 January 2023 in “Case Reports in Obstetrics and Gynecology”
January 2023 in “Case Reports in Obstetrics and Gynecology” A woman's high testosterone levels and related symptoms improved after ovary removal surgery.
 9 citations,
May 2008 in “Journal of Clinical Oncology”
9 citations,
May 2008 in “Journal of Clinical Oncology” A woman's ovarian tumor causing high testosterone was successfully removed, and her symptoms improved.
 December 2013 in “Open Access Macedonian Journal of Medical Sciences”
December 2013 in “Open Access Macedonian Journal of Medical Sciences” A woman's excessive hair growth and high testosterone were caused by a rare ovarian tumor, which was successfully treated with surgery.
 December 2013 in “Macedonian Journal of Medical Sciences”
December 2013 in “Macedonian Journal of Medical Sciences” Ovarian steroid cell tumors should be considered in adults with hirsutism and high testosterone, with surgery as the main treatment.
 2 citations,
August 2011 in “Revista Medica De Chile”
2 citations,
August 2011 in “Revista Medica De Chile” A postmenopausal woman's high testosterone levels and symptoms improved after removing a tumor from her ovary.
 April 2019 in “Journal of the Endocrine Society”
April 2019 in “Journal of the Endocrine Society” A woman's severe male-like symptoms were caused by a rare, benign tumor in her ovary that produced male hormones.
 November 2022 in “Journal of the Endocrine Society”
November 2022 in “Journal of the Endocrine Society” A woman's masculine symptoms were caused by a rare tumor in her left ovary, which was found using a special blood test.
 4 citations,
January 2019 in “Obstetrics & gynecology science”
4 citations,
January 2019 in “Obstetrics & gynecology science” A PET-CT scan successfully located a hard-to-find Leydig cell tumor in a woman with hormonal symptoms.
 4 citations,
December 2012 in “Arquivos Brasileiros De Endocrinologia E Metabologia”
4 citations,
December 2012 in “Arquivos Brasileiros De Endocrinologia E Metabologia” A postmenopausal woman's masculine symptoms improved after surgery for a hormone-producing ovarian tumor.
 April 2020 in “Journal of the Endocrine Society”
April 2020 in “Journal of the Endocrine Society” A rare ovarian tumor that produced testosterone caused a blood clot in the lungs and increased red blood cells in a woman.
A 73-year-old woman's unusual hair loss and growth led to the discovery of a rare condition causing too much testosterone, which improved after her ovaries were removed.
 36 citations,
May 2011 in “The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism”
36 citations,
May 2011 in “The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism” Treatment with a hormone agonist can reduce excess male hormones in postmenopausal women without surgery.
22 citations,
January 2019 in “Climacteric” Oophorectomy lowers testosterone and estrogen levels in both premenopausal and postmenopausal women, with postmenopausal women still producing significant testosterone.
 17 citations,
February 2003 in “Australasian Journal of Dermatology”
17 citations,
February 2003 in “Australasian Journal of Dermatology” Hair loss in postmenopausal woman caused by ovarian issue.
 12 citations,
January 2009 in “Gynecological Endocrinology”
12 citations,
January 2009 in “Gynecological Endocrinology” A postmenopausal woman's hair loss and excess hair growth improved after surgery for ovarian hyperthecosis.
 6 citations,
April 2019 in “Endocrinology and Metabolism Clinics of North America”
6 citations,
April 2019 in “Endocrinology and Metabolism Clinics of North America” Testosterone therapy for transmasculine individuals is generally safe with medical supervision, improves mental health, and has mixed effects on physical health.
 5 citations,
October 2013 in “Endocrine”
5 citations,
October 2013 in “Endocrine” Blood tests can detect ovarian Leydig cell tumors when scans don't, and surgery can confirm and treat these tumors.
 4 citations,
March 2017 in “Development”
4 citations,
March 2017 in “Development” Estrogen is important for keeping adult mouse nipple skin healthy by controlling certain cell signals.
 2 citations,
October 2015 in “Obstetrics and gynaecology cases - reviews”
2 citations,
October 2015 in “Obstetrics and gynaecology cases - reviews” Removing both ovaries may better treat increased male hormone levels and related symptoms in postmenopausal women when hormone therapy doesn't work.
 2 citations,
October 2015 in “The New England Journal of Medicine”
2 citations,
October 2015 in “The New England Journal of Medicine” The woman's surgery lowered her testosterone and improved scalp hair loss but did not change her excessive body hair.
 1 citations,
February 2022 in “Case reports in endocrinology”
1 citations,
February 2022 in “Case reports in endocrinology” An unusual growth of Leydig cells in a woman's ovaries caused her excessive hair growth, which was treated successfully with surgery.
 1 citations,
May 2011 in “Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology”
1 citations,
May 2011 in “Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology” Hair loss in postmenopausal women due to ovarian hyperthecosis is rare, but removing the ovaries can significantly improve the condition.
1 citations,
August 2022 in “Case Reports” A rare ovarian tumor caused high testosterone, hair loss, and missed periods, but surgery fixed these issues and led to pregnancy.

A thorough diagnostic process and teamwork are crucial for managing complex hyperandrogenism in postmenopausal women.
 October 2023 in “Journal of the Endocrine Society”
October 2023 in “Journal of the Endocrine Society” The document concludes that doctors should thoroughly check postmenopausal women with sudden increased male traits for rare conditions like androgen-producing endometrial cancer.
 April 2020 in “Journal of the Endocrine Society”
April 2020 in “Journal of the Endocrine Society” A woman's severe hirsutism was caused by Leydig cell tumors in her ovaries, which improved after surgery.
April 2019 in “Journal of the Endocrine Society” A woman's severe insulin resistance improved with treatment, but she still had high testosterone levels due to ovarian issues.
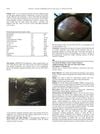 October 2014 in “Journal of Minimally Invasive Gynecology”
October 2014 in “Journal of Minimally Invasive Gynecology” Genetic testing for cancer risk can lead to early and life-saving treatments in people without symptoms.
 January 2013 in “Revista Clínica Española”
January 2013 in “Revista Clínica Española” A postmenopausal woman's increased male hormone levels were successfully treated with surgery.
July 1998 in “Annals of saudi medicine/Annals of Saudi medicine” A misdiagnosed case of HAIR-AN syndrome led to unnecessary surgeries and highlighted the importance of correct diagnosis and treatment.


























