 January 2025 in “Frontiers in Medicine”
January 2025 in “Frontiers in Medicine” Hair follicles are key to treating vitiligo and alopecia areata, but challenges exist.
 September 2024 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
September 2024 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” Baricitinib effectively reduces hair loss in severe alopecia areata with mild side effects.
 July 2024 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences”
July 2024 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences” Hemp seed biomaterials may reduce hair loss and improve hair growth.
 April 2024 in “Journal of translational medicine”
April 2024 in “Journal of translational medicine” MJ04, a new compound, effectively promotes hair growth and is a potential topical treatment for hair loss.
 November 2023 in “Indian Dermatology Online Journal”
November 2023 in “Indian Dermatology Online Journal” Tofacitinib was effective for severe, treatment-resistant hair loss without side effects.
 October 2023 in “The Cochrane library”
October 2023 in “The Cochrane library” The medicine baricitinib was found to notably improve hair regrowth in alopecia areata, but more research is needed on its side effects and other treatments.
December 2022 in “Scientific Reports” Compound 4 is a promising treatment for hair loss with low toxicity.
 January 2024 in “Journal of Crohn's and colitis”
January 2024 in “Journal of Crohn's and colitis” Janus Kinase inhibitors are effective and have an acceptable safety profile for treating moderate to severe Ulcerative Colitis.
 116 citations,
February 2017 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
116 citations,
February 2017 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” JAK inhibitors help with skin conditions but need more research on dosing and safety.
 66 citations,
June 2021 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
66 citations,
June 2021 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Baricitinib is effective and safe for treating severe alopecia areata.
138 citations,
March 2021 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Ritlecitinib and brepocitinib effectively regrow hair in alopecia areata patients.
88 citations,
August 2019 in “Frontiers in immunology” Tyrosine kinases are important in skin autoimmune diseases and could be targets for new treatments.
 24 citations,
January 2018 in “International Journal of Trichology”
24 citations,
January 2018 in “International Journal of Trichology” Tofacitinib helped regrow hair in patients with alopecia, with few side effects.
 4 citations,
January 2023 in “Skin health and disease”
4 citations,
January 2023 in “Skin health and disease” Blocking Janus kinase 1 helps stop inflammation and regrow hair, making it a good treatment for hair loss from alopecia areata.
 2 citations,
June 2023 in “Indian journal of dermatology, venereology, and leprology”
2 citations,
June 2023 in “Indian journal of dermatology, venereology, and leprology” Janus kinase inhibitors can regrow hair in alopecia areata but may cause side effects and hair loss may return if treatment stops.
 223 citations,
September 2018 in “Rheumatology”
223 citations,
September 2018 in “Rheumatology” JAK inhibitors are effective in treating various immune-related diseases, not just rheumatoid arthritis.
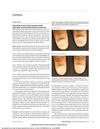 41 citations,
December 2015 in “JAMA Dermatology”
41 citations,
December 2015 in “JAMA Dermatology” Tofacitinib citrate improved nail dystrophy and pain in patients with alopecia universalis without causing side effects.
 2 citations,
May 2017 in “InTech eBooks”
2 citations,
May 2017 in “InTech eBooks” Stem cells could improve hair growth and new treatments for baldness are being researched.
 75 citations,
June 2019 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences”
75 citations,
June 2019 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences” Costunolide may have multiple health benefits, including promoting hair growth and protecting against cancer and diabetes, but more research is needed.
 6 citations,
May 2023 in “Drugs”
6 citations,
May 2023 in “Drugs” Baricitinib helps regrow hair in adults with severe alopecia better than a placebo and is approved for treatment, but long-term effects are still unknown.
 October 2023 in “International journal of rheumatic diseases”
October 2023 in “International journal of rheumatic diseases” New treatments targeting the JAK signaling pathway, especially JAK inhibitors, show promise for alopecia areata.
 July 2023 in “IntechOpen eBooks”
July 2023 in “IntechOpen eBooks” New treatments for alopecia areata show promise, but more research is needed to confirm their effectiveness.
701 citations,
August 2014 in “Nature medicine” Alopecia areata can be reversed by JAK inhibitors, promoting hair regrowth.
 8 citations,
May 2017 in “Singapore Medical Journal”
8 citations,
May 2017 in “Singapore Medical Journal” A Korean woman with complete hair loss regrew her hair after taking tofacitinib, with no side effects.
 14 citations,
March 2022 in “Journal of inflammation research”
14 citations,
March 2022 in “Journal of inflammation research” Baricitinib shows promise as a new treatment for certain skin conditions like alopecia areata.
 9 citations,
January 2023 in “Dermatology and therapy”
9 citations,
January 2023 in “Dermatology and therapy” A 14-year-old girl with severe hair loss regrew her hair using upadacitinib.
 4 citations,
April 2019 in “Cell Stem Cell”
4 citations,
April 2019 in “Cell Stem Cell” Certain immune cells in the skin can stop hair from growing.
 148 citations,
December 2018 in “Journal of autoimmunity”
148 citations,
December 2018 in “Journal of autoimmunity” Alopecia areata is an autoimmune disease causing patchy hair loss, often with other autoimmune disorders, but its exact causes are unknown.
 119 citations,
November 2014 in “Trends in Cell Biology”
119 citations,
November 2014 in “Trends in Cell Biology” Fibroblast growth factor receptor signaling controls cell development and repair, and its malfunction can cause disorders and cancer, but it also offers potential for targeted therapies.
 42 citations,
April 2012 in “Seminars in Oncology”
42 citations,
April 2012 in “Seminars in Oncology” Targeted cancer therapies often cause skin problems that need careful management to improve patient quality of life and treatment success.


























