 18 citations,
September 1990 in “Veterinary Dermatology”
18 citations,
September 1990 in “Veterinary Dermatology” Lambs' skin showed similar but more severe responses to a second orf virus infection, involving immune cells and new skin formation.
 3 citations,
May 2019 in “BMJ case reports”
3 citations,
May 2019 in “BMJ case reports” A boy with severe immune deficiency and Epstein-Barr virus died from high-grade B-cell lymphoma.
 8 citations,
January 2008 in “European Journal of Pediatrics”
8 citations,
January 2008 in “European Journal of Pediatrics” Children with autoimmune gastritis showed improved intestinal health over time and should be checked for other autoimmune conditions.
 January 2016 in “Human & Experimental Toxicology”
January 2016 in “Human & Experimental Toxicology” A specific DNA sequence caused hair loss in male mice by activating immune cells and increasing a certain immune signal.
 17 citations,
July 1994 in “Journal of Dermatological Science”
17 citations,
July 1994 in “Journal of Dermatological Science” The cause of alopecia areata is likely a mix of genetics, immune system issues, and environmental factors, with more research needed to understand it fully.
 4 citations,
January 2013 in “Acta dermato-venereologica”
4 citations,
January 2013 in “Acta dermato-venereologica” Some patients with Alopecia Areata experience itch due to immune cells and enzymes that cause itching.
245 citations,
October 2015 in “Nature medicine” Hair follicle-derived IL-7 and IL-15 are crucial for maintaining skin-resident memory T cells and could be targeted for treating skin diseases and lymphoma.
 185 citations,
August 2005 in “Autoimmunity Reviews”
185 citations,
August 2005 in “Autoimmunity Reviews” Alopecia areata is an autoimmune condition causing hair loss due to the immune system attacking hair follicles, often influenced by genetics and stress.
 57 citations,
April 2019 in “British journal of dermatology/British journal of dermatology, Supplement”
57 citations,
April 2019 in “British journal of dermatology/British journal of dermatology, Supplement” Alopecia areata involves immune system imbalances that may lead to depression and anxiety.
 46 citations,
January 1996 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
46 citations,
January 1996 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” People with late-stage HIV-1 often experience a specific type of hair loss linked to multiple factors, including nutritional issues and immune responses.
 18 citations,
January 2017 in “Annals of dermatology/Annals of Dermatology”
18 citations,
January 2017 in “Annals of dermatology/Annals of Dermatology” Certain immune cells contribute to severe hair loss in chronic alopecia areata, with Th17 cells possibly having a bigger impact than cytotoxic T cells.
 May 2023 in “Frontiers in Immunology”
May 2023 in “Frontiers in Immunology” Treg cell-based therapies might help treat hair loss from alopecia areata, but more research is needed to confirm safety and effectiveness.
55 citations,
October 2019 in “The journal of allergy and clinical immunology/Journal of allergy and clinical immunology/The journal of allergy and clinical immunology” The review suggests that other immune cells besides CD8+ T cells may contribute to alopecia areata and that targeting regulatory cell defects could improve treatment.
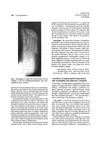 4 citations,
January 1987 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
4 citations,
January 1987 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” A man with both skin lesions and lung cancer improved quickly with chemotherapy, suggesting the skin condition might be a reaction to immune system injury.
 August 2001 in “Veterinary Dermatology”
August 2001 in “Veterinary Dermatology” The meeting presented findings on effective treatments for various pet skin conditions and insights into the immune responses of dogs with atopic dermatitis.
 159 citations,
December 2007 in “American Journal of Pathology”
159 citations,
December 2007 in “American Journal of Pathology” Stress-related substance P may lead to hair loss and negatively affect hair growth.
 421 citations,
April 2012 in “The New England Journal of Medicine”
421 citations,
April 2012 in “The New England Journal of Medicine” Alopecia Areata is an autoimmune condition causing hair loss with no cure and treatments that often don't work well.
38 citations,
February 2021 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Aging slows wound healing due to weaker cells and immune response.
 162 citations,
July 2011 in “Biomacromolecules”
162 citations,
July 2011 in “Biomacromolecules” Chitosan nanofiber scaffolds improve skin healing and are promising for wound treatment.
 150 citations,
October 2010 in “The American Journal of Pathology”
150 citations,
October 2010 in “The American Journal of Pathology” The document concludes that more research is needed to better understand and treat primary cicatricial alopecias, and suggests a possible reclassification based on molecular pathways.
 31 citations,
May 2008 in “Drug Discovery Today: Disease Mechanisms”
31 citations,
May 2008 in “Drug Discovery Today: Disease Mechanisms” Different hair growth problems are caused by genetic issues or changes in hair growth cycles, and new treatments are being developed.
 21 citations,
July 2020 in “Stem Cell Research & Therapy”
21 citations,
July 2020 in “Stem Cell Research & Therapy” Fat stem cells from diabetic mice can still help heal wounds.
 8 citations,
August 1997 in “Australasian Journal of Dermatology”
8 citations,
August 1997 in “Australasian Journal of Dermatology” Most HIV patients develop skin symptoms that can indicate the stage of their disease.
 1 citations,
January 2015 in “Journal of nutrition & health”
1 citations,
January 2015 in “Journal of nutrition & health” Fish oil improves skin health in people with diabetes and high cholesterol.
 38 citations,
September 2014 in “Cell and Tissue Research”
38 citations,
September 2014 in “Cell and Tissue Research” The hair follicle infundibulum plays a key role in skin health and disease, and understanding it better could lead to new skin disease treatments.
 7 citations,
February 2023 in “Inflammation and Regeneration”
7 citations,
February 2023 in “Inflammation and Regeneration” The protein interleukin-1 alpha helps regenerate hair follicles and increase stem cell growth in mice.
15 citations,
December 2018 in “International journal of environmental research and public health/International journal of environmental research and public health” EGCG may help treat alopecia areata by blocking certain immune responses and reducing specific harmful immune cells.
 59 citations,
July 2015 in “Journal of Immunology”
59 citations,
July 2015 in “Journal of Immunology” Certain proteins, caspases-1 and -11, are important in the early development of skin inflammation in mice.
 August 2022 in “Research Square (Research Square)”
August 2022 in “Research Square (Research Square)” Implanted special stem cells from hair follicles helped heal wounds faster and with less scarring in mice.
 7 citations,
February 2015 in “Journal of comparative pathology”
7 citations,
February 2015 in “Journal of comparative pathology” CD8+ T cells play a key role in graft-versus-host disease in certain mice models.

























