 December 2022 in “Dermatology and Therapy”
December 2022 in “Dermatology and Therapy” Alopecia areata needs more recognition and better treatment access in Latin America to improve patient care and outcomes.
 September 2014 in “SciBX”
September 2014 in “SciBX” JAK inhibitors may help treat alopecia areata and promote hair regrowth.
 16 citations,
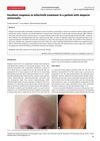
January 2017 in “Acta dermatovenerologica Alpina, Pannonica et Adriatica (Tiskana izd.)”
16 citations,
January 2017 in “Acta dermatovenerologica Alpina, Pannonica et Adriatica (Tiskana izd.)” A patient with complete hair loss regrew all her hair using tofacitinib.
[object Object]  1 citations,
January 2023 in “SAGE open medical case reports”
1 citations,
January 2023 in “SAGE open medical case reports” A new treatment called deucravacitinib helped a patient with severe hair loss grow their hair back quickly.
 May 2023 in “Journal of Clinical Medicine”
May 2023 in “Journal of Clinical Medicine” New understanding and treatments for hair loss are improving, but more research is needed.
 March 2023 in “PARIPEX INDIAN JOURNAL OF RESEARCH”
March 2023 in “PARIPEX INDIAN JOURNAL OF RESEARCH” Tofacitinib helped regrow hair in most patients with severe hair loss.
 December 2017 in “The journal of investigative dermatology. Symposium proceedings/The Journal of investigative dermatology symposium proceedings”
December 2017 in “The journal of investigative dermatology. Symposium proceedings/The Journal of investigative dermatology symposium proceedings” The summit aimed to speed up finding treatments for alopecia areata.
 4 citations,
January 2024 in “JEADV. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology/Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
4 citations,
January 2024 in “JEADV. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology/Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” Baricitinib and ritlecitinib are recommended for severe alopecia areata, with other treatments available off-label.
26 citations,
October 2016 in “American journal of clinical dermatology” New treatments like JAK inhibitors show promise for reversing alopecia areata.
11 citations,
February 2022 in “JAAD case reports” Abrocitinib, a JAK inhibitor, may help treat atopic dermatitis and alopecia universalis together.
 3 citations,
January 2015 in “Nasza Dermatologia Online”
3 citations,
January 2015 in “Nasza Dermatologia Online” Some treatments for autoimmune hair loss work, but JAK inhibitors like tofacitinib are promising for regrowth.

Alopecia Areata has no cure, treatments are limited, and the condition often recurs, but new therapies like JAK inhibitors show promise.
46 citations,
October 2018 in “JCI insight” CD8+ T cells are involved in alopecia areata and may cause disease relapse.
 May 2024 in “Journal of cosmetic dermatology”
May 2024 in “Journal of cosmetic dermatology” Tofacitinib is an effective and safe treatment for alopecia areata.
 January 2024 in “Revista de la Asociación Colombiana de Dermatología y Cirugía Dermatológica/Revista de la Asociacion Colombiana de Dermatologia y Cirugia Dermatologica”
January 2024 in “Revista de la Asociación Colombiana de Dermatología y Cirugía Dermatológica/Revista de la Asociacion Colombiana de Dermatologia y Cirugia Dermatologica” Baricitinib successfully treated severe hair loss.
 60 citations,
September 2013 in “Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics”
60 citations,
September 2013 in “Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics” Immunosuppressive and anti-TNF therapies in IBD patients can increase the risk of skin cancer and cause various skin issues.
 11 citations,
February 2021 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology”
11 citations,
February 2021 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology” Oral tofacitinib helped regrow hair in over half of the patients with severe alopecia, but relapses and side effects were common.
 271 citations,
May 2019 in “Cells”
271 citations,
May 2019 in “Cells” The secretome from mesenchymal stem cells is a promising treatment that may repair tissue and avoid side effects of stem cell transplantation.

COVID-19 can cause skin problems and affect dermatology treatments, with recommendations for skin care and cautious use of certain drugs.
 June 2022 in “Frontiers in Immunology”
June 2022 in “Frontiers in Immunology” Tofacitinib regrew hair in a man with total hair loss but raised cytokine levels, needing more research on possible side effects.
August 2024 in “Bioorganic Chemistry” Cedrol from ginger can promote hair growth when taken orally.
 December 2023 in “International journal of multidisciplinary research and analysis”
December 2023 in “International journal of multidisciplinary research and analysis” SH-MSCs gel can effectively treat alopecia by increasing IL-10 and decreasing TNF-α gene expression.
 3 citations,
June 2023 in “Frontiers in medicine”
3 citations,
June 2023 in “Frontiers in medicine” Oxidative stress may contribute to hair loss in alopecia areata and antioxidants could potentially help as a treatment.
[object Object]  April 2024 in “Bioscience trends”
April 2024 in “Bioscience trends” Higher levels of certain DNAs in blood may indicate hair follicle damage in alopecia areata patients.
 April 2019 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
April 2019 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Women with scarring alopecia are less likely to have used hormone replacement therapy or oral contraceptives compared to those with female pattern hair loss.
 April 2019 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
April 2019 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Calcium signals and SHH guide the direction of feather growth in chicken skin.
 April 2019 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
April 2019 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Eating grape powder may reduce the severity of skin allergy symptoms.
 7 citations,
February 2021 in “Dermatologic Therapy”
7 citations,
February 2021 in “Dermatologic Therapy” Sebaceous glands are involved in various skin disorders, some treatable with medications like finasteride and minoxidil.
 May 2023 in “Sučasna pedìatrìâ. Ukraïna”
May 2023 in “Sučasna pedìatrìâ. Ukraïna” An 11-year-old child with total hair loss may have a genetic autoimmune disease, and the outlook for hair regrowth is not good.
 April 2023 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
April 2023 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” Too much IKZF1 and Ikaros protein may cause alopecia areata.


























