
Deleting Smad4 and PTEN genes in mice causes rapid, invasive stomach cancer.
[object Object] 
Deleting Smad4 and PTEN genes in mice causes rapid, invasive forestomach cancer.
 159 citations,
October 2015 in “Science Advances”
159 citations,
October 2015 in “Science Advances” Blocking JAK-STAT signaling can lead to hair growth.
 78 citations,
June 2005 in “Annals of oncology”
78 citations,
June 2005 in “Annals of oncology” Cetuximab can cause excessive eyelash growth.
 44 citations,
September 2014 in “Cell Death & Differentiation”
44 citations,
September 2014 in “Cell Death & Differentiation” Tumor suppressors help control inflammation in cancer and restoring their function could lead to new treatments.
1 citations,
December 2023 in “Molecules/Molecules online/Molecules annual” JAK inhibitors show promise for treating various skin diseases.
 January 2025 in “Cell Communication and Signaling”
January 2025 in “Cell Communication and Signaling” CXXC5 can both suppress and promote cancer, making it a complex target for treatment.
 1160 citations,
November 2018 in “Physiological Reviews”
1160 citations,
November 2018 in “Physiological Reviews” The document concludes that better targeted treatments are needed for wound healing, and single-cell technologies may improve cell-based therapies.
 238 citations,
March 2013 in “Development”
238 citations,
March 2013 in “Development” Fat cells help recruit healing cells and build skin structure during wound healing.
 237 citations,
December 2001 in “Urology”
237 citations,
December 2001 in “Urology” Blocking the enzyme 5α-reductase can shrink the prostate and help treat enlarged prostate issues.
 196 citations,
May 2001 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
196 citations,
May 2001 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” Sebocytes play a key role in controlling androgen levels in human skin.
 182 citations,
November 2017 in “Molecular Aspects of Medicine”
182 citations,
November 2017 in “Molecular Aspects of Medicine” The PDGF/PDGFR pathway is a potential drug target with mixed success in treating various diseases, including some cancers and fibrosis.
138 citations,
March 2021 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Ritlecitinib and brepocitinib effectively regrow hair in alopecia areata patients.
 138 citations,
July 2015 in “Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology”
138 citations,
July 2015 in “Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology” Eating less sugar, milk, and saturated fats and more vegetables and fish may help treat and prevent acne.
127 citations,
August 2016 in “The oncologist” Understanding and managing side effects of hedgehog pathway inhibitors can improve treatment for advanced basal cell carcinoma.
 103 citations,
June 2018 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences”
103 citations,
June 2018 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences” FGF signaling is a promising target for developing treatments for wounds, metabolic diseases, and cancer.
 98 citations,
December 2008 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
98 citations,
December 2008 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Prolactin affects hair growth and skin conditions, and could be a target for new skin disease treatments.
 89 citations,
November 2017 in “Journal of Cellular Physiology”
89 citations,
November 2017 in “Journal of Cellular Physiology” The Wnt/β-catenin pathway is important for tissue development and has potential in regenerative medicine, but requires more research for therapeutic use.
 47 citations,
August 2016 in “Fitoterapia”
47 citations,
August 2016 in “Fitoterapia” Some herbs and their components might help treat hair loss by affecting various biological pathways, but more research and regulation are needed.
 42 citations,
April 2021 in “Journal of clinical pharmacology”
42 citations,
April 2021 in “Journal of clinical pharmacology” Baricitinib helps treat several diseases, including COVID-19, but has side effects and needs careful monitoring.
 32 citations,
January 2005 in “Advances in Biochemical Engineering / Biotechnology”
32 citations,
January 2005 in “Advances in Biochemical Engineering / Biotechnology” Fetal wounds heal without scarring because of different biological factors, which could help improve adult wound healing.
[object Object]  26 citations,
June 2019 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
26 citations,
June 2019 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” Regenerative therapies show promise for treating vitiligo and alopecia areata.
 11 citations,
January 2000 in “Journal of Cutaneous Pathology”
11 citations,
January 2000 in “Journal of Cutaneous Pathology” Short telomeres contribute to aging and cancer, and while telomerase can delay aging, it may also promote cancer.
 3 citations,
February 2019 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology”
3 citations,
February 2019 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology” The effects of estrogen on human scalp hair growth are unclear and need more research.
 2 citations,
February 2023 in “BMC women's health”
2 citations,
February 2023 in “BMC women's health” Birth control pills change the activity of certain inflammation and blood clotting genes in women with PCOS.
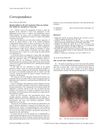 2 citations,
June 2005 in “Clinical Oncology”
2 citations,
June 2005 in “Clinical Oncology” A man's bald spot grew hair after starting cancer treatment with gefitinib.
 1 citations,
May 2023 in “Prospects in Pharmaceutical Sciences”
1 citations,
May 2023 in “Prospects in Pharmaceutical Sciences” New cytokine-targeted therapies show promise for treating alopecia areata.
 December 2023 in “Frontiers in pharmacology”
December 2023 in “Frontiers in pharmacology” Progesterone initially worsens but later reduces neuropathic pain in mice, through different mechanisms.
 January 2018 in “Springer eBooks”
January 2018 in “Springer eBooks” Cancer treatments targeting specific cells often cause skin, hair, and nail problems, affecting patients' lives and requiring careful management.
 192 citations,
January 2015 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
192 citations,
January 2015 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Targeted cancer therapies often cause serious skin problems that need careful management.



























