals” Natural products and phytochemicals may help with hair regrowth, but more research is needed.
 99 citations,
July 2017 in “Clinical Reviews in Allergy & Immunology”
99 citations,
July 2017 in “Clinical Reviews in Allergy & Immunology” New treatments for Alopecia Areata show promise but need to be more effective and affordable.
 4 citations,
January 2005 in “Elsevier eBooks”
4 citations,
January 2005 in “Elsevier eBooks” Follicular Unit Transplantation is a precise hair restoration technique that requires careful planning and a skilled team, and Follicular Unit Extraction offers a less invasive option.

Afro-textured hair is more fragile and prone to certain scalp conditions, requiring careful treatment and more research for effective management.
 35 citations,
January 2019 in “Clinics in Dermatology”
35 citations,
January 2019 in “Clinics in Dermatology” Syphilis has a wide range of symptoms that can look like other diseases, and if not treated, it can progress to a more serious stage, especially in HIV-positive patients.
 68 citations,
September 2003 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
68 citations,
September 2003 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Shrinking skin cancer increases the chance of cancer in nearby lymph nodes.
 November 2012 in “South African Family Practice”
November 2012 in “South African Family Practice” The article concludes that early treatment of alopecia is crucial to prevent permanent hair loss.
January 2021 in “Indian dermatology online journal” The document lists various skin conditions and structures named "corona" that are not related to the coronavirus.
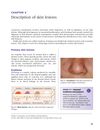
The document explains different types of skin lesions and their characteristics, causes, and related conditions.
 45 citations,
January 2015 in “Dermatology”
45 citations,
January 2015 in “Dermatology” Hair loss in secondary syphilis is more common than thought and can be reversed with antibiotics.
 24 citations,
July 1987 in “Dermatologic Clinics”
24 citations,
July 1987 in “Dermatologic Clinics” Systemic diseases can cause hair loss, which is often reversible with treatment.
 7 citations,
November 2006 in “Pediatric Dermatology”
7 citations,
November 2006 in “Pediatric Dermatology” A newborn with congenital syphilis had unusual hair loss possibly caused by the infection.
 83 citations,
May 1999 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
83 citations,
May 1999 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Hair loss that spreads out can often fix itself or be treated by finding and handling the cause.
 2 citations,
December 2004 in “Medicine”
2 citations,
December 2004 in “Medicine” Different hair and scalp disorders cause hair loss or excess hair growth, with various treatments available depending on the specific condition.
 29 citations,
January 2017 in “Skin appendage disorders”
29 citations,
January 2017 in “Skin appendage disorders” Hair loss due to syphilis can be identified using trichoscopy and is treatable with antibiotics.
 1 citations,
January 2013 in “Mayo Clinic Proceedings”
1 citations,
January 2013 in “Mayo Clinic Proceedings” A woman's chronic headaches and hair loss were cured by treating her syphilis.




























