 22 citations,
November 2018 in “Brazilian Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences”
22 citations,
November 2018 in “Brazilian Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences” New physical methods like electrical currents, ultrasound, and microneedles show promise for improving drug delivery through the skin.
 21 citations,
August 2011 in “Clinics in Dermatology”
21 citations,
August 2011 in “Clinics in Dermatology” Looking at skin can help find and treat serious diseases early.
 19 citations,
July 1993 in “Journal of Applied Toxicology”
19 citations,
July 1993 in “Journal of Applied Toxicology” Different oil products cause varying levels of skin irritation in mice, which could potentially lead to tumors.
 18 citations,
June 2017 in “Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America”
18 citations,
June 2017 in “Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America” A gene called Gk5 controls lipid production in the skin and affects hair growth.
 17 citations,
June 2017 in “Journal of pharmaceutical sciences”
17 citations,
June 2017 in “Journal of pharmaceutical sciences” Researchers developed a nanomedicine for acne treatment that delivers medication with less irritation and is non-irritating for oily skin.
 12 citations,
May 2020 in “Dermatology and therapy”
12 citations,
May 2020 in “Dermatology and therapy” A young woman had a rare skin reaction to a medication for her joint disease, and a combination therapy improved her condition.
 12 citations,
June 2003 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
12 citations,
June 2003 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” Some psychoactive drugs can cause skin reactions, with carbamazepine having a higher risk, and stopping the drug and seeing a dermatologist is important.
 9 citations,
November 2018 in “Journal of cosmetic dermatology”
9 citations,
November 2018 in “Journal of cosmetic dermatology” Orobanche rapum extract rejuvenates skin and protects skin bacteria, leading to healthier skin.
 8 citations,
June 2021 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology”
8 citations,
June 2021 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology” The review found that COVID-19 can cause skin problems, including rashes and issues from wearing PPE, and suggests more research and protective measures for healthcare workers.
 7 citations,
October 2019 in “Elsevier eBooks”
7 citations,
October 2019 in “Elsevier eBooks” Maintaining skin health is crucial for overall well-being and involves protecting against environmental damage and using skincare products.
 7 citations,
April 2011 in “Expert review of dermatology”
7 citations,
April 2011 in “Expert review of dermatology” The document concludes that patients with skin of color need specialized dermatological care and education to manage unique skin conditions effectively.
 6 citations,
December 2016 in “Springer eBooks”
6 citations,
December 2016 in “Springer eBooks” Environmental stressors like UV radiation, pollution, and extreme temperatures can damage skin and lead to diseases and aging.
 6 citations,
January 2009 in “Elsevier eBooks”
6 citations,
January 2009 in “Elsevier eBooks” The skin has multiple layers and cells, serves as a protective barrier, helps regulate temperature, enables sensation, affects appearance, and is involved in vitamin D synthesis.
 5 citations,
October 2014 in “Journal of cosmetic and laser therapy”
5 citations,
October 2014 in “Journal of cosmetic and laser therapy” Combining physical dermabrasion with chemical peeling is more effective for skin treatment than chemical peeling alone.
 4 citations,
November 2014
4 citations,
November 2014 The skin protects the body, regulates temperature, senses touch, and makes vitamin D.
 3 citations,
April 2015 in “International research journal of pharmacy”
3 citations,
April 2015 in “International research journal of pharmacy” Gentamicin penetrates pig skin better through open hair follicles than blocked ones.
 1 citations,
July 2016 in “Elsevier eBooks”
1 citations,
July 2016 in “Elsevier eBooks” Understanding skin structure and development helps diagnose and treat skin disorders.

The document concludes that dermatology training and grading scales need to better represent dark-skinned individuals to improve diagnosis and assessment of skin conditions.
 1 citations,
January 2012 in “Elsevier eBooks”
1 citations,
January 2012 in “Elsevier eBooks” The document concludes that the skin is a complex organ providing protection, sensation, and healing, with challenges in treating conditions like itchiness.
 1 citations,
July 2005 in “Drugs and the pharmaceutical sciences”
1 citations,
July 2005 in “Drugs and the pharmaceutical sciences” Targeting drugs to hair follicles can treat skin conditions, but reaching deep follicle areas is hard and needs more research.
 April 2024 in “Cell death and differentiation”
April 2024 in “Cell death and differentiation” Cell death shapes skin stem cell environments, affecting inflammation, repair, and cancer.
 January 2024 in “Archives of pharmacy practice”
January 2024 in “Archives of pharmacy practice” The skin is vital for protection, temperature control, fluid balance, immunity, and sensing, with damage affecting daily life and mental health.
 January 2024 in “Journal of cellular immunology”
January 2024 in “Journal of cellular immunology” Hair follicle stem cells are important for maintaining healthy skin and interact with many signals.

Tailored nonsurgical cosmetic procedures are crucial for safely treating diverse skin types, especially skin of color.
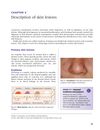
The document explains different types of skin lesions and their characteristics, causes, and related conditions.
 September 2014 in “Aktuelle Dermatologie”
September 2014 in “Aktuelle Dermatologie” The symposium concluded that environmental factors significantly contribute to skin aging.
 June 2012 in “Springer eBooks”
June 2012 in “Springer eBooks” Skin changes can indicate starvation and nutritional deficiencies in anorexia nervosa.
 138 citations,
February 2007 in “European journal of cancer”
138 citations,
February 2007 in “European journal of cancer” EGFR inhibitors often cause skin problems and other side effects, but these are usually reversible and can be managed to keep patients comfortable.
 52 citations,
January 2005 in “International journal of experimental pathology”
52 citations,
January 2005 in “International journal of experimental pathology” Melatonin may reduce skin damage caused by X-rays in rats.
 6 citations,
February 1974 in “The BMJ”
6 citations,
February 1974 in “The BMJ” The document concludes that scalp disorders can be treated with hair washing, specific shampoos, medications, and sometimes surgery or hair transplants, but hereditary baldness is untreatable.






























