 9 citations,
January 2019 in “Postepy Dermatologii I Alergologii”
9 citations,
January 2019 in “Postepy Dermatologii I Alergologii” The skin acts like an endocrine organ, making hormones that affect skin diseases and respond to stress.
 11 citations,
July 2015 in “Gene”
11 citations,
July 2015 in “Gene” DHT affects bone growth by altering gene activity in osteoblasts, potentially complicating steroid use.
 12 citations,
March 2017 in “Journal of obstetrics and gynaecology Canada”
12 citations,
March 2017 in “Journal of obstetrics and gynaecology Canada” Testosterone therapy can modestly improve sexual function in menopausal women but should be used cautiously and is not recommended for routine measurement in sexual dysfunction or hirsutism.
 20 citations,
March 2005 in “Current Medicinal Chemistry”
20 citations,
March 2005 in “Current Medicinal Chemistry” New compounds show promise for treating hair loss, enlarged prostate, and prostate cancer, with some being more effective and having different side effects than current treatments.
61 citations,
April 2018 in “Frontiers in endocrinology” Sex steroids produced in the hippocampus are crucial for brain functions like memory and learning in rodents.
2 citations,
May 2023 in “Frontiers in Pharmacology” Natural products may help treat skin inflammation from abnormal adrenal hormones.
 96 citations,
January 1997 in “Clinics in Dermatology”
96 citations,
January 1997 in “Clinics in Dermatology” Pregnancy can cause skin pigmentation, stretch marks, and changes in hair, nails, and sweat glands, with most resolving after birth.
31 citations,
September 2020 in “Clinical endocrinology” Some antiandrogens may lower testosterone better than others, but it's unclear which is best for feminization in transgender women; more research is needed.
 16 citations,
January 2003 in “Nuclear Receptor Signaling”
16 citations,
January 2003 in “Nuclear Receptor Signaling” Androgens and SARMs play a role in body mass, frailty, skin health, and hair growth, and are used in treating prostate cancer, acne, and hair loss, with potential for new uses and improved versions in the future.
 57 citations,
May 1986 in “Clinics in endocrinology and metabolism”
57 citations,
May 1986 in “Clinics in endocrinology and metabolism” Androstanediol glucuronide is a reliable marker for hirsutism in women.
 October 2021 in “Cosmoderma”
October 2021 in “Cosmoderma” Hair loss can be managed with treatments like minoxidil, finasteride, and others, but there are still gaps in effectiveness and off-label usage is increasing.
 14 citations,
March 2017 in “Brain research”
14 citations,
March 2017 in “Brain research” Progesterone and its byproducts control a specific receptor in the brain independently of progesterone receptors, affecting conditions related to the menstrual cycle.
 25 citations,
August 2014 in “Endocrinology”
25 citations,
August 2014 in “Endocrinology” Researchers created a mouse model of a type of rickets that does not cause hair loss.
 3 citations,
May 2014 in “InTech eBooks”
3 citations,
May 2014 in “InTech eBooks” Copper deficiency may cause hair loss, and treating it could involve nutrition and hormones.
 6 citations,
November 2010 in “International Journal of Andrology”
6 citations,
November 2010 in “International Journal of Andrology” New oral testosterone formulations show potential for safer, effective hormone replacement in men with low testosterone.
 23 citations,
February 2021 in “Journal of Endocrinological Investigation”
23 citations,
February 2021 in “Journal of Endocrinological Investigation” Betacoronaviruses, like COVID-19, may cause hormone system dysfunction and affect disease susceptibility and severity.
 54 citations,
December 2007 in “Best Practice & Research Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism”
54 citations,
December 2007 in “Best Practice & Research Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism” Targeting glucocorticoid action might help treat type-2 diabetes, but human trials are needed.
 January 2023 in “Theranostics”
January 2023 in “Theranostics” A patch with curcumin-zinc can improve hair growth and health by delivering beneficial particles to the skin, increasing hair follicles, and reversing effects of a hair loss hormone.
 1 citations,
July 2018 in “Journal of dermatology & cosmetology”
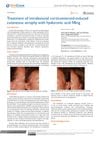
1 citations,
July 2018 in “Journal of dermatology & cosmetology” Hyaluronic acid successfully treated skin atrophy caused by corticosteroid injections.
![Activity of 17β-(N-Alkyl/Arylformamido) and 17β-[(N-Alkyl/Aryl) Alkyl/Arylamido]-4-Methyl-4-Aza-5α-Androstan-3-Ones as 5α-Reductase Inhibitors in the Hamster Flank Organ and Ear](/images/research/861159f1-7bd4-420c-a16b-4829458efe68/small/15592.jpg) 10 citations,
August 1998 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
10 citations,
August 1998 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” The compounds tested could potentially treat hair loss and alopecia.
 12 citations,
July 1993 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
12 citations,
July 1993 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” Certain sex hormones and antiandrogens can either slow down or speed up the growth of human hair follicle cells depending on their concentration.
 124 citations,
July 2012 in “Archives of Dermatological Research”
124 citations,
July 2012 in “Archives of Dermatological Research” Targeting androgen receptors could be a promising way to treat skin disorders with fewer side effects.
 March 2014 in “Medicina cutánea ibero-latino-americana”
March 2014 in “Medicina cutánea ibero-latino-americana” Melatonin applied to the scalp helps increase hair density in people with early hair loss.
 81 citations,
March 2009 in “Seminars in Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery”
81 citations,
March 2009 in “Seminars in Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery” Effective hair loss treatment in women requires correct diagnosis and can include medications like minoxidil, antiandrogens, and treatments for underlying conditions like PCOS.
 1 citations,
November 1996 in “Journal of Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery”
1 citations,
November 1996 in “Journal of Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery” Hormones, especially androgens, play a key role in causing acne, and treatments like hormone control pills and hormone-blocking medications can help.
 48 citations,
January 2017 in “Skin Pharmacology and Physiology”
48 citations,
January 2017 in “Skin Pharmacology and Physiology” Finasteride-loaded nanoparticles may help treat alopecia.
 4 citations,
October 2013 in “Springer eBooks”
4 citations,
October 2013 in “Springer eBooks” Melatonin receptors, found in many body parts, can help treat various diseases like depression and diabetes due to their effects on inflammation, tumor progression, sleep disorders, and body mass regulation.
 5 citations,
March 2020 in “Current Opinion in Endocrine and Metabolic Research”
5 citations,
March 2020 in “Current Opinion in Endocrine and Metabolic Research” Skin problems in PCOS, like excess hair, acne, and hair loss, may not always indicate high male hormone levels and need careful diagnosis for proper treatment.
 185 citations,
February 2018 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
185 citations,
February 2018 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Melatonin may benefit skin health and could be a promising treatment in dermatology.
 July 2019 in “Mayo Clinic proceedings”
July 2019 in “Mayo Clinic proceedings” The man's fatigue and erectile dysfunction were improved by treating his obesity-related low testosterone without needing testosterone replacement.

















![Activity of 17β-(N-Alkyl/Arylformamido) and 17β-[(N-Alkyl/Aryl) Alkyl/Arylamido]-4-Methyl-4-Aza-5α-Androstan-3-Ones as 5α-Reductase Inhibitors in the Hamster Flank Organ and Ear](/images/research/861159f1-7bd4-420c-a16b-4829458efe68/small/15592.jpg)









