 6 citations,
July 2017 in “Clinics in Plastic Surgery”
6 citations,
July 2017 in “Clinics in Plastic Surgery” The document concludes that individualized reconstruction plans are essential for improving function and appearance after head and neck burns.
[object Object]  37 citations,
November 2003 in “Veterinary pathology”
37 citations,
November 2003 in “Veterinary pathology” Hair loss in mice starts with immune cells damaging hair roots before it becomes visible.
 25 citations,
January 2001 in “Facial Plastic Surgery”
25 citations,
January 2001 in “Facial Plastic Surgery” Both tissue expansion and serial excision are effective for scar revision in the head and neck area.
5 citations,
March 2016 in “Experimental and molecular pathology” Mice with alopecia areata had wider lymphatic vessels in their skin.
 September 2024 in “Journal of Cutaneous and Aesthetic Surgery”
September 2024 in “Journal of Cutaneous and Aesthetic Surgery” A young man with severe neck and beard burns was successfully treated, restoring neck movement and improving skin appearance.
 18 citations,
September 2006 in “Dermatologic Surgery”
18 citations,
September 2006 in “Dermatologic Surgery” Aggressive scalp squamous cell carcinomas have a high death rate and need early, strong treatment.
[object Object]  January 2022 in “Plastic and Aesthetic Research”
January 2022 in “Plastic and Aesthetic Research” Choose the simplest, most fitting scalp reconstruction method for each patient's unique needs.
Local flaps are effective for covering small to large scalp and forehead defects with good cosmetic results.
 55 citations,
October 2009 in “Clinics in Plastic Surgery”
55 citations,
October 2009 in “Clinics in Plastic Surgery” Burn reconstruction improves with new techniques, materials, and tissue engineering.
34 citations,
July 2013 in “Clinical Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology” Erosive pustular dermatosis is a rare skin disease that's hard to treat and affects the scalp or legs.
 15 citations,
January 2023 in “Biomaterials Research”
15 citations,
January 2023 in “Biomaterials Research” 3D bioprinting in plastic surgery could lead to personalized grafts and fewer complications.
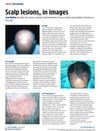 January 2015 in “Independent Nurse”
January 2015 in “Independent Nurse” Different scalp conditions can lead to hair loss or tumors, with treatments varying from creams to surgery; early detection is crucial.
 20 citations,
January 2014 in “Journal of skin cancer”
20 citations,
January 2014 in “Journal of skin cancer” Most people with basal cell carcinoma on their head or neck were 60-70 years old, and it often came back even after being fully removed, especially in certain areas and types.
 70 citations,
February 2021 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences”
70 citations,
February 2021 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences” Fat-derived stem cells, platelet-rich plasma, and biomaterials show promise for healing chronic skin wounds and improving soft tissue with few side effects.
 3 citations,
August 2011 in “InTech eBooks”
3 citations,
August 2011 in “InTech eBooks” The document concludes that skin grafts are essential for repairing tissue loss, with various types available and ongoing research into substitutes to improve outcomes and reduce donor site issues.
 5 citations,
March 2017 in “Cell and Tissue Banking”
5 citations,
March 2017 in “Cell and Tissue Banking” Researchers developed a new method to quickly prepare skin cells that improve wound healing in rats.
 19 citations,
January 2007 in “Journal of medical investigation”
19 citations,
January 2007 in “Journal of medical investigation” GFP transgenic mice help study cell origins in skin grafts.
 4 citations,
January 2008 in “Facial Plastic Surgery”
4 citations,
January 2008 in “Facial Plastic Surgery” Improve skin paddle appearance after head and neck reconstruction using tissue expansion, rearrangement, and flaps.
 1 citations,
November 2014 in “Elsevier eBooks”
1 citations,
November 2014 in “Elsevier eBooks” Future research should focus on making bioengineered skin that completely restores all skin functions.
 January 2024 in “Burns and trauma”
January 2024 in “Burns and trauma” The skin microbiome helps heal wounds and can be targeted to improve healing.
 October 1987 in “Clinics in Dermatology”
October 1987 in “Clinics in Dermatology” Scalp reduction can improve hair distribution in certain baldness cases but requires careful patient selection and understanding of facial structure.
 202 citations,
August 2007 in “Biomaterials”
202 citations,
August 2007 in “Biomaterials” Artificial skin development has challenges, but new materials and understanding cell behavior could improve tissue repair. Also, certain growth factors and hydrogel technology show promise for advanced skin replacement therapies.
 83 citations,
January 2015 in “World Journal of Stem Cells”
83 citations,
January 2015 in “World Journal of Stem Cells” Hair follicle regeneration needs special conditions and young cells.
 72 citations,
December 1996 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
72 citations,
December 1996 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Human hair follicles can regenerate after removal, but with low success rate.
 24 citations,
September 2018 in “Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Medicine”
24 citations,
September 2018 in “Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Medicine” Hyaluronic acid-based HA2 hydrogel helps heal skin wounds better with less scarring.
 23 citations,
September 2015 in “PLOS ONE”
23 citations,
September 2015 in “PLOS ONE” Mesenchymal stem cells, especially injected into the skin, heal wounds faster and better than chitosan gel or other treatments.
 October 2016 in “Elsevier eBooks”
October 2016 in “Elsevier eBooks” Common noncancerous skin diseases have various treatments, including topical applications, light therapy, surgery, and medications, with psychological support being important.
 232 citations,
October 2015 in “International journal of molecular sciences”
232 citations,
October 2015 in “International journal of molecular sciences” Stem cells are crucial for skin repair and new treatments for chronic wounds.
 132 citations,
January 2017 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences”
132 citations,
January 2017 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences” Fat-derived stem cells show promise for skin repair and reducing aging signs but need more research for consistent results.
 65 citations,
March 2018 in “Journal of Dermatological Science”
65 citations,
March 2018 in “Journal of Dermatological Science” Skin problems can be caused or worsened by physical forces and pressure on the skin.




























