 September 2022 in “Dermato”
September 2022 in “Dermato” Adult acne is often related to hormonal disorders, especially in women, and may need long-term treatment involving specialists.
 12 citations,
August 2011 in “European Journal of Endocrinology”
12 citations,
August 2011 in “European Journal of Endocrinology” Anti-Müllerian hormone is a specific marker for ovarian issues in women with conditions like PCOS.
 42 citations,
February 1985 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
42 citations,
February 1985 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Excessive hair growth can be assessed by history, exam, and blood tests, and treated with medication like dexamethasone, birth control pills, and spironolactone.
 47 citations,
December 2006 in “Therapy”
47 citations,
December 2006 in “Therapy” The dietary supplement helped increase hair growth in women with hair loss.
 2 citations,
January 2002 in “Hormone Research in Paediatrics”
2 citations,
January 2002 in “Hormone Research in Paediatrics” Molecular diagnostics help identify genetic defects causing endocrine diseases, improving diagnosis and treatment options.
 1 citations,
August 2012 in “Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft”
1 citations,
August 2012 in “Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft” A woman's hyperandrogenism was caused by a genetic mutation leading to non-classic adrenogenital syndrome.
 151 citations,
December 2004 in “Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences”
151 citations,
December 2004 in “Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences” Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia is a genetic disorder with two forms, causing symptoms like early puberty and severe acne, but can be identified through screening and treated with glucocorticoids.
 January 2019 in “Springer eBooks”
January 2019 in “Springer eBooks” Acne is linked to inflammation and insulin resistance, and is associated with various syndromes that require different treatments.
 12 citations,
November 1993 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
12 citations,
November 1993 in “International Journal of Dermatology” The document explains that hirsutism, often caused by hormonal issues, can be managed with treatment to improve both physical appearance and mental health.
 53 citations,
October 1984 in “Endocrine reviews”
53 citations,
October 1984 in “Endocrine reviews” Excessive hair growth in women often has no known cause and is not linked to race or other hormonal symptoms.
 10 citations,
December 2015 in “Clinics in Dermatology”
10 citations,
December 2015 in “Clinics in Dermatology” Diabetes can lead to blindness and skin problems, and managing blood sugar and blood pressure is crucial to prevent these complications.
 54 citations,
April 2010 in “Baillière's best practice and research in clinical endocrinology and metabolism/Baillière's best practice & research. Clinical endocrinology & metabolism”
54 citations,
April 2010 in “Baillière's best practice and research in clinical endocrinology and metabolism/Baillière's best practice & research. Clinical endocrinology & metabolism” Impaired androgen production in 46,XY DSDs causes ambiguous genitalia and requires long-term care.
 3 citations,
May 1990 in “Journal of Steroid Biochemistry”
3 citations,
May 1990 in “Journal of Steroid Biochemistry” Some women with excess hair growth have a hormone condition that can't be diagnosed by blood or urine tests alone.
 70 citations,
April 2014 in “Annales d'endocrinologie”
70 citations,
April 2014 in “Annales d'endocrinologie” New genes and pathways are important for testosterone production and male sexual development.
 5 citations,
January 2017 in “Endocrinology”
5 citations,
January 2017 in “Endocrinology” Genetic defects in testosterone production can cause hormonal and developmental disorders, and more research is needed to understand androgen regulation and develop safer treatments.
 1 citations,
November 1996 in “Journal of Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery”
1 citations,
November 1996 in “Journal of Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery” Hormones, especially androgens, play a key role in causing acne, and treatments like hormone control pills and hormone-blocking medications can help.

Hormones, especially testosterone and DHT, are key for penis development and function, and testosterone therapy may help with erectile dysfunction in those with low levels.
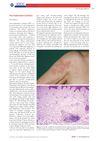 October 2012 in “Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft”
October 2012 in “Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft” Post-implantation erythema is a red skin condition after medical device implantation that sometimes goes away on its own.
5 citations,
March 2013 in “BMJ case reports” Gastric bypass surgery improved a woman's hormonal disorder without the need for medication.
 21 citations,
May 2016 in “The Cochrane library”
21 citations,
May 2016 in “The Cochrane library” Topical minoxidil helps treat female pattern hair loss, but more research needed for other treatments.
 35 citations,
March 2012 in “Experimental and Clinical Endocrinology & Diabetes”
35 citations,
March 2012 in “Experimental and Clinical Endocrinology & Diabetes” The conclusion is that accurately identifying the cause of high androgen levels in women with PCOS is crucial and requires specific tests.
280 citations,
May 2005 in “Andrology” Testosterone treatment for older men can have short-term benefits, but long-term risks are unclear, requiring careful evaluation and monitoring.
227 citations,
November 2004 in “Medicine” Older adults diagnosed with lupus show less severe symptoms but have a lower survival rate, often due to age-related factors.
129 citations,
February 2006 in “Andrology” Men with low testosterone should be carefully evaluated and monitored before and during treatment.
 21 citations,
February 2012 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
21 citations,
February 2012 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” Late-onset alopecia areata in Taiwanese patients is more common in women, usually starts at age 57, often involves less than 10% hair loss, and may have a minimal link to thyroid issues.
 20 citations,
January 2005 in “Australasian Journal of Dermatology”
20 citations,
January 2005 in “Australasian Journal of Dermatology” A woman had a skin condition with increased normal elastic fibers, not related to other known disorders, likely due to aging.
 17 citations,
February 2019 in “Journal of Clinical Medicine”
17 citations,
February 2019 in “Journal of Clinical Medicine” Testosterone replacement therapy should be used for men with low testosterone levels and symptoms of hypogonadism, after careful diagnosis and considering individual needs.
 7 citations,
January 2017 in “Dermatology”
7 citations,
January 2017 in “Dermatology” People who get alopecia areata after age 50 usually have mild symptoms, high chances of hair regrowth, and often have other health conditions.
 2 citations,
December 2023 in “Mediterranean Journal of Rheumatology”
2 citations,
December 2023 in “Mediterranean Journal of Rheumatology” Late onset SLE has different symptoms and antibody profiles compared to young onset SLE.
 September 1997 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
September 1997 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” Adults can develop late-onset loose anagen syndrome, which may often be misdiagnosed.


























