 September 2017 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology Symposium Proceedings”
September 2017 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology Symposium Proceedings” Non-melanoma skin cancer in darker-skinned people can be misdiagnosed, so doctors need to be more aware to diagnose it correctly and early.
24 citations,
November 2003 in “Australasian Journal of Dermatology” A rare skin cancer caused hair loss and spread, needing multiple treatments.
 January 2014 in “Pathology”
January 2014 in “Pathology” The document concludes that understanding nail anatomy is key for diagnosing nail diseases, early signs of nail melanoma may allow for less aggressive treatment, and specific genetic mutations are important in thyroid cancer prognosis and treatment.
 January 2013 in “International journal of trichology”
January 2013 in “International journal of trichology” Vitamin D3 and its receptor are important for hair growth, and understanding receptors could help treat hair graying and skin cancer.
2 citations,
December 2015 in “Journal of dermatology” β-interferon injections for melanoma can cause excessive hair growth at the injection sites.
 17 citations,
April 2006 in “Dermatologic Clinics”
17 citations,
April 2006 in “Dermatologic Clinics” Older women face various skin issues like dryness and thinning, and treatments are available but can have side effects; proper skin care and legal health decisions are important.
 April 2023 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
April 2023 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” People with Alopecia Areata are more likely to have certain health issues like ulcerative colitis and type 1 diabetes, but less likely to have others like hypertension and type 2 diabetes.
 April 2016 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
April 2016 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Decreasing MIG6 can increase the movement and invasiveness of MEK-inhibited mutant NRAS melanoma, particularly when stimulated by EGF.
 6 citations,
February 2015 in “Dermatologic Surgery”
6 citations,
February 2015 in “Dermatologic Surgery” The document concludes that a new training model could improve dermatology residents' skills in nail procedures and lead to more nail cases being treated by dermatologists.
 February 2024 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
February 2024 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Vascular patterns in dermoscopy help tell apart malignant and benign skin tumors.
 July 2018 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
July 2018 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Mindfulness reduces anxiety and depression in skin disease patients; dermatologists and psychiatrists often lack confidence in treating psychodermatological conditions.
 May 1992 in “Reactions Weekly”
May 1992 in “Reactions Weekly” Some patients lost hair after taking interferon alpha 2B, but it improved for some while still on the treatment and for others after stopping it.
 128 citations,
September 2011 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
128 citations,
September 2011 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Obesity is linked to various skin problems and may increase the risk of skin cancer.
 May 2021 in “IP Indian journal of clinical and experimental dermatology”
May 2021 in “IP Indian journal of clinical and experimental dermatology” Dermoscopy is useful for diagnosing various skin conditions, and new patterns for diagnosis are emerging.
 4 citations,
June 2013 in “The Journal of Rheumatology”
4 citations,
June 2013 in “The Journal of Rheumatology” The document concludes that various findings in rheumatology offer insights into disease severity, treatment responses, and potential risks in medication, with some limitations due to unspecified participant numbers.
149 citations,
January 2015 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Targeted cancer therapies often cause skin side effects, needing dermatologist care.
 1 citations,
August 2018 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
1 citations,
August 2018 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Dutasteride and minoxidil mesotherapy effectively treats hair loss with minimal side effects.
 7 citations,
December 2014 in “Journal of dermatology”
7 citations,
December 2014 in “Journal of dermatology” Hair shaft miR-221 levels can help detect malignant melanoma.
 August 2023 in “Journal of Dermatological Treatment”
August 2023 in “Journal of Dermatological Treatment” Mesotherapy might improve hair growth, but more research is needed to confirm its safety and effectiveness.
 November 2021 in “World Family Medicine Journal /Middle East Journal of Family Medicine”
November 2021 in “World Family Medicine Journal /Middle East Journal of Family Medicine” The document's conclusion cannot be provided because the document is not readable or understandable.
10 citations,
September 2016 in “Journal of cutaneous medicine and surgery” Patients on dabrafenib and trametinib for melanoma often experience skin side effects.
1 citations,
January 2007 in “Side effects of drugs annual” Dermatological treatments can have significant side effects, including allergic reactions, sexual dysfunction, and increased cancer risk.
 2 citations,
December 2019 in “Cureus”
2 citations,
December 2019 in “Cureus” A patient with a scalp condition and benign skin tumor experienced hair loss and did not improve with treatment, choosing not to have surgery despite a small cancer risk.
 14 citations,
April 2019 in “PLOS ONE”
14 citations,
April 2019 in “PLOS ONE” Skin cancer is common in elderly nursing home residents, with risk factors including being male, having light skin, outdoor work history, and smoking. Regular skin checks are recommended.
 8 citations,
October 2018 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
8 citations,
October 2018 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” Mohs micrographic surgery is effective for early-stage non-melanoma skin cancers on the lips, with basal cell carcinoma more common on the upper cutaneous lip and squamous cell carcinoma more common on the lower vermilion lip.
 April 2016 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
April 2016 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” People with certain allergic conditions or higher white blood cell counts have more severe hair loss, and treating hair and nail side effects early in melanoma therapy can improve quality of life.
 21 citations,
March 2015 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
21 citations,
March 2015 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Vemurafenib therapy can cause hair loss, but clobetasol propionate foam can help regrow hair.
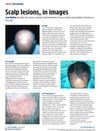 January 2015 in “Independent Nurse”
January 2015 in “Independent Nurse” Different scalp conditions can lead to hair loss or tumors, with treatments varying from creams to surgery; early detection is crucial.
 27 citations,
December 2014 in “Current problems in dermatology”
27 citations,
December 2014 in “Current problems in dermatology” Photodynamic therapy is the preferred treatment for skin precancer due to its effectiveness and safety.
 36 citations,
March 2014 in “Biomaterials”
36 citations,
March 2014 in “Biomaterials” A new skin-whitening agent using a peptide from wheat is safe and effective at reducing skin pigmentation.

























