May 2012 in “International Journal of Dermatology and Venereology” New treatments are improving options for female hair loss.
 18 citations,
July 2011 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
18 citations,
July 2011 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Familial factors affect hair loss types in Koreans, with M type in men, L type in women, and paternal factors influencing male hair loss more.
 11 citations,
December 2018 in “Journal of Dermatology”
11 citations,
December 2018 in “Journal of Dermatology” Finasteride effectively treats hair loss in Korean men for at least 5 years, with V type responding better.
 30 citations,
January 2014 in “Annals of Dermatology”
30 citations,
January 2014 in “Annals of Dermatology” Scalp dermatoscopy helps diagnose and monitor hair loss severity.
 January 2023 in “Annals of Dermatology”
January 2023 in “Annals of Dermatology” Men with a family history of hair loss on their mother's side are more likely to have female pattern hair loss.

Different genes cause Female Pattern Hair Loss compared to male hair loss, and treatments vary, but more research is needed to understand it fully.
 January 2012 in “Human health handbooks”
January 2012 in “Human health handbooks” Low-level light therapy is FDA-approved for male pattern hair loss, increases hair count and strength, and is considered safe for use.
 81 citations,
March 2009 in “Seminars in Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery”
81 citations,
March 2009 in “Seminars in Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery” Effective hair loss treatment in women requires correct diagnosis and can include medications like minoxidil, antiandrogens, and treatments for underlying conditions like PCOS.

The document concludes that hair loss in women can be treated with topical treatments or hormone therapy depending on the cause.
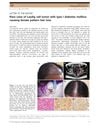 August 2019 in “Journal of Dermatology”
August 2019 in “Journal of Dermatology” Woman with diabetes had hair loss due to rare ovarian tumor; surgery improved hair growth.
 66 citations,
June 2018 in “International Journal of Women's Dermatology”
66 citations,
June 2018 in “International Journal of Women's Dermatology” No cure for female pattern hair loss, but various effective treatments exist.
 May 2023 in “Journal of Clinical Medicine”
May 2023 in “Journal of Clinical Medicine” New understanding and treatments for hair loss are improving, but more research is needed.
12 citations,
January 2020 in “Indian Dermatology Online Journal” Female pattern hair loss has multiple causes and treatments, with new therapies showing promise.
 1 citations,
July 2017 in “Clinical research in dermatology”
1 citations,
July 2017 in “Clinical research in dermatology” Hair loss, known as Androgenetic Alopecia, is often caused by hormones and can be diagnosed using noninvasive techniques. Treatments include topical minoxidil and oral finasteride, with new treatments being explored. There may also be a link between this type of hair loss and heart disease risk.
 6 citations,
November 2017 in “Skin appendage disorders”
6 citations,
November 2017 in “Skin appendage disorders” Topical botanical lotion increases hair density and improves quality of life in women with hair loss.
 91 citations,
August 2015 in “Anais Brasileiros De Dermatologia”
91 citations,
August 2015 in “Anais Brasileiros De Dermatologia” Female Pattern Hair Loss affects women's self-esteem and needs more research for better treatment.
 4 citations,
May 2020 in “PLOS ONE”
4 citations,
May 2020 in “PLOS ONE” Ingenol mebutate gel changes gene expression related to skin development and immune response in actinic keratosis.
 43 citations,
November 2019 in “American Journal of Clinical Dermatology”
43 citations,
November 2019 in “American Journal of Clinical Dermatology” FAGA diagnosis uses blood tests and trichoscopy, with treatments like topical minoxidil, oral anti-androgens, and hormone-modulating drugs.
 1 citations,
January 2021 in “Acta dermatovenerologica Alpina, Pannonica et Adriatica (Tiskana izd.)”
1 citations,
January 2021 in “Acta dermatovenerologica Alpina, Pannonica et Adriatica (Tiskana izd.)” High prolactin levels might be linked to hair loss in autoimmune thyroid disease, but more research is needed.
 6 citations,
November 2018 in “Photodiagnosis and Photodynamic Therapy”
6 citations,
November 2018 in “Photodiagnosis and Photodynamic Therapy” A wearable cap-like device using light therapy reduced scalp skin lesions by 71% and was painless.
 101 citations,
January 2016 in “Journal of Cutaneous and Aesthetic Surgery”
101 citations,
January 2016 in “Journal of Cutaneous and Aesthetic Surgery” Different types of hair loss need specific treatments, and while many classification systems exist, each has its flaws; more research is needed to refine these systems and treatments.
 23 citations,
January 2013 in “Indian Journal of Dermatology, Venereology and Leprology”
23 citations,
January 2013 in “Indian Journal of Dermatology, Venereology and Leprology” FPHL causes hair loss in women due to genetics and hormones; minoxidil and anti-androgens are treatments, and early intervention is advised.
 10 citations,
March 2007 in “Skinmed”
10 citations,
March 2007 in “Skinmed” The conclusion is that in the Indian subcontinent, socioeconomic status, stress, and family structure affect the severity of alopecia areata, and its psychological impact is generally mild or moderate.
 July 2007 in “Faculty Opinions – Post-Publication Peer Review of the Biomedical Literature”
July 2007 in “Faculty Opinions – Post-Publication Peer Review of the Biomedical Literature” The BASP classification is a detailed system for categorizing hair loss in both men and women, but it may be complex for beginners and not fully suitable for grading female hair loss.
 8 citations,
January 2013 in “International Journal of Trichology”
8 citations,
January 2013 in “International Journal of Trichology” The BASP classification is effective for diagnosing pattern hair loss in Indian men and women.

Combining PRP with low-level laser therapy is better for hair growth than PRP alone.
 August 2023 in “Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology”
August 2023 in “Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology” Different types of female pattern hair loss have unique characteristics and are associated with various health conditions.
 32 citations,
June 2000 in “Dermatologic Surgery”
32 citations,
June 2000 in “Dermatologic Surgery” Different factors help diagnose and treat hair loss accurately.
January 2022 in “Springer eBooks”  January 2007 in “Revista del Centro Dermatológico Pascua”
January 2007 in “Revista del Centro Dermatológico Pascua” Hair loss in women, often not related to male hormones, increases with age and can cause significant emotional distress.


























