 January 2024 in “Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft”
January 2024 in “Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft” Non-biologic immunosuppressive drugs are crucial for treating autoimmune and chronic inflammatory skin diseases.
 6 citations,
September 2012 in “Our Dermatology Online”
6 citations,
September 2012 in “Our Dermatology Online” Retinoids are effective for various skin conditions and hair loss but have serious side effects, so low doses are recommended.
 January 2025 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences”
January 2025 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences” Psoriasis involves immune and genetic factors, and understanding these can improve treatments.
 126 citations,
January 2009 in “International Journal of Trichology”
126 citations,
January 2009 in “International Journal of Trichology” Oxidative stress contributes to hair graying and loss as we age.
 3 citations,
October 2007 in “Expert Review of Dermatology”
3 citations,
October 2007 in “Expert Review of Dermatology” Hair ages due to various factors and treatments like minoxidil and finasteride can help, but more research and better public awareness are needed.
 80 citations,
April 2006 in “Clinical Interventions in Aging”
80 citations,
April 2006 in “Clinical Interventions in Aging” Minoxidil and Finasteride are effective for male baldness; more research is needed for hair aging treatments.
 5 citations,
October 2014 in “Scottish medical journal”
5 citations,
October 2014 in “Scottish medical journal” Nitrofurantoin may cause sub-acute cutaneous lupus erythematosus.
 37 citations,
September 2008 in “The American journal of surgical pathology”
37 citations,
September 2008 in “The American journal of surgical pathology” Hair follicle hyperplasia is common in both benign and malignant skin lymphoproliferative disorders, with a proposed new term "pseudolymphomatous adnexitis."
 3 citations,
May 2023 in “Frontiers in immunology”
3 citations,
May 2023 in “Frontiers in immunology” Faulty inflammasome activation may lead to autoimmune skin diseases and could be a target for new treatments.
 January 2011 in “Side effects of drugs annual”
January 2011 in “Side effects of drugs annual” Tretinoin gel is safe for sun exposure, but tacalcitol doesn't significantly improve non-segmental vitiligo.
 15 citations,
March 2015 in “Australasian Journal of Dermatology”
15 citations,
March 2015 in “Australasian Journal of Dermatology” Seborrhoeic dermatitis may cause a condition called "seborrhoeic folliculitis," leading to chronic scalp inflammation and scarring hair loss.
 17 citations,
May 1987 in “Clinical and Experimental Dermatology”
17 citations,
May 1987 in “Clinical and Experimental Dermatology” A patient with Sézary syndrome showed improvement after treatment and the study suggested follicular mucinosis might indicate future lymphoma risk.
 7 citations,
July 2011 in “Survey of Ophthalmology”
7 citations,
July 2011 in “Survey of Ophthalmology” The document concludes that periocular hair disorders have various causes and treatments, and proper evaluation by specialists is important for management and prognosis.
 4 citations,
January 2012 in “Elsevier eBooks”
4 citations,
January 2012 in “Elsevier eBooks” The document concludes that various skin conditions have specific treatments, ranging from antihistamines for urticaria to surgery and medication for tumors and chronic skin diseases.
 1 citations,
July 1973 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
1 citations,
July 1973 in “British Journal of Dermatology” The document concludes that secondary syphilis cases are increasing and often misdiagnosed, pityriasis rubra pilaris can be distinguished from psoriasis by skin cell features, and different skin layers produce specific components during skin repair.
82 citations,
March 2013 in “PLoS ONE” Vemurafenib causes skin side effects similar to RASopathies, requiring regular skin checks and UVA protection.
 September 2022 in “Dermatology and therapy”
September 2022 in “Dermatology and therapy” Contact immunotherapy might help treat various skin conditions, but more research is needed to confirm its safety and effectiveness.
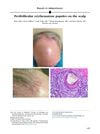 January 2016 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
January 2016 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” The woman has a type of scarring hair loss with red bumps around hair follicles.
 1 citations,
October 2023 in “Skin research and technology”
1 citations,
October 2023 in “Skin research and technology” LC-OCT is an effective new method for diagnosing classic lichen planopilaris.
 13 citations,
January 2019 in “Skin appendage disorders”
13 citations,
January 2019 in “Skin appendage disorders” FAPD is a possible diagnosis for hair loss in patients of color and requires multiple evaluations for accurate diagnosis.
 179 citations,
December 2004 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
179 citations,
December 2004 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Some postmenopausal women with frontal fibrosing alopecia stopped losing hair with finasteride treatment, hinting at a possible hormonal cause.
 158 citations,
February 2000 in “Archives of dermatology”
158 citations,
February 2000 in “Archives of dermatology” Some people with pattern hair loss may also have scalp inflammation and scarring similar to lichen planopilaris.
 126 citations,
April 2006 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
126 citations,
April 2006 in “International Journal of Dermatology” The conclusion is that FFA and LPP have similar scalp biopsy features, making them hard to distinguish histologically, and FFA may be a specific kind of scarring hair loss.
 15 citations,
December 2017 in “Journal of The European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
15 citations,
December 2017 in “Journal of The European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” Frontal fibrosing alopecia and androgenetic alopecia may be related, with a possible shared cause.

Lichen planopilaris and frontal fibrosing alopecia are likely the same disease with different clinical appearances.
8 citations,
August 2017 in “Skin appendage disorders” Red dots on the upper chest may be an early sign of certain types of hair loss.
 4 citations,
January 2020 in “Skin appendage disorders”
4 citations,
January 2020 in “Skin appendage disorders” A woman with an unusual pattern of hair loss was confirmed to have Frontal Fibrosing Alopecia and treated with specific medications.
 July 2018 in “Elsevier eBooks”
July 2018 in “Elsevier eBooks” Frontal Fibrosing Alopecia is a type of hair loss affecting mostly older women, with no agreed best treatment.
 102 citations,
April 2014 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
102 citations,
April 2014 in “International Journal of Dermatology” The treatment helped reduce symptoms and stabilize the hairline in most patients with Frontal Fibrosing Alopecia, but hair regrowth was limited.
 3 citations,
April 2015 in “Dermatology practical & conceptual”
3 citations,
April 2015 in “Dermatology practical & conceptual” Postmenopausal women can experience hairline recession, affecting their quality of life, and more research is needed for treatments.




























