 8 citations,
August 2015 in “Journal of dermatological science”
8 citations,
August 2015 in “Journal of dermatological science” Rhododendrol in skin-whitening products can cause skin depigmentation and immune reactions.
3 citations,
October 2020 in “The journal of investigative dermatology. Symposium proceedings/The Journal of investigative dermatology symposium proceedings” Alopecia areata is a hair loss disease caused by complex immune reactions, and new targeted treatments show promise.
[object Object]  1 citations,
July 2014 in “Our Dermatology Online”
1 citations,
July 2014 in “Our Dermatology Online” The patient with both scarring and non-scarring hair loss showed complex immune reactions and improved with steroid treatment.
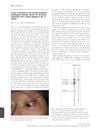 7 citations,
February 2010 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
7 citations,
February 2010 in “British Journal of Dermatology” A woman with a rare autoimmune disorder had a blister on her eye and unique immune reaction, which was effectively treated with medication.
3 citations,
September 2021 in “JAAD case reports” Denosumab, a bone loss treatment, may cause hair loss and skin reactions due to immune system effects.
57 citations,
May 1980 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Langerhans cells are crucial for skin immunity and allergic reactions.
 44 citations,
November 1998 in “Australasian Journal of Dermatology”
44 citations,
November 1998 in “Australasian Journal of Dermatology” Accurate diagnosis is key for treating different kinds of hair loss, and immune response variations may affect the condition and treatment results.
 March 2013 in “Hair transplant forum international”
March 2013 in “Hair transplant forum international” Inflammation linked to the immune response may play a role in causing various types of hair loss.
 3 citations,
July 1996 in “Clinics in Dermatology”
3 citations,
July 1996 in “Clinics in Dermatology” Cytokines are important for immune responses and treating diseases, but they can cause side effects like fever and skin issues.
 January 2023 in “International journal of dermatology, venereology and leprosy sciences”
January 2023 in “International journal of dermatology, venereology and leprosy sciences” People with alopecia areata have different blood markers that suggest inflammation and immune system issues compared to healthy individuals.
 57 citations,
March 2019 in “Immunity”
57 citations,
March 2019 in “Immunity” The document concludes that the skin's immune system is complex, involving interactions with hair follicles, nerves, and microbes, and can protect or cause disease, offering targets for new treatments.
June 2020 in “Comparative medicine” NSG mice had the most mites, and genetic factors affect immune response and susceptibility.
 26 citations,
June 2018 in “Australasian Journal of Dermatology”
26 citations,
June 2018 in “Australasian Journal of Dermatology” Stopping sunscreen use on the forehead led to hair regrowth in a woman with frontal fibrosing alopecia.
 4 citations,
November 2014
4 citations,
November 2014 The skin protects the body, regulates temperature, senses touch, and makes vitamin D.

Modern skin cancer treatments can cause skin side effects and hair loss, affecting patients' quality of life.
 68 citations,
May 2011 in “European Journal of Dermatology”
68 citations,
May 2011 in “European Journal of Dermatology” Acne is caused by genetics, diet, hormones, and bacteria, with treatments not yet curative.
17 citations,
January 2007 in “Annals of Medicine” Cutaneous gene therapy could become a viable treatment for skin and hair disorders with improved vector development and gene expression control.
 January 2015 in “Journal of clinical & experimental dermatology research”
January 2015 in “Journal of clinical & experimental dermatology research” A protein combining parathyroid hormone and collagen helped hair regrow in mice with a hair loss condition.
 16 citations,
January 2006 in “The Aging Male”
16 citations,
January 2006 in “The Aging Male” Hormone imbalances can cause skin diseases, and understanding these links is important for diagnosis and treatment.
 41 citations,
December 2015 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
41 citations,
December 2015 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” The conclusion is that a new biopsy technique and humidity chamber help study skin mites better and suggest mite overpopulation may cause skin diseases.
 2 citations,
October 2010 in “Reviews in Medical Microbiology”
2 citations,
October 2010 in “Reviews in Medical Microbiology” Syphilis is becoming more common and remains a major health problem due to challenges in prevention and treatment.
 18 citations,
January 1999 in “CNS Drugs”
18 citations,
January 1999 in “CNS Drugs” Some anticonvulsant drugs can cause skin reactions, ranging from mild to severe, and managing these reactions is important for patient care.
 10 citations,
September 2014 in “European Journal of Dermatology”
10 citations,
September 2014 in “European Journal of Dermatology” A woman's hair loss worsened after starting hepatitis C treatment due to immune changes in her hair follicles.
 273 citations,
May 2017 in “The Lancet”
273 citations,
May 2017 in “The Lancet” Some drugs can cause rare but potentially deadly skin reactions, and early treatment and avoiding the drug again are key.
 6 citations,
March 2009 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
6 citations,
March 2009 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” Mexican patients had a lower incidence of skin reactions to drugs and no significant link between these reactions and the TNF2 gene variant.
 August 2023 in “JOJ dermatology & cosmetics”
August 2023 in “JOJ dermatology & cosmetics” Antibiotics often cause skin reactions, making them a major health concern.
 110 citations,
July 2017 in “Immunology”
110 citations,
July 2017 in “Immunology” Skin's Regulatory T cells are crucial for maintaining skin health and could be targeted to treat immune-related skin diseases and cancer.
 43 citations,
June 2018 in “Clinics in dermatology”
43 citations,
June 2018 in “Clinics in dermatology” People with atopic dermatitis are more likely to develop other skin conditions due to shared genetics and immune pathways.
 25 citations,
March 2012 in “Journal of Dermatological Science”
25 citations,
March 2012 in “Journal of Dermatological Science” Genetic variants linked to ten skin diseases were found, showing both immune and non-immune factors play a role.
[object Object]  15 citations,
July 1999 in “Dermatologic Clinics”
15 citations,
July 1999 in “Dermatologic Clinics” The document concludes that immune system abnormalities cause alopecia areata, but the exact process is still not completely understood.

























