 October 2022 in “Research Square (Research Square)”
October 2022 in “Research Square (Research Square)” Key genes linked to immune response are highly active in lupus-affected hair follicles.
 1 citations,
January 2009 in “CRC Press eBooks”
1 citations,
January 2009 in “CRC Press eBooks” Finasteride increases hair count and improves hair growth with low risk of side effects.
 4 citations,
November 2021 in “Biomedicines”
4 citations,
November 2021 in “Biomedicines” New digital tools are improving the diagnosis and understanding of irreversible hair loss conditions.
 3 citations,
July 2022 in “BJOG: An International Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology”
3 citations,
July 2022 in “BJOG: An International Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology” Some birth control pills increase young women's risk of blood clots more than others.
 May 2024 in “Frontiers in Immunology”
May 2024 in “Frontiers in Immunology” Type-2 immunity may influence skin diseases and could be targeted for treatment.
April 2024 in “International journal of molecular sciences” Light-based treatment, Photobiomodulation, shows promise for non-invasive skin therapy with few side effects.
 18 citations,
April 2013 in “Inflammatory Bowel Diseases”
18 citations,
April 2013 in “Inflammatory Bowel Diseases” People with Inflammatory Bowel Disease often lose hair due to stress, medication side effects, or lack of nutrients, and treatment depends on the specific cause.
 7 citations,
December 2008 in “Expert Review of Dermatology”
7 citations,
December 2008 in “Expert Review of Dermatology” The document concludes that various childhood hair and nail disorders exist, some may improve on their own, and advances in genetics and immunology could enhance treatment and counseling.
 26 citations,
June 2018 in “The journal of immunology/The Journal of immunology”
26 citations,
June 2018 in “The journal of immunology/The Journal of immunology” AIRE-deficient rats developed severe autoimmune disease similar to APECED, useful for testing treatments.
 April 2003 in “Experimental Dermatology”
April 2003 in “Experimental Dermatology” The workshop highlighted the genetic links and psychological impacts of hair loss and skin disorders.
5 citations,
January 2016 in “Open Journal of Regenerative Medicine” Myoblast transplantation shows promise for treating various muscle and heart conditions.
 353 citations,
February 2022 in “Nature Immunology”
353 citations,
February 2022 in “Nature Immunology” Long-haul COVID can cause lasting symptoms affecting many body systems and may be linked to ongoing inflammation and immune system issues.
 May 2021 in “Journal of the Endocrine Society”
May 2021 in “Journal of the Endocrine Society” The 18-year-old girl likely has a condition called müllerian agenesis, which caused her to not have a uterus and experience no menstrual periods.
 September 2003 in “Current Paediatrics”
September 2003 in “Current Paediatrics” The document concludes that accurate diagnosis and understanding the type of hair disorder are crucial for treating hair loss in children.
 24 citations,
October 2014 in “Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Medicine”
24 citations,
October 2014 in “Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Medicine” Genetic research has advanced our understanding of skin diseases, but complex conditions require an integrative approach for deeper insight.
 97 citations,
July 2006 in “Dermatologic therapy”
97 citations,
July 2006 in “Dermatologic therapy” The document concludes that accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment are important for skin problems in women with PCOS.
 21 citations,
November 2012 in “Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery”
21 citations,
November 2012 in “Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery” Both genetic and lifestyle factors significantly affect female hair loss.
 421 citations,
April 2012 in “The New England Journal of Medicine”
421 citations,
April 2012 in “The New England Journal of Medicine” Alopecia Areata is an autoimmune condition causing hair loss with no cure and treatments that often don't work well.
 5 citations,
May 2023 in “Frontiers in immunology”
5 citations,
May 2023 in “Frontiers in immunology” Environmental factors like diet and vitamin levels, especially Vitamin D, can affect autoimmune diseases differently, with lifestyle changes potentially improving outcomes.
 January 1989 in “Clinical and Experimental Dermatology”
January 1989 in “Clinical and Experimental Dermatology” The symposium concluded that hair growth involves complex processes, including the hair follicle life cycle, the role of the dermal papilla, hair strength, pigmentation, and the impact of diseases and treatments like minoxidil on hair and skin.
 64 citations,
August 2014 in “The journal of allergy and clinical immunology/Journal of allergy and clinical immunology/The journal of allergy and clinical immunology”
64 citations,
August 2014 in “The journal of allergy and clinical immunology/Journal of allergy and clinical immunology/The journal of allergy and clinical immunology” A deficiency in the TTC7A gene causes immune problems, gut issues, and hair loss.
 12 citations,
May 2020 in “Dermatology and therapy”
12 citations,
May 2020 in “Dermatology and therapy” A young woman had a rare skin reaction to a medication for her joint disease, and a combination therapy improved her condition.
 May 2021 in “Journal of the Endocrine Society”
May 2021 in “Journal of the Endocrine Society” A 23-year-old woman's missed periods were caused by a rare genetic disorder treated with hormone patches.
 22 citations,
April 1985 in “Australasian Journal of Dermatology”
22 citations,
April 1985 in “Australasian Journal of Dermatology” Beta-blockers can cause rare skin side-effects, which usually improve after stopping the medication.
 17 citations,
November 2002 in “Australasian Journal of Dermatology”
17 citations,
November 2002 in “Australasian Journal of Dermatology” Saw palmetto causes allergic reaction, minoxidil causes skin irritation; use cautiously for hair loss.
 3 citations,
January 2010 in “Journal of The European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
3 citations,
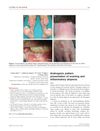
January 2010 in “Journal of The European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” Many people diagnosed with androgenic alopecia might actually have hidden scarring or inflammation.
 October 2021 in “Dermatology Reports”
October 2021 in “Dermatology Reports” Higher IL-17A levels indicate more severe alopecia areata.
 1 citations,
January 2019 in “Springer eBooks”
1 citations,
January 2019 in “Springer eBooks” Hidradenitis Suppurativa is a chronic skin condition best treated early with surgery for better outcomes and less recurrence.
 119 citations,
July 2016 in “Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences”
119 citations,
July 2016 in “Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences” Vitamin D has potential benefits for cancer prevention, heart health, diabetes, obesity, muscle function, skin health, and immune function, but clinical results are mixed and more research is needed.
 August 2016 in “InTech eBooks”
August 2016 in “InTech eBooks” Esthetic surgery complications can include infections, nerve injury, and more; proper evaluation and technique help prevent them.




























