 July 2024 in “Clinical Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology”
July 2024 in “Clinical Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology” Exosomes can help promote hair growth and may treat hair loss.
278 citations,
May 2013 in “Ca” Targeted anticancer therapies can cause severe side effects similar to traditional chemotherapy, but with different types.
 August 2024 in “Stem Cell Research & Therapy”
August 2024 in “Stem Cell Research & Therapy” New regenerative therapies show promise for treating hair loss.
 January 2023 in “Skin appendage disorders”
January 2023 in “Skin appendage disorders” Hair loss is common in autoimmune diseases and can be an early sign of the condition, often requiring prompt treatment to prevent permanent damage.
March 2024 in “Current issues in molecular biology” Personalized medicine in dermatology uses molecular biomarkers to improve diagnosis and treatment but needs further advancements for practical use.
 1 citations,
April 2018 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
1 citations,
April 2018 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Tofacitinib helped most patients with alopecia areata regrow hair and changes in immune cells were linked to the treatment's effectiveness.
 January 2023 in “Indian Dermatology Online Journal”
January 2023 in “Indian Dermatology Online Journal” No single ideal JAK inhibitor for alopecia areata has been determined; JAK3 inhibitors may be promising with fewer side effects.
 September 2014 in “SciBX”
September 2014 in “SciBX” JAK inhibitors may help treat alopecia areata and promote hair regrowth.
 6 citations,
November 2022 in “Journal of autoimmunity”
6 citations,
November 2022 in “Journal of autoimmunity” JAK inhibitors like tofacitinib may effectively treat Alopecia Areata.
 2 citations,
July 2023 in “Journal of cosmetic dermatology”
2 citations,
July 2023 in “Journal of cosmetic dermatology” JAK inhibitors are more effective and safer for treating alopecia areata than dupilumab and apremilast.

Alopecia Areata has no cure, treatments are limited, and the condition often recurs, but new therapies like JAK inhibitors show promise.
 66 citations,
June 2021 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
66 citations,
June 2021 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Baricitinib is effective and safe for treating severe alopecia areata.
 82 citations,
March 2016 in “Autoimmunity reviews”
82 citations,
March 2016 in “Autoimmunity reviews” Animal models have helped understand hair loss from alopecia areata and find new treatments.
 2 citations,
March 2015 in “Expert opinion on orphan drugs”
2 citations,
March 2015 in “Expert opinion on orphan drugs” New treatments for hair loss show promise but need more research to confirm safety and effectiveness.
 1 citations,
March 2024 in “Signal transduction and targeted therapy”
1 citations,
March 2024 in “Signal transduction and targeted therapy” NF-κB signaling is crucial in many diseases and can be targeted for new treatments.
 1 citations,
January 2024 in “Curēus”
1 citations,
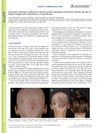
January 2024 in “Curēus” Upadacitinib significantly improved a man's severe scalp condition when other treatments failed.
 24 citations,
June 2016 in “Acta dermato-venereologica”
24 citations,
June 2016 in “Acta dermato-venereologica” Tofacitinib helped a young woman's severe hair loss and arthritis but not her plaque psoriasis.
 1 citations,
October 2018 in “InTech eBooks”
1 citations,
October 2018 in “InTech eBooks” Only minoxidil and finasteride are FDA-approved for hair loss, with other treatments available but less effective or with side effects.
 24 citations,
September 2005 in “Journal of Cellular Biochemistry”
24 citations,
September 2005 in “Journal of Cellular Biochemistry” Retinoids increase steroid sulfatase activity in leukemia cells through RARα/RXR and involves certain pathways like phosphoinositide 3-kinase and ERK-MAP kinase.
 60 citations,
September 2013 in “Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics”
60 citations,
September 2013 in “Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics” Immunosuppressive and anti-TNF therapies in IBD patients can increase the risk of skin cancer and cause various skin issues.
3 citations,
July 2023 in “International journal of molecular sciences” Stress may contribute to hair loss in alopecia areata by affecting immune responses and cell death in hair follicles.

Tofacitinib may effectively treat hair loss and improve symptoms in autoimmune conditions like alopecia areata and Sjögren's syndrome, but long-term treatment might be necessary.
 January 2024 in “Revista de la Asociación Colombiana de Dermatología y Cirugía Dermatológica/Revista de la Asociacion Colombiana de Dermatologia y Cirugia Dermatologica”
January 2024 in “Revista de la Asociación Colombiana de Dermatología y Cirugía Dermatológica/Revista de la Asociacion Colombiana de Dermatologia y Cirugia Dermatologica” Baricitinib successfully treated severe hair loss.
 16 citations,
January 2017 in “Acta dermatovenerologica Alpina, Pannonica et Adriatica (Tiskana izd.)”
16 citations,
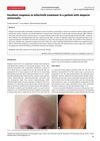
January 2017 in “Acta dermatovenerologica Alpina, Pannonica et Adriatica (Tiskana izd.)” A patient with complete hair loss regrew all her hair using tofacitinib.
 2 citations,
July 2023 in “JAAD Case Reports”
2 citations,
July 2023 in “JAAD Case Reports” A woman with a type of hair loss saw hair regrowth after two months of taking baricitinib.
2 citations,
February 2023 in “Actas Dermo-Sifiliográficas” Baricitinib effectively improved both atopic dermatitis and alopecia areata symptoms in a patient.
33 citations,
January 2018 in “Blood” Ruxolitinib helps protect skin stem cells and keeps skin healthy in mice with skin GVHD.
 3 citations,
March 2021 in “Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology”
3 citations,
March 2021 in “Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology” Early treatment of Lupus Erythematosus Alopecia can prevent permanent hair loss, and various medications are effective.
 47 citations,
December 2019 in “Frontiers in immunology”
47 citations,
December 2019 in “Frontiers in immunology” A new mutation in the STING protein causes a range of symptoms and its severity may be affected by other genetic variations; treatment with a specific inhibitor showed improvement in one patient.
 23 citations,
April 2021 in “Journal of Clinical Medicine”
23 citations,
April 2021 in “Journal of Clinical Medicine” Frontal Fibrosing Alopecia's cause is unclear, affects mainly postmenopausal women, and current treatments focus on stopping hair loss rather than regrowth.

























