 30 citations,
December 1999 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology Symposium Proceedings”
30 citations,
December 1999 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology Symposium Proceedings” Steroids, particularly estrogens and 5α-reductase inhibitors, affect blood vessel-related hair growth processes in hair follicle cells.
 23 citations,
September 2015 in “PLOS ONE”
23 citations,
September 2015 in “PLOS ONE” Mesenchymal stem cells, especially injected into the skin, heal wounds faster and better than chitosan gel or other treatments.
[object Object]  19 citations,
September 2019 in “EMBO molecular medicine”
19 citations,
September 2019 in “EMBO molecular medicine” Blocking TSLP reduces skin inflammation and cell overgrowth in psoriasis.
 13 citations,
January 2022 in “Stem cell reviews and reports”
13 citations,
January 2022 in “Stem cell reviews and reports” Mouse stem cells from hair follicles can improve wound healing and reduce scarring.
 11 citations,
August 2018 in “Facial Plastic Surgery Clinics of North America”
11 citations,
August 2018 in “Facial Plastic Surgery Clinics of North America” Adipose-derived stem cells show potential for skin rejuvenation and wound healing but require more research to overcome challenges and ensure safety.
 2 citations,
May 2023 in “Frontiers in immunology”
2 citations,
May 2023 in “Frontiers in immunology” Skin stem cells remember past inflammation, helping them respond better to future injuries and possibly aiding in treating skin issues.

Stem cells regenerate tissues and their behavior varies by environment, suggesting the hematopoietic system model may need revision.

Dermal stem cells help regenerate hair follicles and heal skin wounds.
 77 citations,
April 2016 in “Science Advances”
77 citations,
April 2016 in “Science Advances” Researchers created a fully functional, bioengineered skin system with hair from stem cells that successfully integrated when transplanted into mice.
 11 citations,
July 2016 in “Current Opinion in Cell Biology”
11 citations,
July 2016 in “Current Opinion in Cell Biology” New techniques have enhanced our understanding of how stem cells function and the role of mutations in aging tissues, which may influence future cancer therapies.
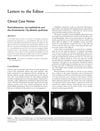 9 citations,
February 2004 in “Clinical and Experimental Ophthalmology”
9 citations,
February 2004 in “Clinical and Experimental Ophthalmology” The document discusses various eye conditions and their treatments, including a rare eye cancer in a baby, vision loss from a cancer drug, cataracts from a baldness treatment, a rare skin disorder, and a specific type of eye disease diagnosed with a special imaging technique.
 48 citations,
February 2013 in “Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology”
48 citations,
February 2013 in “Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology” The protein StAR is found in 17 different organs and can affect hair loss and brain functions, but its full role is not yet fully understood.
 29 citations,
December 2005 in “BioEssays”
29 citations,
December 2005 in “BioEssays” Wnt/ß-catenin signaling is crucial for regulating skin stem cells and hair growth, with the right levels and timing needed for proper function.

New treatments for hair loss show promise, including plasma, stem cells, and hair-stimulating complexes, but more research is needed to fully understand them.
[object Object]  211 citations,
May 2018 in “Trends in cell biology”
211 citations,
May 2018 in “Trends in cell biology” Different types of skin cells play specific roles in development, healing, and cancer.
 135 citations,
December 2013 in “Seminars in Cell & Developmental Biology”
135 citations,
December 2013 in “Seminars in Cell & Developmental Biology” Stem cells in the hair follicle are regulated by their surrounding environment, which is important for hair growth.
 62 citations,
November 2009 in “Aging Cell”
62 citations,
November 2009 in “Aging Cell” Hedgehog signaling helps keep hair follicle stem cells the same in both young and old human skin.
 39 citations,
September 2011 in “Tissue Engineering Part B-reviews”
39 citations,
September 2011 in “Tissue Engineering Part B-reviews” Hair follicle regeneration in skin grafts may be possible using stem cells and tissue engineering.
 November 2023 in “bioRxiv (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory)”
November 2023 in “bioRxiv (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory)” Disrupted cholesterol production impairs hair follicle stem cells, leading to hair loss.
 September 2013 in “Experimental Dermatology”
September 2013 in “Experimental Dermatology” The document concluded that stem cells are crucial for skin repair, regeneration, and may help in developing advanced skin substitutes.
 438 citations,
October 2010 in “Oncogene”
438 citations,
October 2010 in “Oncogene” Keratins help protect cells, aid in cancer diagnosis, and influence cancer behavior and treatment.
 87 citations,
January 2016 in “Development”
87 citations,
January 2016 in “Development” Blocking β-catenin in skin cells improves hair growth during wound healing.
 59 citations,
March 2020 in “Journal of Biomedical Science”
59 citations,
March 2020 in “Journal of Biomedical Science” Understanding how hair follicle stem cells work can help find new ways to prevent hair loss and promote hair growth.
 58 citations,
April 2012 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
58 citations,
April 2012 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Graft-versus-host disease is a complication where donor immune cells attack the recipient's body, often affecting the skin, liver, and gastrointestinal tract.
 28 citations,
January 2021 in “Parkinsonism & related disorders (Online)/Parkinsonism & related disorders”
28 citations,
January 2021 in “Parkinsonism & related disorders (Online)/Parkinsonism & related disorders” Parkinson's disease is linked to skin disorders and skin cells help in studying the disease.
 21 citations,
October 2017 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
21 citations,
October 2017 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” The document concludes that understanding dermal papilla cells is key to improving hair regeneration treatments.
 8 citations,
May 2021 in “Bioengineering & translational medicine”
8 citations,
May 2021 in “Bioengineering & translational medicine” Hair growth environment recreated with challenges; stem cells make successful skin organoids.
 1 citations,
November 2018 in “bioRxiv (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory)”
1 citations,
November 2018 in “bioRxiv (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory)” Signals from skin cells controlled by Rac proteins help turn certain precursor cells into white fat cells.
 April 2021 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
April 2021 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Stem cells control their future role by changing ERK signal timing, affecting tissue regeneration and cancer.
 May 2009 in “The American Journal of Dermatopathology”
May 2009 in “The American Journal of Dermatopathology” Mast cells play a significant role in hair loss conditions like male pattern hair loss and alopecia areata.






























