 139 citations,
June 2003 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology Symposium Proceedings”
139 citations,
June 2003 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology Symposium Proceedings” Androgenetic alopecia in women needs more research and better management strategies.
 35 citations,
November 2020 in “Dermatologic Therapy”
35 citations,
November 2020 in “Dermatologic Therapy” Severe COVID-19 may cause hair loss, and doctors recommend supplements and topical treatments to manage it.
 19 citations,
June 2015 in “Actas Dermo-Sifiliográficas”
19 citations,
June 2015 in “Actas Dermo-Sifiliográficas” Chronic kidney disease can cause skin problems that affect patient quality of life, and treating these conditions can improve outcomes.
 8 citations,
January 1996 in “Gynecological Endocrinology”
8 citations,
January 1996 in “Gynecological Endocrinology” Cyproterone acetate is the preferred treatment for women's hyperandrogenism when estrogen/progestogen use is safe.
 1 citations,
July 2015 in “The European research journal”
1 citations,
July 2015 in “The European research journal” Stopping aripiprazole can reverse its side effect of hair loss.
 January 2020 in “Medpulse International Journal of General Medicine/Medpulse International Journal of Medicine”
January 2020 in “Medpulse International Journal of General Medicine/Medpulse International Journal of Medicine” Premature graying of hair is often linked with other health issues, but treatment with biotin, zinc, and calcium pantothenate is not very effective.
 September 2015 in “Actas Dermo-Sifiliográficas”
September 2015 in “Actas Dermo-Sifiliográficas” People with advanced chronic kidney disease often have skin problems, which can be treated with various medications and procedures to improve their quality of life.

Hair can accurately predict iron levels in cattle muscle, helping diagnose mineral imbalances.
 January 2020 in “Journal of dermatology research and therapy”
January 2020 in “Journal of dermatology research and therapy” Most over-the-counter hair loss treatments lack strong evidence of effectiveness but cost nearly as much as the proven treatment, minoxidil.
 March 2022 in “IP Indian journal of clinical and experimental dermatology”
March 2022 in “IP Indian journal of clinical and experimental dermatology” Low ferritin and cobalamin levels are better indicators of chronic hair loss in reproductive-age women than hemoglobin levels.
 1 citations,
January 2002 in “Journal of Clinical Dermatology”
1 citations,
January 2002 in “Journal of Clinical Dermatology” Low iron levels in the blood may be linked to chronic hair loss in women.
 40 citations,
July 2015 in “Journal of Cellular Biochemistry”
40 citations,
July 2015 in “Journal of Cellular Biochemistry” Cysteine helps maintain keratin production in skin cells even when iron is low.
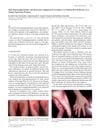 16 citations,
January 2008 in “Acta dermato-venereologica”
16 citations,
January 2008 in “Acta dermato-venereologica” Vitamin B12 deficiency can cause skin darkening and increased blood vessels, but treatment can improve symptoms.
 October 2019 in “Turkderm”
October 2019 in “Turkderm” Patients with pernio have lower vitamin B12 and ferritin levels than healthy people.

Low vitamin D3 and ferritin levels may cause hair loss in pregnant women.
 November 2023 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology”
November 2023 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology” People with non-scarring hair loss often have lower vitamin D levels than those without hair loss.
 July 2022 in “Journal of Dermatology and Dermatologic Surgery”
July 2022 in “Journal of Dermatology and Dermatologic Surgery” People with chronic hair loss often have lower Vitamin B12 levels.
 January 2022 in “United Research Forum eBooks”
January 2022 in “United Research Forum eBooks” Picky eating in children is linked to lower zinc levels and various nutritional deficiencies.
August 2024 in “Jordan Medical Journal” Picky eating in children is linked to lower weight, hemoglobin, vitamin D, and zinc levels.
 4 citations,
March 2023 in “Journal of medical case reports”
4 citations,
March 2023 in “Journal of medical case reports” Taking too much vitamin E caused a young man's blood clotting problems, which improved after he stopped the vitamin E and got treatment.
 January 2012 in “Vitamins & trace elements”
January 2012 in “Vitamins & trace elements” Smoking and drinking can lower vitamin levels and potentially trigger early hair loss, but overall vitamin levels don't seem to affect hair loss duration.

Iron deficiency anemia can cause itching, which often improves with iron supplements.
 15 citations,
January 2010 in “Experimental Dermatology”
15 citations,
January 2010 in “Experimental Dermatology” Hair loss in certain young mice is linked to a specific gene and can be caused by lack of iron.
 October 2024 in “Journal of the Pakistan Medical Association”
October 2024 in “Journal of the Pakistan Medical Association” Genetics, nutrition, lifestyle, and hormones affect early grey hair, but more research is needed.
26 citations,
October 2011 in “Biological trace element research” Low copper levels might cause premature graying of hair.
9 citations,
September 2019 in “Journal of clinical sleep medicine” Vitamin B12 deficiency can rarely cause excessive daytime sleepiness.
 9 citations,
January 2014 in “World journal of gastroenterology”
9 citations,
January 2014 in “World journal of gastroenterology” A gluten-free diet stopped a child's hair-eating behavior and suggested she had celiac disease.
 5 citations,
May 2020 in “Diagnostics”
5 citations,
May 2020 in “Diagnostics” Lower zinc levels may predict less effective hair loss treatment.
 June 2024 in “Al- Anbar Medical Journal”
June 2024 in “Al- Anbar Medical Journal” Acute telogen effluvium can be resolved by addressing causes, but chronic telogen effluvium is harder to treat.
 May 2024 in “Portuguese journal of dermatology and venereology”
May 2024 in “Portuguese journal of dermatology and venereology” Reassurance and counseling are key in managing acute telogen effluvium, with supplements possibly offering a placebo effect.



























