 7 citations,
January 2015 in “Biological & Pharmaceutical Bulletin”
7 citations,
January 2015 in “Biological & Pharmaceutical Bulletin” Rice Bran Supercritical CO2 Extract significantly increased hair density and diameter in male alopecia patients without any side effects.
 17 citations,
December 2015 in “International Journal of Cosmetic Science”
17 citations,
December 2015 in “International Journal of Cosmetic Science” Visible light can improve skin disorders and hair loss, but more research is needed to understand long-term effects.
 51 citations,
May 2011 in “Phytotherapy Research”
51 citations,
May 2011 in “Phytotherapy Research” Ginseng, especially red ginseng, may help regrow hair and block a hair loss-related enzyme.
 October 2023 in “Dermatology practical & conceptual”
October 2023 in “Dermatology practical & conceptual” Many patients experienced hair loss after COVID-19, with women affected more, starting on average 49 days post-infection.
 February 2024 in “International journal of biology, pharmacy and allied sciences”
February 2024 in “International journal of biology, pharmacy and allied sciences” Plant-based treatments can effectively and safely treat hair loss.
 52 citations,
September 2018 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences”
52 citations,
September 2018 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences” Ginseng and its compounds may help hair growth and prevent hair loss, but more human trials are needed to confirm this.
 January 2022 in “Journal of Dermatology and Dermatologic Surgery”
January 2022 in “Journal of Dermatology and Dermatologic Surgery” Trichoscopy is useful for quickly diagnosing different types of hair loss without needing biopsies.

The man's scalp tightness after hair surgery affects his life and work, and it's unclear if it's due to the surgery or a mental health issue.
 January 2024 in “Annals of Agricultural and Environmental Medicine”
January 2024 in “Annals of Agricultural and Environmental Medicine” Red LED light therapy helps reduce hair loss and improves hair regrowth in long COVID patients.

Low-level laser therapy may help uninfected cells but has different effects on coronavirus-infected cells.
 July 1998 in “Proceedings of SPIE”
July 1998 in “Proceedings of SPIE” Low-power laser therapy is an effective, side-effect-free treatment that speeds up hair regrowth and crural ulcer healing.
 55 citations,
July 1999 in “Clinics in Sports Medicine”
55 citations,
July 1999 in “Clinics in Sports Medicine” Athletes use steroids to enhance performance despite health risks and legal issues, and education on their dangers is needed.
 33 citations,
January 2021 in “Aesthetic Surgery Journal”
33 citations,
January 2021 in “Aesthetic Surgery Journal” Low-Level Light Therapy (LLLT) is a safe and effective method for skin rejuvenation, acne treatment, wound healing, body contouring, and hair growth, but more well-designed trials are needed for confirmation.
 January 2015 in “Przegla̧d dermatologiczny”
January 2015 in “Przegla̧d dermatologiczny” 308 nm excimer light therapy may help hair regrowth in alopecia areata with delayed results and no serious side effects.
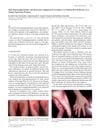 16 citations,
January 2008 in “Acta dermato-venereologica”
16 citations,
January 2008 in “Acta dermato-venereologica” Vitamin B12 deficiency can cause skin darkening and increased blood vessels, but treatment can improve symptoms.
 27 citations,
July 2017 in “Facial Plastic Surgery”
27 citations,
July 2017 in “Facial Plastic Surgery” Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) shows promise for hair growth and skin improvement in aesthetic surgery.
 14 citations,
January 2014 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
14 citations,
January 2014 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Minoxidil with Korean red ginseng improves hair density and thickness more than minoxidil alone.
 September 2002 in “Dermatologic Surgery”
September 2002 in “Dermatologic Surgery” The evaluation system improves patient selection for hair loss surgery, leading to fewer but more successful surgeries.
 247 citations,
August 2011 in “European Journal of Epidemiology”
247 citations,
August 2011 in “European Journal of Epidemiology” The Rotterdam Study updated its design and objectives in 2012, providing insights into various diseases in the elderly, including skin cancer, bone health, liver disease, neurological and psychiatric conditions, and respiratory issues.
 70 citations,
January 2009 in “The Journal of clinical endocrinology and metabolism/Journal of clinical endocrinology & metabolism”
70 citations,
January 2009 in “The Journal of clinical endocrinology and metabolism/Journal of clinical endocrinology & metabolism” Androgens slow hair growth by altering Wnt signaling in balding cells.
 3 citations,
July 2017 in “Current sports medicine reports”
3 citations,
July 2017 in “Current sports medicine reports” Athletes can experience various skin issues, which can be treated and prevented with appropriate care and protective measures.
 October 2024 in “Dermatologic Surgery”
October 2024 in “Dermatologic Surgery” PRP and PRF show promise for hair growth but need more research for consistent and safe use.
 5 citations,
May 2023 in “Frontiers in immunology”
5 citations,
May 2023 in “Frontiers in immunology” Environmental factors like diet and vitamin levels, especially Vitamin D, can affect autoimmune diseases differently, with lifestyle changes potentially improving outcomes.
 4 citations,
January 2020 in “Cells”
4 citations,
January 2020 in “Cells” The research found that the gene activity in mouse skin stem cells changes significantly as they age.
April 2023 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Use a 3-mm spot size and specific protective eyewear for safer and more effective laser treatment of facial veins.
 18 citations,
February 2016 in “The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism”
18 citations,
February 2016 in “The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism” Advancements in male reproductive medicine are ongoing, but more research and improved treatments are needed in several areas.
 10 citations,
January 2007 in “Journal of cosmetic and laser therapy”
10 citations,
January 2007 in “Journal of cosmetic and laser therapy” The IPL device is safe, effective, and has high patient satisfaction for hair removal.
 14 citations,
November 2013 in “Journal of the American Society for Horticultural Science”
14 citations,
November 2013 in “Journal of the American Society for Horticultural Science” Glycine slows main root growth but boosts root hair growth in habanero peppers.
 1 citations,
July 2007 in “Regenerative Medicine”
1 citations,
July 2007 in “Regenerative Medicine” Stem cell research and regenerative medicine have made significant advancements in treating various diseases and conditions.
 July 2021 in “IntechOpen eBooks”
July 2021 in “IntechOpen eBooks” Ginseng, especially its component ginsenosides, can promote hair growth, reduce hair loss, and potentially treat conditions like alopecia by affecting cell pathways and cytokines.




























