April 2017 in “Al-Azhar Medical Journal” PRP is an effective and safe treatment for alopecia areata.
 32 citations,
January 2019 in “American Journal of Clinical Dermatology”
32 citations,
January 2019 in “American Journal of Clinical Dermatology” Minoxidil helps treat eyebrow thinning, monilethrix, early hair loss, and shortens chemo-related hair loss.
7 citations,
December 2021 in “Pharmaceutics” The nanoemulsion with garlic oil, apple cider vinegar, and minoxidil could effectively treat alopecia areata.
December 2023 in “Journal of clinical medicine” Some leukemia treatments can cause skin reactions similar to keratosis pilaris.
 1 citations,
April 2024 in “Journal of Autoimmunity”
1 citations,
April 2024 in “Journal of Autoimmunity” Interleukin-15 can help hair growth and protect hair follicles.
 January 2023 in “Frontiers in medicine”
January 2023 in “Frontiers in medicine” Early diagnosis and personalized treatments are crucial for better hair loss management.
 June 2013 in “Annals of the rheumatic diseases”
June 2013 in “Annals of the rheumatic diseases” Methotrexate dose has little effect on its toxicity when used with adalimumab for early rheumatoid arthritis.
 18 citations,
October 2014 in “Experimental Biology and Medicine”
18 citations,
October 2014 in “Experimental Biology and Medicine” Eating vitamin A affects hair growth and health by changing cell signals in mice.
 February 2021 in “International journal of men's social and community health”
February 2021 in “International journal of men's social and community health” Online forums help understand men's concerns about baldness and show the need for better support that changes how baldness is viewed.
 February 2024 in “International neuropsychiatric disease journal”
February 2024 in “International neuropsychiatric disease journal” Alopecia areata severely impacts quality of life, mental health, and work productivity.
 1 citations,
August 2019 in “Australasian journal of dermatology”
1 citations,
August 2019 in “Australasian journal of dermatology” Immunotherapy can help treat severe alopecia areata.
 1 citations,
September 2020 in “Cochrane library (CD-ROM)”
1 citations,
September 2020 in “Cochrane library (CD-ROM)” The analysis aims to identify the most effective and safest treatments for alopecia areata.
 August 2023 in “Indian journal of pediatrics/Indian Journal of Pediatrics”
August 2023 in “Indian journal of pediatrics/Indian Journal of Pediatrics” Topical treatments helped a child with Down syndrome and severe hair loss regrow most of his hair.

OCT can effectively screen and diagnose various medical conditions non-invasively.
 1 citations,
November 2019 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
1 citations,
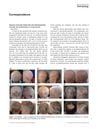
November 2019 in “International Journal of Dermatology” A 6-year-old girl with alopecia universalis regrew most of her hair after treatment with simvastatin/ezetimibe, minoxidil, and prednisolone.
 December 2023 in “Journal of dermatology”
December 2023 in “Journal of dermatology” Adults and adolescents with severe alopecia areata are willing to take significant health risks for a better chance of hair regrowth.
 June 2023 in “Journal of cosmetic dermatology”
June 2023 in “Journal of cosmetic dermatology” Both DPCP alone and with PRP are effective and safe for treating severe alopecia areata.
 14 citations,
January 2017 in “Skin appendage disorders”
14 citations,
January 2017 in “Skin appendage disorders” Simvastatin/ezetimibe did not effectively treat severe alopecia areata and caused side effects in some patients.
 3 citations,
May 2023 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences”
3 citations,
May 2023 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences” A new treatment using nanoparticles can effectively prevent and reduce hair loss caused by chemotherapy.
 May 2023 in “Plastic and reconstructive surgery. Global open”
May 2023 in “Plastic and reconstructive surgery. Global open” Activated PRP injections are effective in treating hair loss and improving hair density.
 17 citations,
January 2019 in “Dermatologic Therapy”
17 citations,
January 2019 in “Dermatologic Therapy” Tofacitinib is effective and safe for long-term treatment of severe alopecia areata, with many patients achieving complete hair regrowth.
 1 citations,
February 2024 in “JEADV. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology/Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
1 citations,
February 2024 in “JEADV. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology/Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” Baricitinib effectively promotes long-term hair regrowth in alopecia areata patients.
 5 citations,
November 2011 in “Expert Review of Dermatology”
5 citations,
November 2011 in “Expert Review of Dermatology” The document concludes that early diagnosis and a comprehensive treatment plan are crucial for managing hair loss in children, with a focus on both medical and psychological support.
3 citations,
November 2022 in “The Egyptian Rheumatologist” Macrophage activation syndrome can be a deadly first sign of systemic lupus erythematosus.
 3 citations,
May 2018 in “Experimental Dermatology”
3 citations,
May 2018 in “Experimental Dermatology” Young HS patients often have other physical and mental health issues, and research on HS covers a wide range of topics including genetics, triggers, treatments, and the need for more data.
 January 2025 in “Frontiers in Pediatrics”
January 2025 in “Frontiers in Pediatrics” Baricitinib significantly improved hair regrowth and skin condition in a 14-year-old with alopecia areata and atopic dermatitis.
 82 citations,
June 2020 in “Inflammation Research”
82 citations,
June 2020 in “Inflammation Research” Skin problems in COVID-19 patients are rare and may be due to the body's complex immune response or blood clotting issues.
 July 2024 in “Clinical Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology”
July 2024 in “Clinical Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology” Exosomes can help promote hair growth and may treat hair loss.
 1 citations,
September 2023 in “Journal of drugs in dermatology”
1 citations,
September 2023 in “Journal of drugs in dermatology” Alopecia areata causes unpredictable hair loss and emotional distress, with no cure and limited treatment options.
 22 citations,
July 2019 in “PLOS ONE”
22 citations,
July 2019 in “PLOS ONE” Skin lymphatic vessels are essential for hair growth.

























