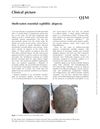
 3 citations,
July 2014 in “QJM”
3 citations,
July 2014 in “QJM” A 35-year-old man had patchy hair loss that was actually due to syphilis, not alopecia areata.
[object Object]  2 citations,
January 2013 in “Elsevier eBooks”
2 citations,
January 2013 in “Elsevier eBooks” The chapter explains the causes of excessive hair growth and masculinization in women and how to measure hormone levels related to these conditions.
 1 citations,
January 2018 in “Acta dermato-venereologica”
1 citations,
January 2018 in “Acta dermato-venereologica” A teenager's hair with alternating white and dark bands, known as Pili annulati, is a genetic condition that is usually harmless and often considered attractive.
 1 citations,
August 2012 in “Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft”
1 citations,
August 2012 in “Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft” A woman's hyperandrogenism was caused by a genetic mutation leading to non-classic adrenogenital syndrome.
 November 2022 in “Journal of the Endocrine Society”
November 2022 in “Journal of the Endocrine Society” An 8-year-old boy's early puberty was caused by a rare hormone-secreting brain tumor, which was successfully treated with surgery.

Hormones, especially testosterone and DHT, are key for penis development and function, and testosterone therapy may help with erectile dysfunction in those with low levels.
 January 2016 in “Springer eBooks”
January 2016 in “Springer eBooks” A 19-year-old male with delayed puberty was successfully treated for a condition that prevents normal hormone production.
 January 2016 in “Journal of The Korean Medical Association”
January 2016 in “Journal of The Korean Medical Association” The document says how to diagnose and treat hair loss from alopecia areata, but there's no cure and treatments vary.
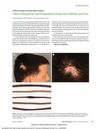 May 2014 in “JAMA Dermatology”
May 2014 in “JAMA Dermatology” Mother and son diagnosed with a rare genetic hair loss condition with no effective treatment.
 November 2009 in “Journal of Pediatric Nursing”
November 2009 in “Journal of Pediatric Nursing” Nonclassic congenital adrenal hyperplasia is a common genetic disorder that can cause a range of symptoms and requires personalized treatment.
 May 2006 in “Women's Health Medicine”
May 2006 in “Women's Health Medicine” Excessive hair growth in women, often from high androgen levels, is usually caused by PCOS, and can be treated with hair removal, medication, and possibly weight loss.
 November 2004 in “John Wiley & Sons, Ltd eBooks”
November 2004 in “John Wiley & Sons, Ltd eBooks” Insulin resistance is linked to PCOS and can lead to other health issues, but treatments like metformin can help manage symptoms.
 September 2002 in “Dermatologic Surgery”
September 2002 in “Dermatologic Surgery” The recipient site can affect the growth and survival of transplanted hair but not its thickness.
 April 1955 in “Archives of pediatrics & adolescent medicine”
April 1955 in “Archives of pediatrics & adolescent medicine” Children's skin diseases need special care and treatment.
 271 citations,
December 2005 in “New England journal of medicine/The New England journal of medicine”
271 citations,
December 2005 in “New England journal of medicine/The New England journal of medicine” The document likely offers guidance on treating a woman's excessive hair growth, considering her symptoms and obesity.
 227 citations,
January 1998 in “Journal of Endocrinology”
227 citations,
January 1998 in “Journal of Endocrinology” Cells from balding scalps have more androgen receptors than cells from non-balding scalps.
 190 citations,
October 2002 in “The FASEB journal”
190 citations,
October 2002 in “The FASEB journal” Androgens may cause hair loss by increasing TGF-beta1 from scalp cells, which inhibits hair cell growth.
 169 citations,
August 2004 in “Baillière's best practice & research. Clinical obstetrics & gynaecology/Baillière's best practice and research in clinical obstetrics and gynaecology”
169 citations,
August 2004 in “Baillière's best practice & research. Clinical obstetrics & gynaecology/Baillière's best practice and research in clinical obstetrics and gynaecology” Lower doses of treatments for hirsutism and acne in PCOS are effective and cause fewer side effects.
 151 citations,
February 2007 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
151 citations,
February 2007 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Alopecia areata causes hair loss, has no cure, and various treatments exist.
 115 citations,
September 2012 in “Experimental Dermatology”
115 citations,
September 2012 in “Experimental Dermatology” Androgens have complex effects on hair growth, promoting it in some areas but causing hair loss in others, and our understanding of this is still evolving.
 114 citations,
March 2002 in “Current opinion in oncology/Current opinion in oncology, with cancerlit”
114 citations,
March 2002 in “Current opinion in oncology/Current opinion in oncology, with cancerlit” Cancer therapy can cause various skin problems, including hair loss, skin darkening, painful hand-foot syndrome, and severe skin damage.
 101 citations,
April 1994 in “Baillière's clinical endocrinology and metabolism”
101 citations,
April 1994 in “Baillière's clinical endocrinology and metabolism” 5α-reductase is essential for male sexual development and its inhibitors have potential in treating various conditions related to hormone action.
 90 citations,
July 2008 in “Dermatologic therapy”
90 citations,
July 2008 in “Dermatologic therapy” Lichen planopilaris is a chronic, scarring hair loss condition with no definitive cure, requiring accurate diagnosis and treatment to manage symptoms.
 85 citations,
April 2007 in “Dermatologic Clinics”
85 citations,
April 2007 in “Dermatologic Clinics” Some drugs can cause hair loss, change hair color and shape, or increase hair growth, and treatment may involve stopping the drug or using specific hair growth treatments.
 83 citations,
January 2001 in “American journal of clinical dermatology”
83 citations,
January 2001 in “American journal of clinical dermatology” Clomipramine may significantly reduce hair-pulling in Trichotillomania, but more research is needed on treatments and early onset cases.
 78 citations,
February 2011 in “Canadian Medical Association Journal”
78 citations,
February 2011 in “Canadian Medical Association Journal” Acne treatment varies, with topical and systemic therapies effective, and more research needed on treatment order and long-term effects.
 75 citations,
May 1986 in “Clinics in endocrinology and metabolism”
75 citations,
May 1986 in “Clinics in endocrinology and metabolism” Male hormones are important for hair and oil gland development and can cause conditions like excessive hair growth and acne.
[object Object]  70 citations,
January 2009 in “The Journal of clinical endocrinology and metabolism/Journal of clinical endocrinology & metabolism”
70 citations,
January 2009 in “The Journal of clinical endocrinology and metabolism/Journal of clinical endocrinology & metabolism” Androgens slow hair growth by altering Wnt signaling in balding cells.
 68 citations,
May 2012 in “Annals of Oncology”
68 citations,
May 2012 in “Annals of Oncology” Some breast cancer chemotherapy can cause permanent hair loss.
 64 citations,
May 2003 in “Journal of health psychology”
64 citations,
May 2003 in “Journal of health psychology” Women with excess body hair feel psychological distress influenced by societal beauty standards, but distress isn't directly linked to the amount of hair.






























