 June 2023 in “Stem cell reviews and reports”
June 2023 in “Stem cell reviews and reports” Stem cell therapies could be a promising alternative for hair loss treatment, but more research is needed to understand their full potential and safety.
 15 citations,
September 2007 in “Cell & tissue research/Cell and tissue research”
15 citations,
September 2007 in “Cell & tissue research/Cell and tissue research” Embryonic and adult stem cells are valuable for improving skin grafts and cell therapy.
 July 2023 in “Regenerative Therapy”
July 2023 in “Regenerative Therapy” Stem cell and platelet-rich plasma therapies show promise for COVID-19 related hair loss, but more research is needed.
 4 citations,
April 2012 in “Medical Hypotheses”
4 citations,
April 2012 in “Medical Hypotheses” Finasteride may improve stem cell therapy for heart attacks by increasing cell survival.
2 citations,
May 2015 in “International Journal of Scientific Reports” Neonatal mesenchymal stem cell therapy shows promise for treating hair loss but needs more research.
 28 citations,
December 2012 in “The American Journal of Cosmetic Surgery”
28 citations,
December 2012 in “The American Journal of Cosmetic Surgery” Proteins from stem cells improved hair growth in patients with hair loss.
 25 citations,
November 2014 in “Ageing Research Reviews”
25 citations,
November 2014 in “Ageing Research Reviews” Skin aging is caused by stem cell damage and can potentially be delayed with treatments like antioxidants and stem cell therapy.
21 citations,
August 2017 in “Journal of veterinary internal medicine” Combining amino acid and stem cell therapy may help manage hepatocutaneous syndrome in dogs.
 21 citations,
October 2009 in “Biochemical Engineering Journal”
21 citations,
October 2009 in “Biochemical Engineering Journal” Stem cell therapy is a promising approach for hair regrowth despite potential side effects.
 15 citations,
July 2021 in “Bosnian Journal of Basic Medical Sciences”
15 citations,
July 2021 in “Bosnian Journal of Basic Medical Sciences” Stem cell therapy is promising for treating various health conditions, but more research is needed to understand its full potential and address challenges.
 12 citations,
May 2019 in “Aesthetic Surgery Journal”
12 citations,
May 2019 in “Aesthetic Surgery Journal” Platelet-Rich Plasma and stem cell therapy can increase hair count and density, but the best method for preparation and treatment still needs to be determined.
 2 citations,
October 2022 in “Journal of Biomedical Science”
2 citations,
October 2022 in “Journal of Biomedical Science” Stem cells and their secretions could potentially treat stress-induced hair loss, but more human trials are needed.

Stem cell therapy is more effective than minoxidil for hair growth in androgenic alopecia.
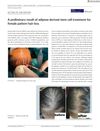 April 2021 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology”
April 2021 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology” Stem cell treatment improved hair density in female hair loss patient.
 3 citations,
May 2008 in “Hair transplant forum international”
3 citations,
May 2008 in “Hair transplant forum international” Common hair loss disorders may not need stem cell therapy, but could benefit from other treatments like hair cycle control and immune restoration therapy.
 December 2022 in “International journal of drug regulatory affairs”
December 2022 in “International journal of drug regulatory affairs” The US and EU lead in cell and gene therapy regulations with more approvals and clinical trials, while India is in early stages with fewer approvals and expedited processes.
 55 citations,
May 2017 in “Current stem cell research & therapy”
55 citations,
May 2017 in “Current stem cell research & therapy” Using fat-derived stem cells for hair loss treatment is safe and effective, improving hair growth and patient satisfaction.
23 citations,
July 2020 in “Aging Cell” Aging changes sugar molecules on skin stem cells, which may affect their ability to repair skin.

Low-level laser therapy may help stem cells grow and function better, aiding in healing and tissue repair.
 15 citations,
May 2021 in “British journal of dermatology/British journal of dermatology, Supplement”
15 citations,
May 2021 in “British journal of dermatology/British journal of dermatology, Supplement” Cell therapy shows promise for treating severe psoriasis but needs more research to confirm safety and effectiveness.
 4 citations,
May 2014 in “Biochemical Society Transactions”
4 citations,
May 2014 in “Biochemical Society Transactions” Environmental cues can change the fate and function of epithelial cells, with potential for cell therapy.
9 citations,
May 2022 in “Frontiers in Cellular Neuroscience” Mesenchymal stromal cell therapies show promise for treating various diseases but need more research and standardization.
1 citations,
February 2020 in “Regenerative Medicine” Significant progress and collaborations in stem cell research and regenerative medicine were made, including advancements in hair growth, cancer therapies, and treatments for neurological disorders.
 April 2012 in “Annals of Neurosciences”
April 2012 in “Annals of Neurosciences” The document concludes that stem cell therapies lack solid proof of effectiveness, except for blood system treatments, and criticizes the ethical issues and commercial exploitation in the field.
 773 citations,
August 2017 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences”
773 citations,
August 2017 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences” The secretions of mesenchymal stem cells could be used for healing without using the cells themselves.
 88 citations,
January 2019 in “Journal of Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine”
88 citations,
January 2019 in “Journal of Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine” Conditioned media from mesenchymal stem cell cultures could be a more effective alternative for regenerative therapies, but more research is needed.
December 2022 in “Nature Communications” Bead-jet printing of stem cells improves muscle and hair regeneration.
 17 citations,
January 2014 in “Stem Cells Translational Medicine”
17 citations,
January 2014 in “Stem Cells Translational Medicine” Canine epidermal neural crest stem cells could be a promising treatment for spinal cord injuries in dogs.
 8 citations,
July 2022 in “BMC neuroscience”
8 citations,
July 2022 in “BMC neuroscience” Transplanted hair follicle stem cells improved brain function and reduced damage after a stroke in rats.
 August 2019 in “Regenerative Medicine”
August 2019 in “Regenerative Medicine” In June 2019, the stem cell research field saw major progress, including new clinical trials, FDA approvals, and industry collaborations.
























