 33 citations,
February 1996 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
33 citations,
February 1996 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Treat scalp and beard fungal infections early with oral antifungal medication and sometimes topical therapy, avoiding unnecessary allergy tests and surgery.
 10 citations,
May 2017 in “CMAJ. Canadian Medical Association journal”
10 citations,
May 2017 in “CMAJ. Canadian Medical Association journal” The boy had a fungal scalp infection called kerion, which was cured with oral antifungal medication.
 1 citations,
November 2001 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
1 citations,
November 2001 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Oral cyclosporin doesn't stop hair loss.
 January 2025 in “Journal of Clinical Medicine”
January 2025 in “Journal of Clinical Medicine” Unsanitary barber practices can spread scalp infections, treatable with oral antifungals.
4 citations,
November 1998 in “Pediatrics in review” Scalp fungal infections need oral antifungals, while other skin fungal infections can be treated with creams; keep areas dry and don't stop treatment early.
 113 citations,
August 2016 in “Mycopathologia”
113 citations,
August 2016 in “Mycopathologia” New topical antifungals and delivery systems are improving treatment for fungal skin infections, but patient education and prevention are key.
 2 citations,
August 2021 in “Skin appendage disorders”
2 citations,
August 2021 in “Skin appendage disorders” White piedra is a rare hair infection treated with oral and topical antifungals.
May 2024 in “Journal of Fungi” Tinea capitis in adults, especially postmenopausal Black women, needs prompt treatment with oral antifungals to avoid scarring.
 38 citations,
July 2010 in “Clinical, cosmetic and investigational dermatology”
38 citations,
July 2010 in “Clinical, cosmetic and investigational dermatology” To treat tinea capitis in children, oral antifungal medication is necessary, with newer drugs offering shorter treatment times than the traditional griseofulvin.
3 citations,
November 1998 in “Pediatrics in review” For hair fungal infections, take oral antifungals; for skin and nail infections, use topical antifungals, and keep affected areas cool and dry.
 41 citations,
September 2007 in “Pediatric emergency care”
41 citations,
September 2007 in “Pediatric emergency care” Oral medication is necessary to treat scalp fungus in children, with griseofulvin being the usual choice.
 32 citations,
August 2003 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
32 citations,
August 2003 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Tinea capitis can be misdiagnosed as bacterial infection in adult women but is treatable with antifungal medication.
12 citations,
August 2016 in “Mycopathologia” A man's pubic hair infection was treated by shaving and using antifungal medications.
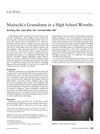 2 citations,
October 2019 in “Current sports medicine reports”
2 citations,
October 2019 in “Current sports medicine reports” A high school wrestler's skin rash was cured with antifungal medication after a misdiagnosis and incorrect treatment led to a fungal infection.
 2 citations,
January 2022 in “Boletín médico del Hospital infantil de México/Boletín médico del Hospital Infantil de México”
2 citations,
January 2022 in “Boletín médico del Hospital infantil de México/Boletín médico del Hospital Infantil de México” Some immunosuppressed patients can get unusual skin infections from Malassezia, which can be treated with antifungal medication.
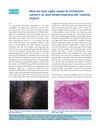 1 citations,
January 2015 in “Indian journal of dermatology, venereology, and leprology”
1 citations,
January 2015 in “Indian journal of dermatology, venereology, and leprology” A woman's scalp infection caused by a fungus led to permanent hair loss and was hard to treat but responded to a specific antifungal.
1 citations,
November 2009 in “Nurse prescribing” Oral griseofulvin for 6-12 weeks cures most scalp fungal infections in children.
 June 2024 in “Infection and Drug Resistance”
June 2024 in “Infection and Drug Resistance” An adult woman with scalp infection recovered after antifungal treatment, with no return of symptoms.
 March 2023 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
March 2023 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Treating underlying conditions and using antifungals effectively resolve Pityrosporum folliculitis in immunocompromised people.
8 citations,
March 2010 in “Chinese medical journal/Chinese Medical Journal” Malassezia infection may cause refractory acne, and antifungal treatments can help.
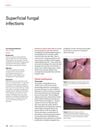 54 citations,
October 2019 in “Australian Journal of General Practice”
54 citations,
October 2019 in “Australian Journal of General Practice” Accurate diagnosis and treatment are crucial for managing superficial fungal infections, with terbinafine being the best oral treatment for nail infections.
 2 citations,
January 2022 in “Eduvest”
2 citations,
January 2022 in “Eduvest” A teenage girl with a fungal scalp infection got better with antifungal and allergy medication, and special shampoo.
 January 2022 in “Eduvest”
January 2022 in “Eduvest” A teenage girl with a fungal scalp infection got better with antifungal and allergy medication, plus medicated shampoo.
125 citations,
May 2010 in “Pediatric dermatology” Systemic treatment is necessary for tinea capitis in children, with griseofulvin preferred for Microsporum infections.
 51 citations,
January 2014 in “Pediatric Clinics of North America”
51 citations,
January 2014 in “Pediatric Clinics of North America” The guide explains how to identify and treat children's hair loss, including fungal infections, autoimmune disorders, hairstyle changes, self-correcting conditions, and behavioral therapy for hair-pulling.
 18 citations,
May 1988 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
18 citations,
May 1988 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Itraconazole helps improve tough skin infections but may not prevent them from coming back.
 10 citations,
June 2000 in “Primary Care”
10 citations,
June 2000 in “Primary Care” The document explains different hair loss types and treatments, emphasizing diagnosis through examination and tests, and specific treatments for each condition.
 6 citations,
August 1991 in “Pediatric Clinics of North America”
6 citations,
August 1991 in “Pediatric Clinics of North America” The document concludes that various hair and scalp disorders in children have specific treatments and proper diagnosis is essential.
 6 citations,
October 1993 in “The journal of the Royal Society of Health”
6 citations,
October 1993 in “The journal of the Royal Society of Health” Children's hair loss has many causes and requires careful diagnosis and personalized treatment, including emotional support.
 4 citations,
October 2018
4 citations,
October 2018 Hair loss in children is often caused by scalp infections, immune disorders, hair pulling, stress, and requires careful treatment due to emotional effects.






















