
Nanocarriers with plant extracts show promise for safe and effective hair growth treatment.
88 citations,
June 2019 in “Cell reports” Certain small molecules can promote hair growth by activating a cellular cleanup process called autophagy.
 July 2022 in “Biomedicines”
July 2022 in “Biomedicines” 4-Aminopyridine improves skin wound healing and tissue regeneration by increasing cell growth and promoting nerve repair.
February 2024 in “Pharmaceutics” Microneedles with extracellular vesicles show promise for treating various conditions with targeted delivery.
 2 citations,
August 2023 in “Pharmaceutics”
2 citations,
August 2023 in “Pharmaceutics” New skin disease treatments using TDDS are improving but face challenges like side effects and high costs.
 January 2025 in “Applied Sciences”
January 2025 in “Applied Sciences” Sulforaphane from broccoli may help treat certain cancers, hormone issues, and hair loss.
43 citations,
January 2016 in “Oxidative medicine and cellular longevity” THSG from a Chinese plant helps with aging and related diseases.
 2 citations,
March 2023 in “Experimental neurology”
2 citations,
March 2023 in “Experimental neurology” Pregnenolone might help manage movement issues caused by Parkinson's disease treatment without reducing the medicine's effectiveness.
 October 2023 in “Biomaterials”
October 2023 in “Biomaterials” Nanotechnology could improve hair regrowth but faces challenges like complexity and safety concerns.
 21 citations,
January 2022 in “Biomaterials Science”
21 citations,
January 2022 in “Biomaterials Science” RNA delivery is best for in-body use, while RNP delivery is good for outside-body use. Both methods are expected to greatly impact future treatments.
 5 citations,
October 2022 in “Cosmetics”
5 citations,
October 2022 in “Cosmetics” Cell-based models help test if cosmetic ingredients really work for hair growth and skin health.
 1 citations,
May 2023 in “Cell reports medicine”
1 citations,
May 2023 in “Cell reports medicine” Sons of mothers with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) have a higher risk of obesity and insulin resistance, possibly due to certain genes and factors passed down from their mothers.
5 citations,
August 2021 in “Journal of biological chemistry/The Journal of biological chemistry” Retinoic acid affects male and female muscle energy use and function differently.
 2 citations,
September 2022 in “Cytotherapy”
2 citations,
September 2022 in “Cytotherapy” Fat-derived stem cells show promise for treating skin issues and improving wound healing, but more research is needed to confirm the best way to use them.
1 citations,
December 2022 in “Bioactive Materials” The microneedle patch with quercetin, zinc, and copper effectively promotes hair regrowth for androgenic alopecia.
March 2024 in “Biomedicines” Mesenchymal stem cells show promise for effective skin repair and regeneration.

Plant-based compounds can improve wound dressings and skin medication delivery.

Diet and supplements can significantly affect acne, with some foods and nutrients reducing and others worsening it.
 1 citations,
June 2023 in “Genes”
1 citations,
June 2023 in “Genes” Hair loss from Alopecia Areata is caused by both genes and environment, with several treatments available but challenges in cost and relapse remain.
 20 citations,
May 2016 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology”
20 citations,
May 2016 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology” Low vitamin D receptor levels found in hair loss patients; topical vitamin D treatment suggested.
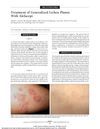 52 citations,
February 2006 in “Archives of Dermatology”
52 citations,
February 2006 in “Archives of Dermatology” Alefacept may effectively treat severe lichen planus, with patients showing significant improvement and no side effects.
 2 citations,
January 2014 in “Elsevier eBooks”
2 citations,
January 2014 in “Elsevier eBooks” The document concludes that reactivation of herpesviruses, especially HHV-6, is linked to severe symptoms and complications in drug-induced hypersensitivity syndrome.
 5 citations,
January 2019 in “Elsevier eBooks”
5 citations,
January 2019 in “Elsevier eBooks” Current therapies cannot fully regenerate adult skin without scars; more research is needed for scar-free healing.
 21 citations,
November 2017 in “Livestock science”
21 citations,
November 2017 in “Livestock science” Nellore cattle have genetic variations linked to their adaptation to tropical environments.
 7 citations,
July 2008 in “Experimental Dermatology”
7 citations,
July 2008 in “Experimental Dermatology” The study concluded that a protein important for hair strength is regulated by certain molecular processes and is affected by growth phases.
September 2023 in “Membranes” 3D-printed membranes with smart sensors can greatly improve tissue healing and have many medical applications.
1 citations,
March 2023 in “Pharmaceutics” PBMCsec can help reduce and improve thick skin scars.
 29 citations,
May 2018 in “Clinical Endocrinology”
29 citations,
May 2018 in “Clinical Endocrinology” Recent genetic insights show that low-renin hypertension includes a range from essential hypertension to secondary or familial forms, affecting diagnosis and treatment.
 232 citations,
October 2015 in “International journal of molecular sciences”
232 citations,
October 2015 in “International journal of molecular sciences” Stem cells are crucial for skin repair and new treatments for chronic wounds.

Female hair loss is often hereditary and can be treated with medication, hair transplants, and lasers.






















