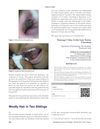
 January 2012 in “International Journal of Trichology”
January 2012 in “International Journal of Trichology” Two siblings have a rare genetic condition causing curly, coarse hair.
[object Object]  May 2011 in “Expert Review of Endocrinology & Metabolism”
May 2011 in “Expert Review of Endocrinology & Metabolism” Breast cancer survivors may have a higher risk of falls, tamoxifen could prevent breast cancer and deaths, new guidelines urge caution with prostate cancer therapy, and early balding in men may indicate a higher prostate cancer risk.
 March 2011 in “European Urology Supplements”
March 2011 in “European Urology Supplements” Blood tests for tumor cells could improve prostate cancer diagnosis and treatment; hair loss severity linked to a gene affecting prostate conditions.
 March 2011 in “European Urology Supplements”
March 2011 in “European Urology Supplements” The document concludes that a new biosensor can efficiently detect prostate cancer cells and that standardized referrals help find significant cancers effectively.
 March 2011 in “European Urology Supplements”
March 2011 in “European Urology Supplements” CEC levels may be a useful marker for predicting prostate cancer progression.
 October 2008 in “Clin-alert”
October 2008 in “Clin-alert” Certain medications can reduce mortality risk in COPD patients, but others can increase risks of cardiovascular issues, postoperative delirium, and other adverse effects.
[object Object]  July 2008 in “Expert Review of Dermatology”
July 2008 in “Expert Review of Dermatology” Proper planning for hair transplants is crucial for natural results, with careful patient selection and strategic graft placement being key factors.
 February 2007 in “Lancet Oncology”
February 2007 in “Lancet Oncology” Using a single PSA level to decide on a prostate biopsy is not effective; a more personalized approach considering various factors is recommended.
 September 2002 in “Dermatologic Surgery”
September 2002 in “Dermatologic Surgery” The best results in surgical hair restoration come from careful techniques, optimal use of limited hair supply, correct hair direction, saving hair for key areas, understanding scarring effects, and adjusting hair graft density.
 February 2002 in “Dermatologic Surgery”
February 2002 in “Dermatologic Surgery” A cheap stainless steel container from a retail store can store liquid nitrogen effectively for 8-12 hours, offering a cost-effective alternative to specialized medical containers.










