 January 2023 in “National Journal of Physiology, Pharmacy and Pharmacology”
January 2023 in “National Journal of Physiology, Pharmacy and Pharmacology” Tofacitinib effectively reduced hair loss in alopecia areata patients without adverse effects.
 489 citations,
November 2021 in “Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy”
489 citations,
November 2021 in “Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy” The JAK/STAT pathway is important in cell processes and disease, and JAK inhibitors are promising for treating related conditions.
63 citations,
July 2018 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” JAK inhibitors can effectively reverse hair loss in people with alopecia areata.
 6 citations,
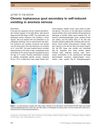
May 2010 in “The Journal of Dermatology”
6 citations,
May 2010 in “The Journal of Dermatology” A woman with anorexia developed gout from self-induced vomiting.
 34 citations,
August 2002 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
34 citations,
August 2002 in “British Journal of Dermatology” ALA-PDT is effective and safe for chronic X-ray dermatitis, providing complete or partial remission.
 1 citations,
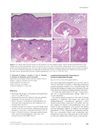
February 2009 in “Clinical and Experimental Dermatology”
1 citations,
February 2009 in “Clinical and Experimental Dermatology” Hormone-replacement therapy improved a woman's skin condition known as lymphomatoid papulosis.

Some dermatologists in Saudi Arabia prescribe Tofacitinib for hair loss, but many don't due to its unavailability and safety concerns.
 January 2016 in “Springer eBooks”
January 2016 in “Springer eBooks” Alopecia Areata is an unpredictable autoimmune hair loss condition with limited and variable treatment effectiveness.
 196 citations,
September 2016 in “JCI insight”
196 citations,
September 2016 in “JCI insight” Ruxolitinib effectively regrows hair in most patients with severe hair loss.
 77 citations,
June 2017 in “Advances in Therapy”
77 citations,
June 2017 in “Advances in Therapy” New treatments for Alopecia Areata, like JAK inhibitors, show promise for hair regrowth and are likely to change future treatment approaches.
1 citations,
May 2023 in “Frontiers in Pharmacology” Genetic screening for NUDT15 polymorphisms is crucial for patients taking azathioprine, especially in Asians.
 91 citations,
August 2014 in “Development”
91 citations,
August 2014 in “Development” The circadian clock is crucial for tissue renewal and regeneration, affecting stem cell functions and having implications for health and disease.
 11 citations,
January 2020 in “Dermatologica Sinica”
11 citations,
January 2020 in “Dermatologica Sinica” Tofacitinib helps regrow hair in severe alopecia patients, but more research is needed.
 39 citations,
November 2015 in “Pediatric Nephrology”
39 citations,
November 2015 in “Pediatric Nephrology” Rituximab leads to longer remission and fewer side effects than cyclophosphamide.
 18 citations,
October 2021 in “Frontiers in Physiology”
18 citations,
October 2021 in “Frontiers in Physiology” Lipocalin-Type Prostaglandin D2 Synthase (L-PGDS) is a protein that plays many roles in the body, including sleep regulation, pain management, food intake, and protection against harmful substances. It also affects fat metabolism, glucose intolerance, cell maturation, and is involved in various diseases like diabetes, cancer, and arthritis. It can influence sex organ development and embryonic cell differentiation, and its levels can be used as a diagnostic marker for certain conditions.
 6 citations,
September 1998 in “The Journal of The British Menopause Society”
6 citations,
September 1998 in “The Journal of The British Menopause Society” Testosterone replacement may help postmenopausal women with sexual function and bone density, but suitable treatments are limited.
 2 citations,
January 2020 in “Skin appendage disorders”
2 citations,
January 2020 in “Skin appendage disorders” Early onset, severe types, nail changes, family history, and body hair loss worsen alopecia areata prognosis; sticking to treatment helps.
 1 citations,
December 2023 in “Annals of Phytomedicine An International Journal”
1 citations,
December 2023 in “Annals of Phytomedicine An International Journal” Nanoemulgel improves delivery and effectiveness of plant-based drugs for various conditions.
 1 citations,
March 2004 in “Military Medicine”
1 citations,
March 2004 in “Military Medicine” The retired colonel's ankle swelling was caused by a reaction to the antibiotic levofloxacin.
 1 citations,
July 2015 in “European Journal of Dermatology”
1 citations,
July 2015 in “European Journal of Dermatology” CO₂ laser treatment is fast and effective for some benign skin tumors with minimal side effects.
 8 citations,
September 2021 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology”
8 citations,
September 2021 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology” Some diets and supplements might help with skin disorders, but their effectiveness varies and more research is needed.
 31 citations,
January 2021 in “Experimental Dermatology”
31 citations,
January 2021 in “Experimental Dermatology” Skin organoids are a promising new model for studying human skin development and testing treatments.
 2 citations,
December 2004 in “Medicine”
2 citations,
December 2004 in “Medicine” Different hair and scalp disorders cause hair loss or excess hair growth, with various treatments available depending on the specific condition.
 March 2022 in “Wound practice & research”
March 2022 in “Wound practice & research” New treatments for alopecia areata show promise, but standardized guidelines are needed.
 117 citations,
March 2013 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
117 citations,
March 2013 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” No effective treatment for frontal fibrosing alopecia was found, but oral 5-alpha-reductase inhibitors had the best response; for lichen planopilaris, topical corticosteroids were commonly used but had a high relapse rate.
 144 citations,
September 2006 in “Clinics in Dermatology”
144 citations,
September 2006 in “Clinics in Dermatology” Lupus affects the body and skin, causing joint pain and skin issues that can be treated with steroids and antimalarial drugs.
 August 2016 in “InTech eBooks”
August 2016 in “InTech eBooks” Esthetic surgery complications can include infections, nerve injury, and more; proper evaluation and technique help prevent them.
 70 citations,
October 2020 in “The journal of allergy and clinical immunology/Journal of allergy and clinical immunology/The journal of allergy and clinical immunology”
70 citations,
October 2020 in “The journal of allergy and clinical immunology/Journal of allergy and clinical immunology/The journal of allergy and clinical immunology” Janus kinase inhibitors are promising drugs for treating autoimmune and inflammatory diseases.
 August 1986 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
August 1986 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Minoxidil showed a 30% success rate for hair growth in a study, and various skin treatments were effective, but some had limitations or side effects.
 49 citations,
October 2014 in “International Scholarly Research Notices”
49 citations,
October 2014 in “International Scholarly Research Notices” Eclipta alba has many health benefits and contains compounds with potential for drug development.




























