40 citations,
July 2015 in “Kidney International” IL-3 worsens lupus nephritis and blocking it improves kidney health.
[object Object]  April 2021 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
April 2021 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” The new skin-targeted COVID-19 vaccine creates strong immune responses and could improve vaccination methods.
 61 citations,
September 2010 in “Genomics”
61 citations,
September 2010 in “Genomics” The study found that immune responses disrupt hair growth cycles, causing hair loss in alopecia areata.
 23 citations,
March 2001 in “Clinics in dermatology”
23 citations,
March 2001 in “Clinics in dermatology” Alopecia areata involves immune response and gene changes affecting hair loss.
14 citations,
December 2001 in “Journal of autoimmunity” Rats can develop an immune response to prion protein peptides, but it may cause severe skin issues in older rats.
 9 citations,
November 2020 in “Medical Hypotheses”
9 citations,
November 2020 in “Medical Hypotheses” Hair loss may link to weaker COVID-19 immunity, suggesting possible need for extra vaccine boost.
 January 2025 in “Frontiers in Immunology”
January 2025 in “Frontiers in Immunology” IVIG therapy significantly improved symptoms in a patient with APS-2 and SPS.
 105 citations,
January 2010 in “Mediators of Inflammation”
105 citations,
January 2010 in “Mediators of Inflammation” Skin surface lipids are important for skin health and altering them could help prevent aging and treat skin conditions.
 21 citations,
January 2021 in “Therapeutic Advances in Endocrinology and Metabolism”
21 citations,
January 2021 in “Therapeutic Advances in Endocrinology and Metabolism” Testosterone may have a dual role in COVID-19, potentially worsening outcomes in men, and testosterone therapy could help some patients, but more research is needed.
 March 2021 in “Research Square (Research Square)”
March 2021 in “Research Square (Research Square)” Patients with RASopathies have a higher risk of autoimmune disorders and should be routinely screened.
11 citations,
October 2021 in “Orphanet journal of rare diseases” Patients with RASopathies are at risk for autoimmune disorders and should be routinely screened.
 34 citations,
October 2011 in “Pathology Research International”
34 citations,
October 2011 in “Pathology Research International” Behçet's Disease may be caused by genetic and environmental factors leading to abnormal immune responses, and stress management and new treatments could improve patient outcomes.
 4 citations,
July 2017 in “Archivum Immunologiae et Therapiae Experimentalis”
4 citations,
July 2017 in “Archivum Immunologiae et Therapiae Experimentalis” Retinol may affect immune responses in people with frequent skin boils.
 June 2023 in “Pharmaceuticals”
June 2023 in “Pharmaceuticals” Men and women respond differently to drugs for COVID-19, high cholesterol, and diabetes, which suggests a need for personalized treatments.
 113 citations,
March 2018 in “Biological reviews/Biological reviews of the Cambridge Philosophical Society”
113 citations,
March 2018 in “Biological reviews/Biological reviews of the Cambridge Philosophical Society” Animals that change color with the seasons mainly do so in response to daylight changes, but climate change is causing camouflage problems that may require evolutionary changes.
 375 citations,
July 2006 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
375 citations,
July 2006 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Stress can worsen skin and hair conditions by affecting the skin's immune response and hormone levels.
 1 citations,
February 2018 in “Orthopedics and rheumatology”
1 citations,
February 2018 in “Orthopedics and rheumatology” Combining Western chemotherapy with Traditional Chinese Medicine can reduce side effects and improve immune response in treating bone and soft tissue tumors.
 44 citations,
November 1998 in “Australasian Journal of Dermatology”
44 citations,
November 1998 in “Australasian Journal of Dermatology” Accurate diagnosis is key for treating different kinds of hair loss, and immune response variations may affect the condition and treatment results.
 119 citations,
October 2011 in “Journal of Veterinary Internal Medicine”
119 citations,
October 2011 in “Journal of Veterinary Internal Medicine” Rhodococcus equi causes severe pneumonia in young foals, and effective vaccines are needed due to foals' weak immune responses.
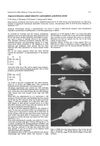 2 citations,
September 1980 in “Experientia”
2 citations,
September 1980 in “Experientia” Polyethylene alanine caused hair loss in young lab animals but not in adults, with hair regrowth occurring within 20 days.
 191 citations,
May 2018 in “British journal of dermatology/British journal of dermatology, Supplement”
191 citations,
May 2018 in “British journal of dermatology/British journal of dermatology, Supplement” Alopecia areata is likely an autoimmune disease with unclear triggers, involving various immune cells and molecules, and currently has no cure.
 89 citations,
May 1999 in “Allergy”
89 citations,
May 1999 in “Allergy” The yeast Pityrosporum ovale can cause skin allergies and infections, and antifungal treatments like ketoconazole are effective against it.
 45 citations,
January 2020 in “Pharmaceutical Biology”
45 citations,
January 2020 in “Pharmaceutical Biology” Dendrobium officinale polysaccharides may help with hair growth, skin moisturization, and protection against oxidative damage.
 41 citations,
December 2015 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
41 citations,
December 2015 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” The conclusion is that a new biopsy technique and humidity chamber help study skin mites better and suggest mite overpopulation may cause skin diseases.
 23 citations,
July 2008 in “British journal of dermatology/British journal of dermatology, Supplement”
23 citations,
July 2008 in “British journal of dermatology/British journal of dermatology, Supplement” Topical contact sensitizers can treat certain skin conditions but are rarely used in the U.K.
 May 2023 in “Sučasna pedìatrìâ. Ukraïna”
May 2023 in “Sučasna pedìatrìâ. Ukraïna” An 11-year-old child with total hair loss may have a genetic autoimmune disease, and the outlook for hair regrowth is not good.
 185 citations,
August 2005 in “Autoimmunity Reviews”
185 citations,
August 2005 in “Autoimmunity Reviews” Alopecia areata is an autoimmune condition causing hair loss due to the immune system attacking hair follicles, often influenced by genetics and stress.
37 citations,
December 2021 in “Cells” Alopecia areata severity and treatment response are linked to specific cytokine levels.
[object Object]  April 2021 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
April 2021 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” People with atopic dermatitis have more CD4+ T cells that respond to a certain bacterial lipid, which may play a role in the skin condition's inflammation.
 34 citations,
July 2020 in “Frontiers in immunology”
34 citations,
July 2020 in “Frontiers in immunology” Androgens may influence T cells, contributing to higher autoimmune liver disease risk in women.

























