97 citations,
January 1999 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Pityriasis rubra pilaris is a rare skin disorder with reddish-orange patches and thickened skin, needing better treatment understanding.
23 citations,
June 1977 in “Clinical and experimental dermatology” Pityriasis amiantacea is likely linked to eczema-related skin changes.
21 citations,
July 2011 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” A man developed a rash similar to pityriasis rubra pilaris after starting sorafenib for cancer, possibly due to the drug's effect on skin cells.
16 citations,
April 1985 in “Archives of dermatology” The summary does not report the effectiveness of Stanozolol in treating Pityriasis rubra pilaris.
13 citations,
January 2019 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Pityriasis rubra pilaris significantly worsens quality of life more than many other health conditions.
12 citations,
September 2020 in “JAMA Dermatology” PRP patients show varied symptoms and need more research to understand related conditions.
 10 citations,
October 2015 in “Journal of the International Association of Providers of AIDS Care”
10 citations,
October 2015 in “Journal of the International Association of Providers of AIDS Care” A woman with HIV had a severe skin condition that improved with antiretroviral therapy.
9 citations,
October 2015 in “Cutaneous and ocular toxicology” Vemurafenib can cause scalp issues but can be managed without changing the dose.
9 citations,
July 1993 in “Archives of dermatology” Pityriasis amiantacea is a scalp condition with thick, greasy scales and sometimes hair loss.
 6 citations,
April 1985 in “Australasian journal of dermatology”
6 citations,
April 1985 in “Australasian journal of dermatology” The cause of the syndrome with scalp scaling and hair loss is unknown.
 4 citations,
March 2020 in “Turkish Journal of Medical Sciences”
4 citations,
March 2020 in “Turkish Journal of Medical Sciences” There may be a link between Helicobacter pylori infection and the skin condition pityriasis versicolor.
 2 citations,
November 2022 in “IP Indian journal of clinical and experimental dermatology”
2 citations,
November 2022 in “IP Indian journal of clinical and experimental dermatology” Dermoscopic and histopathological features combined can help diagnose Pityriasis versicolor.
 1 citations,
September 2023 in “Rheumatology advances in practice”
1 citations,
September 2023 in “Rheumatology advances in practice” A woman's rare scalp condition worsened after using a specific arthritis medication, suggesting such medications can sometimes trigger or aggravate psoriasis.
1 citations,
April 2022 in “JAAD case reports” A woman developed a rare scalp condition after starting minoxidil, which was resolved with specific shampoo and solution.
1 citations,
January 2019 in “PubMed” A woman developed a hair disorder after a bone marrow transplant, which improved with treatment.
 November 2024 in “Medicina”
November 2024 in “Medicina” Recognizing scalp symptoms in PRP is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment.
 June 2023 in “Pediatric investigation”
June 2023 in “Pediatric investigation” A boy's scalp infection, usually found on the body, was effectively treated with antifungal cream.
 April 2023 in “International journal of dermatology and venereology”
April 2023 in “International journal of dermatology and venereology” Dermoscopic features can help identify and differentiate types of pityriasis versicolor.
 February 2023 in “Research Square (Research Square)”
February 2023 in “Research Square (Research Square)” Blocking IL-17 can reduce skin inflammation in a mouse model of pityriasis rubra pilaris.

Seborrheic dermatitis and dandruff are often treated with antifungal and anti-inflammatory medications, which can reduce symptoms and yeast growth on the scalp.
August 2021 in “Indian dermatology online journal” A young boy with a rare skin and nail condition improved significantly with simple topical treatments.
 September 2020 in “Journal of Cutaneous Pathology”
September 2020 in “Journal of Cutaneous Pathology” A patient with a skin condition had unusual scarring hair loss but improved with treatment.
 August 2018 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
August 2018 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” A 5-year-old girl with a rare skin disorder was effectively treated with skin creams instead of oral medication.
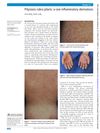 February 2018 in “BMJ case reports”
February 2018 in “BMJ case reports” An 18-year-old woman was diagnosed with a rare skin condition called Pityriasis rubra pilaris.
 May 2017 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
May 2017 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” A woman with a skin disorder was found to have hepatitis C, which may be linked, and was safely treated with methotrexate.
December 2004 in “Microbial Ecology in Health and Disease” Pityriasis amiantacea is linked to Staphylococcus aureus infection and can be effectively treated with antibiotics, corticosteroids, and coal tar.
1 citations,
November 2014 in “Actas dermo-sifiliográficas/Actas dermo-sifiliográficas” 1 citations,
July 2021 in “Clinical Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology” Syphilis should be considered if PLEVA-like symptoms don't improve with treatment.
65 citations,
November 2008 in “Pediatric Dermatology” Phototherapy is effective and well-tolerated for treating childhood psoriasis and pityriasis lichenoides chronica.
 1 citations,
July 1973 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
1 citations,
July 1973 in “British Journal of Dermatology” The document concludes that secondary syphilis cases are increasing and often misdiagnosed, pityriasis rubra pilaris can be distinguished from psoriasis by skin cell features, and different skin layers produce specific components during skin repair.














