303 citations,
August 1971 in “The American Journal of Medicine” Melanocytes are destroyed by factors needed for melanin production, causing vitiligo and gray hair.
 22 citations,
October 2021 in “Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Biology”
22 citations,
October 2021 in “Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Biology” Three types of stem cells help maintain and repair skin, responding to health and environmental changes.
 222 citations,
January 2005 in “Endocrine journal”
222 citations,
January 2005 in “Endocrine journal” Melatonin is important for skin health and protection, and can be made by the skin or applied to it.
 277 citations,
July 2011 in “Journal of the Dermatology Nurses’ Association”
277 citations,
July 2011 in “Journal of the Dermatology Nurses’ Association” The skin's layers protect, sense, and regulate the body's internal balance, but can be prone to cancer.
4 citations,
October 2021 in “International Journal of Cosmetic Science” Cirsium japonicum flower extract increases melanin production and could help treat depigmentation conditions.
The gene Endothelin 3 makes mice's fur darker by increasing pigment cells and pigment levels.
 40 citations,
January 2016 in “Elsevier eBooks”
40 citations,
January 2016 in “Elsevier eBooks” The skin is the largest organ, protecting the body, regulating temperature, and producing hormones.
 15 citations,
July 2016 in “Biochemical Journal”
15 citations,
July 2016 in “Biochemical Journal” Wnt proteins from certain skin cells are crucial for normal hair growth and renewal.
3 citations,
May 2020 in “Acta pharmaceutica” Protocatechuic acid can reduce melanin production and boost antioxidant activity in hair follicles.
10 citations,
April 2022 in “Critical reviews in food science and nutrition” Skin odorant receptors respond to flavors and could be targeted to improve skin health and treat diseases.
 September 2023 in “Cells tissues organs”
September 2023 in “Cells tissues organs” Mice skin matures by day 200, leading to aging signs like curved hair follicles and white hairs due to changes in skin stem cells.
17 citations,
December 2013 in “Dermatologic Surgery” The treatment improved hair color in most vitiligo patients without major side effects.
 1 citations,
July 2016 in “Elsevier eBooks”
1 citations,
July 2016 in “Elsevier eBooks” Understanding skin structure and development helps diagnose and treat skin disorders.
130 citations,
December 1998 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” Hair follicle melanocytes die during hair regression.
 5 citations,
November 2021 in “Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery”
5 citations,
November 2021 in “Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery” Using special stem cells, we can create new hair follicles, potentially making hair restoration easier and more affordable.
 6 citations,
January 2009 in “Elsevier eBooks”
6 citations,
January 2009 in “Elsevier eBooks” The skin has multiple layers and cells, serves as a protective barrier, helps regulate temperature, enables sensation, affects appearance, and is involved in vitamin D synthesis.
 January 2021 in “Journal of clinical and cosmetic dermatology”
January 2021 in “Journal of clinical and cosmetic dermatology” Human skin responds to light with protective mechanisms, but more research is needed to understand these processes and their implications for health and therapy.
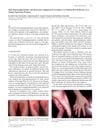 16 citations,
January 2008 in “Acta dermato-venereologica”
16 citations,
January 2008 in “Acta dermato-venereologica” Vitamin B12 deficiency can cause skin darkening and increased blood vessels, but treatment can improve symptoms.
 7 citations,
November 2011 in “Skin Research and Technology”
7 citations,
November 2011 in “Skin Research and Technology” The study found a specific pattern of uneven melanin distribution on balding scalps that could help understand skin diseases caused by light exposure.
86 citations,
August 2000 in “Pigment cell research” Melanocyte activity in hair follicles is linked to the hair growth cycle, being active in growth phases and inactive in rest phases.
6 citations,
July 1976 in “JAMA” Black patients have unique skin conditions that require specific knowledge for proper treatment.
 15 citations,
March 2015 in “Experimental Dermatology”
15 citations,
March 2015 in “Experimental Dermatology” Clotrimazole, an antifungal cream, may safely reduce skin pigmentation by breaking down the enzyme needed for making melanin.
 7 citations,
December 2004 in “Medicine”
7 citations,
December 2004 in “Medicine” Knowing how skin works and its diseases helps doctors diagnose and treat skin conditions better.
42 citations,
August 1995 in “British journal of dermatology/British journal of dermatology, Supplement” RXR-alpha is strongly expressed in both normal and psoriatic skin and may help in skin cell differentiation and hair growth.
 4 citations,
November 2014
4 citations,
November 2014 The skin protects the body, regulates temperature, senses touch, and makes vitamin D.
 60 citations,
June 1997 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
60 citations,
June 1997 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Apoptosis is crucial for healthy skin and treating skin diseases.
 June 2006 in “Experimental Dermatology”
June 2006 in “Experimental Dermatology” Understanding skin patterns can help us learn about skin diseases and their treatments.
Moles may stop growing because of cell cooperation, not just because of aging cells.
29 citations,
June 1998 in “Developmental Biology” More melanoblasts in hair follicles mean better survival and proper hair pigmentation.
5 citations,
August 2012 in “Archives of Dermatology” The immune system can cause permanent skin and hair whitening by attacking pigment cells.
















