 72 citations,
June 2001 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
72 citations,
June 2001 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” S100A4 and S100A6 proteins may activate stem cells for hair follicle regeneration and could be potential targets for hair loss treatments.
62 citations,
December 2007 in “Journal of biological chemistry/The Journal of biological chemistry” A specific chemical change in the S100A3 protein leads to the formation of a four-part structure important for hair formation.
 45 citations,
July 2009 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
45 citations,
July 2009 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” The S100A4 protein is more common in psoriatic skin and could be a target for treating psoriasis.
 40 citations,
November 1998 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
40 citations,
November 1998 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” S100A3 protein is crucial for hair shaft formation in mice.
 17 citations,
December 2002 in “Biochemical and biophysical research communications”
17 citations,
December 2002 in “Biochemical and biophysical research communications” Scientists found out how a specific protein in human hair cuticles behaves and is structured.
 4 citations,
January 2017 in “Biological & pharmaceutical bulletin”
4 citations,
January 2017 in “Biological & pharmaceutical bulletin” Inhibiting ALOX12 can help hair cuticle maturation by increasing S100A3 citrullination.
 1 citations,
January 2015 in “Genetics and Molecular Research”
1 citations,
January 2015 in “Genetics and Molecular Research” Stopping S100A3 activity slows down hair growth in mice.
 January 2025 in “Clinical and Translational Medicine”
January 2025 in “Clinical and Translational Medicine” A specific RNA can help hair growth in baldness by boosting stem cell activity.
September 2019 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” Certain proteins are significantly increased in the skin of people with hidradenitis suppurativa.
68 citations,
April 2014 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Trichohyalin-like proteins are essential for the development of skin structures like hair, nails, and feathers.
 18 citations,
November 2013 in “Molecules and Cells”
18 citations,
November 2013 in “Molecules and Cells” New culture method keeps human skin stem cells more stem-like.
12 citations,
May 2021 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” Laminin 332 is essential for normal skin cell behavior and structure.
 10 citations,
January 2013 in “Stem Cells and Development”
10 citations,
January 2013 in “Stem Cells and Development” Scientists identified a unique type of human skin stem cell that could help with tissue repair.
 8 citations,
June 2016 in “Journal of Cutaneous Pathology”
8 citations,
June 2016 in “Journal of Cutaneous Pathology” Two women were diagnosed with a rare melanoma that looked like hair loss but was actually a type of skin cancer.
 5 citations,
January 2017 in “Molecular Medicine Reports”
5 citations,
January 2017 in “Molecular Medicine Reports” Human hair follicle cells can be turned into neural stem cell-like cells, which might help treat brain diseases.
5 citations,
February 2022 in “Seminars in cell & developmental biology” Recent findings suggest that genetic factors, immune system issues, and skin cell defects might contribute to the development of hidradenitis suppurativa.
 5 citations,
July 2022 in “Journal of Clinical Medicine”
5 citations,
July 2022 in “Journal of Clinical Medicine” Long COVID-19 patients with skin pain might have a nerve condition that responds to a medication called gabapentin.
 4 citations,
June 2021 in “Dermatology”
4 citations,
June 2021 in “Dermatology” Scientists created a 3D skin model to study a chronic skin disease and test treatments.
 3 citations,
May 2023 in “Precision clinical medicine”
3 citations,
May 2023 in “Precision clinical medicine” Researchers found four genes that could help diagnose severe alopecia areata early.
 2 citations,
April 2018 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
2 citations,
April 2018 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Frontal fibrosing alopecia shows increased inflammation and JAK-STAT pathway activity without reduced hair proteins.
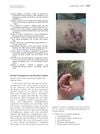
A 72-year-old man was diagnosed with a rare skin form of Rosai-Dorfman disease after years of misdiagnosis.
 November 2024 in “Experimental Dermatology”
November 2024 in “Experimental Dermatology” SKO-derived SKP-like cells may help with hair regeneration and skin restoration.
June 2023 in “Dermatopathology” A woman had a unique skin growth with hair follicle, oil glands, fat cells, spindle cells, and nerve fibers.
 January 2025 in “BMC Genomics”
January 2025 in “BMC Genomics” Key genes and RNA networks regulate hair growth and follicle density in Rex rabbits.
 January 2025 in “bioRxiv (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory)”
January 2025 in “bioRxiv (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory)” Potential therapeutic targets for scarring hair loss are identified.
 November 2022 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
November 2022 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” Skin organoids with NCSTN mutation show changes in hair follicle development and higher inflammation, key features of Hidradenitis Suppurativa.
 March 2022 in “Research Square (Research Square)”
March 2022 in “Research Square (Research Square)” 4-aminopyridine, a FDA-approved drug, speeds up skin wound healing and tissue regeneration.
 September 2019 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
September 2019 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” The 3D-SeboSkin model effectively simulates Hidradenitis suppurativa and is useful for future research.
November 2022 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” NCSTN gene mutation causes abnormal skin cell differentiation and more inflammation, contributing to Hidradenitis Suppurativa.
49 citations,
February 2009 in “Clinical Rheumatology” SLE is more common among Nigerians than previously thought, especially in women, requiring early treatment.





















