 August 2022 in “Revista de la Universidad Industrial de Santander/Salud UIS”
August 2022 in “Revista de la Universidad Industrial de Santander/Salud UIS” Stress-related hair loss was reversed with a special medication.
 August 2024 in “Nature Communications”
August 2024 in “Nature Communications” Softer hydrogels help wounds heal better with less scarring.
November 2023 in “Frontiers in Medicine” The method effectively mimics shaving damage on skin for testing skincare products.
 October 2023 in “Dermatological reviews”
October 2023 in “Dermatological reviews” Fibroblast-derived growth factors and exosomes can significantly improve skin aging.
 January 2024 in “Annals of Dermatology”
January 2024 in “Annals of Dermatology” Korean Red Ginseng may help protect hair from damage and promote growth.
 96 citations,
September 2021 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences”
96 citations,
September 2021 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences” Chitosan, a natural substance, can be used to create tiny particles that effectively deliver various types of drugs, but more work is needed to improve stability and control of drug release.
88 citations,
August 2019 in “Frontiers in immunology” Tyrosine kinases are important in skin autoimmune diseases and could be targets for new treatments.
 8 citations,
July 2022 in “Biomedicines”
8 citations,
July 2022 in “Biomedicines” Autophagy helps keep skin healthy and may improve treatments for skin diseases.
 July 2021 in “Journal of dermatology research and therapy”
July 2021 in “Journal of dermatology research and therapy” COVID-19 may worsen hair loss, and Nourkrin® could be a safe treatment option, but more research is needed.
 39 citations,
August 2021 in “JAAD International”
39 citations,
August 2021 in “JAAD International” COVID-19 patients often experience hair loss and scalp pain, which may be related to the severity of their infection and treatment drugs.
 13 citations,
November 2021 in “Frontiers in Immunology”
13 citations,
November 2021 in “Frontiers in Immunology” Melatonin could be an effective treatment for Alzheimer's Disease and rosacea.
 12 citations,
February 2023 in “Journal of Personalized Medicine”
12 citations,
February 2023 in “Journal of Personalized Medicine” Type 1 diabetes often occurs with other autoimmune diseases, and personalized treatment based on genetics can improve outcomes.
3 citations,
February 2021 in “FEBS open bio” Camellia japonica extract may improve scalp health and promote hair growth.
 1 citations,
June 2023 in “Reproduction”
1 citations,
June 2023 in “Reproduction” Microglia, the brain's immune cells, may contribute to Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) by altering the female brain's structure and function, with kisspeptin neurons and GABA neurotransmitters also playing a role.
 15 citations,
January 2016 in “Biological & Pharmaceutical Bulletin”
15 citations,
January 2016 in “Biological & Pharmaceutical Bulletin” Bee venom helps hair grow and may work better than some common treatments.
 1 citations,
January 1997 in “Dermatology”
1 citations,
January 1997 in “Dermatology” A woman lost her hair from stress after a bee attack and her sister's death.
 182 citations,
November 2017 in “Molecular Aspects of Medicine”
182 citations,
November 2017 in “Molecular Aspects of Medicine” The PDGF/PDGFR pathway is a potential drug target with mixed success in treating various diseases, including some cancers and fibrosis.
 34 citations,
January 1989 in “Toxicologic Pathology”
34 citations,
January 1989 in “Toxicologic Pathology” A study found that minoxidil can damage the hearts of dogs and pigs, cautioning its use in humans.
 August 1995 in “Journal of The European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
August 1995 in “Journal of The European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” New therapy helps treat hair loss.
 August 1995 in “Journal of The European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
August 1995 in “Journal of The European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” New therapy helps treat hair loss.
 7 citations,
August 2018 in “Journal of Cosmetic and Laser Therapy”
7 citations,
August 2018 in “Journal of Cosmetic and Laser Therapy” Microneedling combined with skinbooster effectively treats striae rubrae, with confocal microscopy confirming collagen changes.

Alopecia Areata has no cure, treatments are limited, and the condition often recurs, but new therapies like JAK inhibitors show promise.
 April 2019 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
April 2019 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Lichen planopilaris involves disrupted fat metabolism, increased scarring, and mast cell activity.
 April 2019 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
April 2019 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” Targeting cholesterol, fatty acids, fibrosis, and mast cells may help treat CCCA.
 April 2023 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
April 2023 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Skin cells and immune cells change in a skin condition called hidradenitis suppurativa, and a certain treatment can improve these changes.
 2 citations,
November 1998 in “Journal of The European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
2 citations,
November 1998 in “Journal of The European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” Prednisone reduces organ mast cell infiltration but does not alter the abnormal appearance of mast cells in systemic mastocytosis.
April 2019 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Frontal Fibrosing Alopecia involves disrupted cholesterol pathways, fibrosis, and increased mast cells.
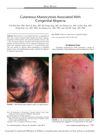 3 citations,
February 2012 in “The American Journal of Dermatopathology”
3 citations,
February 2012 in “The American Journal of Dermatopathology” A 3-year-old girl with skin mast cell buildup and congenital baldness improved with treatment, suggesting a rare link between these conditions.
7 citations,
July 2021 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” Human skin can be reconnected to nerves using stem cells, which may help with skin health and healing.
 18 citations,
October 2021 in “Frontiers in Physiology”
18 citations,
October 2021 in “Frontiers in Physiology” Lipocalin-Type Prostaglandin D2 Synthase (L-PGDS) is a protein that plays many roles in the body, including sleep regulation, pain management, food intake, and protection against harmful substances. It also affects fat metabolism, glucose intolerance, cell maturation, and is involved in various diseases like diabetes, cancer, and arthritis. It can influence sex organ development and embryonic cell differentiation, and its levels can be used as a diagnostic marker for certain conditions.

























