 6 citations,
January 2023 in “Journal of Materials Chemistry B”
6 citations,
January 2023 in “Journal of Materials Chemistry B” The dressing generates hydrogen sulfide to help heal wounds faster by reducing inflammation and promoting cell growth.
 2 citations,
August 2022 in “Frontiers in Veterinary Science”
2 citations,
August 2022 in “Frontiers in Veterinary Science” The research found key RNA networks that may control hair growth in cashmere goats.
 33 citations,
February 1999 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
33 citations,
February 1999 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” IGF-1 increases whisker growth in transgenic mice.
 April 2024 in “The Journal of experimental medicine/The journal of experimental medicine”
April 2024 in “The Journal of experimental medicine/The journal of experimental medicine” Treg cells help repair and regenerate tissues by interacting with local cells.
 May 2015 in “Hair transplant forum international”
May 2015 in “Hair transplant forum international” Androgenetic alopecia causes hair loss by shrinking hair follicles due to androgens, with the connection between the muscle and hair follicle determining if the loss is reversible.
8 citations,
March 2004 in “Mammalian genome” KAP genes are crucial for hair development and show both shared and unique traits in humans, chimpanzees, and baboons.
 April 2015 in “Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery”
April 2015 in “Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery” TLR3 activation helps improve skin and hair follicle healing in mice.
 9 citations,
August 2008 in “Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery”
9 citations,
August 2008 in “Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery” A woman experienced temporary hair loss after jaw surgery, which can be reduced by careful head positioning during the operation.
Pseudofolliculitis causes painful bumps and dark spots from shaving, especially in people with curly hair, and can be treated by changing shaving habits and using specific topical treatments.
212 citations,
August 2004 in “Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences” Hair follicle cells can create new blood vessels in the skin.
 74 citations,
January 2013 in “Expert Opinion on Biological Therapy”
74 citations,
January 2013 in “Expert Opinion on Biological Therapy” The conclusion is that hair growth can be improved by activating hair cycles, changing the surrounding environment, healing wounds to create new hair follicles, and using stem cell technology.
1 citations,
January 2024 in “International journal of molecular sciences” The research identifies genes linked to wool quality in sheep and provides insights to improve wool production.
 September 2004 in “Experimental dermatology”
September 2004 in “Experimental dermatology” Melatonin directly affects mouse hair follicles and may influence hair growth.
 January 2025 in “Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences”
January 2025 in “Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences” BMP4 helps stem cells turn into pigment-producing cells, affecting hair color and growth.
 June 2012 in “Expert Review of Dermatology”
June 2012 in “Expert Review of Dermatology” Japanese researchers created new hair follicles from human cells that grew hair when put into mice, and other findings showed a link between eye disease severity and corneal thickness, gene mutations affecting hearing and touch, and the safety of the shingles vaccine for adults over 50.
 14 citations,
December 2003 in “International Journal of Cosmetic Science”
14 citations,
December 2003 in “International Journal of Cosmetic Science” Hair growth and shedding are linked and can be disrupted, causing a delay known as the hair eclipse phenomenon, which is common in certain hair conditions and could lead to new treatments.
January 2024 in “Animals” Circular RNA ERCC6 helps activate stem cells important for cashmere goat hair growth by interacting with specific molecules in an m6A modification-dependent way.
253 citations,
December 2007 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Hair follicles prevent NK cell attacks to avoid hair loss.
 30 citations,
September 2004 in “Experimental Dermatology”
30 citations,
September 2004 in “Experimental Dermatology” Scalp hair follicle culture has limits for testing minoxidil's hair growth effects.
 June 2023 in “Biochimica and biophysica acta. Molecular and cell biology of lipids”
June 2023 in “Biochimica and biophysica acta. Molecular and cell biology of lipids” Impaired ABCA5 activity disrupts cholesterol balance in hair follicle cells, affecting hair growth.
 67 citations,
July 2016 in “Reviews in Endocrine and Metabolic Disorders”
67 citations,
July 2016 in “Reviews in Endocrine and Metabolic Disorders” Stress can worsen skin conditions by affecting hormone levels and immune response.
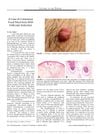 1 citations,
February 2017 in “The American journal of dermatopathology/American journal of dermatopathology”
1 citations,
February 2017 in “The American journal of dermatopathology/American journal of dermatopathology” A man with a skin nodule was diagnosed with a rare skin condition called cutaneous focal mucinosis, which can be confused with other skin cancers.
15 citations,
January 2015 in “Skin Appendage Disorders” Increased scalp sweating in frontal fibrosing alopecia may be linked to local skin inflammation.
April 2018 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Melanogenesis-related proteins may trigger immune responses in alopecia areata patients.
 August 2022 in “Research Square (Research Square)”
August 2022 in “Research Square (Research Square)” Implanted special stem cells from hair follicles helped heal wounds faster and with less scarring in mice.
 December 2012 in “Journal of Dermatological Science”
December 2012 in “Journal of Dermatological Science” Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in the skin helps fat cell development during hair growth and repair.
 32 citations,
January 2006 in “Acta dermato-venereologica”
32 citations,
January 2006 in “Acta dermato-venereologica” SACUMAN, a rare condition causing hair loss without clear signs, is often misdiagnosed and needs scalp biopsies for accurate detection.
 293 citations,
November 2005 in “Trends in Immunology”
293 citations,
November 2005 in “Trends in Immunology” Stress can worsen skin conditions and stop hair growth by affecting the body's stress response system.
 7 citations,
October 2000 in “Allergo Journal”
7 citations,
October 2000 in “Allergo Journal” Stress may affect hair growth by influencing hair follicle development and could contribute to hair loss.
 November 2024 in “Aging Cell”
November 2024 in “Aging Cell” Removing senescent cells can improve hair growth and regeneration.





















