 11 citations,
September 1992 in “Journal of pineal research”
11 citations,
September 1992 in “Journal of pineal research” Immunizing goats against melatonin can temporarily change their cashmere growth cycles and increase fleece production.
26 citations,
October 1996 in “Journal of Endocrinology/Journal of endocrinology” Goat hair follicles have insulin-like growth factor-I receptors that might affect hair growth, but no melatonin receptors were found.
1 citations,
December 2023 in “Animals” Winter provides the best fur quality for Rex rabbits due to seasonal changes in specific signaling pathways.
September 2020 in “Research Square (Research Square)” Goat skin adapts to seasonal changes through genes that respond to daylight length, affecting hormone levels and potentially making skin cells light-sensitive.
 22 citations,
July 2012 in “Journal of integrative agriculture/Journal of Integrative Agriculture”
22 citations,
July 2012 in “Journal of integrative agriculture/Journal of Integrative Agriculture” Hoxc13 is linked to seasonal hair growth in Cashmere goats and is affected by melatonin.
8 citations,
May 2005 in “Australian veterinary journal” A Tibetan Terrier had recurring seasonal hair loss for three years.
 109 citations,
January 2011 in “Frontiers in Systems Neuroscience”
109 citations,
January 2011 in “Frontiers in Systems Neuroscience” Choosing the right model order in brain connectivity analysis can affect the detection of differences between healthy individuals and those with seasonal affective disorder.
 38 citations,
October 1988 in “Clinics in Dermatology”
38 citations,
October 1988 in “Clinics in Dermatology” Hormones, nutrition, and seasonal changes regulate hair growth cycles, with androgens extending growth phases and factors like aging and malnutrition affecting hair loss and thinning.
 59 citations,
February 2012 in “Journal of Dermatological Science”
59 citations,
February 2012 in “Journal of Dermatological Science” Environmental factors at different levels control hair stem cell activity, which could lead to new hair growth and alopecia treatments.
 34 citations,
May 2013 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
34 citations,
May 2013 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” Hair growth slows and shedding increases after childbirth, but most women don't experience excessive hair loss.
 10 citations,
June 1998 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
10 citations,
June 1998 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Inflammation around hair follicles leads to hair loss, and treatments should focus on reducing this inflammation and other factors for effectiveness.
 7 citations,
July 1999 in “In Practice”
7 citations,
July 1999 in “In Practice” The conclusion is that a systematic approach is key for treating symmetrical alopecia in dogs, but treatment may not always be necessary.
 5 citations,
October 2013 in “Veterinary Clinics of North America: Equine Practice”
5 citations,
October 2013 in “Veterinary Clinics of North America: Equine Practice” Some horses lose hair without inflammation or itching due to various conditions, and while mainly a cosmetic issue, diagnosis requires examination and biopsies, and breeding is not advised if it's hereditary.
2 citations,
August 2022 in “Animals” Essential oils may improve dogs' health and melatonin can help with their sleep and anxiety, but both should be used carefully.
 2 citations,
March 2004 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
2 citations,
March 2004 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” The 60-second timed hair count is a reliable and simple way to measure hair shedding at home, showing older women tend to shed more hair than younger women.
The chapter explains causes of hair loss and excessive hair growth in animals.
 July 2017 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
July 2017 in “British Journal of Dermatology” The document concludes that scalp conditions have various causes and can present in many different ways.
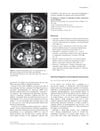 February 2012 in “Clinical and Experimental Dermatology”
February 2012 in “Clinical and Experimental Dermatology” Many adult women experience unexplained excessive hair shedding, often starting before age 40.
 January 2012 in “The Japanese Journal of Veterinary Dermatology”
January 2012 in “The Japanese Journal of Veterinary Dermatology” The dog's hair loss healed on its own without treatment.
 July 2023 in “Frontiers in veterinary science”
July 2023 in “Frontiers in veterinary science” Certain long non-coding RNAs are important for controlling hair growth cycles in sheep.
 3 citations,
September 2022 in “Frontiers in veterinary science”
3 citations,
September 2022 in “Frontiers in veterinary science” Melatonin affects cashmere growth in goats by influencing stem cell and certain signaling pathways.
62 citations,
December 1994 in “Journal of Endocrinology/Journal of endocrinology” Prolactin speeds up hair growth and moulting in cashmere goats.
 48 citations,
October 1996 in “Dermatologic clinics”
48 citations,
October 1996 in “Dermatologic clinics” Some treatments can help with hair regrowth in alopecia areata, but results vary and long-term use is often needed without changing the disease's outcome.
20 citations,
January 1995 in “Cells tissues organs” Changing light periods synchronized wool growth cycles in sheep.
14 citations,
February 2013 in “Veterinary dermatology” Horse alopecia areata is rare and mainly affects their appearance.
 14 citations,
January 2008 in “Dermatology”
14 citations,
January 2008 in “Dermatology” Vitamin D made by the skin plays a role in immune defense and skin health, and more research is needed to understand its full effects.
 13 citations,
October 2011 in “Clinical and Experimental Dermatology”
13 citations,
October 2011 in “Clinical and Experimental Dermatology” Laser hair-comb therapy doesn't improve male-pattern hair loss.
 9 citations,
June 2003 in “Veterinary dermatology”
9 citations,
June 2003 in “Veterinary dermatology” Boxer dogs may have a genetic skin condition that worsens seasonally and can be treated with certain medications.
 3 citations,
January 2019 in “Aesthetic Surgery Journal”
3 citations,
January 2019 in “Aesthetic Surgery Journal” Google Trends is useful for aesthetic surgeons to improve marketing by tracking what and when people search for facial cosmetic procedures.
 3 citations,
May 2011 in “Medical Hypotheses”
3 citations,
May 2011 in “Medical Hypotheses” Transnasal cooling could reveal new insights into various physiological conditions and may be a natural way to transfer heat from the brain.





















