101 citations,
July 1998 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” UVB exposure in human skin causes macrophages to produce more IL-10 and less IL-12, leading to immunosuppression.
54 citations,
July 1994 in “Journal of Dermatological Science” FK506 may stimulate hair growth when applied to the skin.
 48 citations,
April 2010 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
48 citations,
April 2010 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” Men are more likely to get infectious skin diseases, while women are more prone to autoimmune and pigment-related skin conditions, influenced by biological and environmental factors.
 21 citations,
January 2006 in “Pediatrics”
21 citations,
January 2006 in “Pediatrics” Some diseases can improve the outcomes of other diseases, leading to new treatment possibilities.
20 citations,
March 1990 in “Archives of Dermatology” Nonimmunosuppressive cyclosporines might treat skin diseases by affecting cell growth.
19 citations,
April 2019 in “Veterinary dermatology” Oclacitinib effectively treated a skin condition in dogs that didn't respond to other immunosuppressants.
 18 citations,
July 2001 in “Australian veterinary journal”
18 citations,
July 2001 in “Australian veterinary journal” A cat with skin bumps and itching had high blood fats and skin infections, which improved with diet and medication changes.
 16 citations,
May 1998 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
16 citations,
May 1998 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Stress hormones like cortisol may trigger psoriasis flare-ups.
 14 citations,
June 2013 in “Joint Bone Spine”
14 citations,
June 2013 in “Joint Bone Spine” ACTH may be an effective first-line treatment for acute calcium pyrophosphate crystal arthritis.
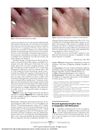 9 citations,
May 2013 in “JAMA Dermatology”
9 citations,
May 2013 in “JAMA Dermatology” Sunlight exposure improved a patient's skin condition, and there may be a link between a certain disease and skin growths; a leukemia treatment caused changes in hair color and growth.
6 citations,
December 2015 in “Medicine” Cronkhite-Canada syndrome may be more treatable and less severe than previously thought.
 6 citations,
November 2015 in “Equine Veterinary Education”
6 citations,
November 2015 in “Equine Veterinary Education” A sick foal with Rhodococcus equi pneumonia was successfully treated for multiple complications with targeted therapy and careful monitoring.
 6 citations,
January 2015 in “Journal of the American Veterinary Medical Association”
6 citations,
January 2015 in “Journal of the American Veterinary Medical Association” A 7-year-old dog with a rare autoimmune disease was euthanized due to severe anemia and poor prognosis.
 5 citations,
January 2021 in “Inflammatory Bowel Diseases”
5 citations,
January 2021 in “Inflammatory Bowel Diseases” Tofacitinib improved ulcerative colitis, skin ulcers, and hair loss in a patient who didn't respond well to other treatments.
3 citations,
June 2019 in “Veterinary record case reports” A dog developed a skin condition called pemphigus foliaceus after taking NexGard, but got better with treatment.
 3 citations,
April 2019 in “Annals of hepatology”
3 citations,
April 2019 in “Annals of hepatology” Peanut allergies can be transferred through organ transplants.
 3 citations,
April 2019 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
3 citations,
April 2019 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” ILC1 cells contribute to hair loss in alopecia areata.
 3 citations,
December 2016 in “Springer eBooks”
3 citations,
December 2016 in “Springer eBooks” Activating TLR3 improves the healing and immune properties of periodontal ligament stem cells.
 2 citations,
February 2014 in “Journal of Crohn's and colitis”
2 citations,
February 2014 in “Journal of Crohn's and colitis” Some IBD patients on anti-TNFs developed severe skin issues, but ustekinumab helped.
1 citations,
July 2021 in “Veterinary Medicine and Science” A cat's skin condition was fully cured with cyclosporine A after other treatments failed.
May 2024 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences” Mouse hair follicle stem cells can help prevent Type 1 Diabetes.
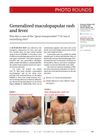 July 2023 in “The Journal of Family Practice”
July 2023 in “The Journal of Family Practice” The man was diagnosed with lupus and improved with treatment.
 November 2022 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
November 2022 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” The medicine Cyclosporin A might cause excessive hair growth by reducing a protein that controls hair growth.
October 2020 in “Stem cells” The document concludes that DNA methylation and the mTOR pathway are important for stem cell function and could impact disease treatment.
 April 2018 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
April 2018 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Cutaneous lupus patients have higher levels of certain immune cells in their blood and skin.
 April 2018 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
April 2018 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” IL-17C is important in inflammatory skin diseases and could be a target for treatment.
 September 2017 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
September 2017 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” The study found that sweat glands normally suppress immune responses, but this is disrupted in certain skin diseases, possibly contributing to their development.
 August 1994 in “Journal of dermatological science”
August 1994 in “Journal of dermatological science” Different substances affect hair and skin cell growth in various ways, with some promoting and others inhibiting cell proliferation.
16 citations,
February 2005 in “British journal of dermatology/British journal of dermatology, Supplement” Lack of Vitamin D receptor changes skin structure and increases certain immune cells in the skin.
 12 citations,
November 1996 in “Australasian journal of dermatology”
12 citations,
November 1996 in “Australasian journal of dermatology” A kidney transplant patient on cyclosporin experienced unexpected severe hair loss, which improved with treatment adjustments.



















