 5 citations,
May 2011 in “Movement Disorders”
5 citations,
May 2011 in “Movement Disorders” Finasteride significantly reduced tics and obsessive-compulsive symptoms in Tourette syndrome patients.
 5 citations,
May 2011 in “Movement Disorders”
5 citations,
May 2011 in “Movement Disorders” Finasteride may help reduce tic severity in male Tourette syndrome patients.
 5 citations,
November 1992 in “Current problems in dermatology”
5 citations,
November 1992 in “Current problems in dermatology” Glucocorticoids are powerful anti-inflammatory drugs that must be used carefully to avoid serious side effects.
 4 citations,
February 2017 in “Journal of Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery”
4 citations,
February 2017 in “Journal of Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery” Compounds from certain trees used by First Nations people show potential for treating skin conditions and promoting hair growth, but more research is needed to confirm their safety and effectiveness.
 4 citations,
November 2016 in “Pediatric Clinics of North America”
4 citations,
November 2016 in “Pediatric Clinics of North America” The document explains the difficulty in diagnosing and treating brain diseases caused by the immune system and stresses the need for quick and accurate tests.
 4 citations,
May 2011 in “Movement Disorders”
4 citations,
May 2011 in “Movement Disorders” A woman's unique dementia was misdiagnosed, a genetic mutation increases Parkinson's risk with age, and finasteride may help with Tourette syndrome.
 3 citations,
May 2021 in “Dermatologic Clinics”
3 citations,
May 2021 in “Dermatologic Clinics” COVID-19 changed dermatology by increasing telemedicine and highlighting healthcare disparities.
 2 citations,
January 2011 in “Elsevier eBooks”
2 citations,
January 2011 in “Elsevier eBooks” Early treatment of acne is crucial to prevent scarring and psychological effects.
 1 citations,
January 2023 in “IEEE access”
1 citations,
January 2023 in “IEEE access” Deep learning helps detect skin conditions and is advancing dermatology diagnosis and treatment.
 1 citations,
April 2020 in “Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology”
1 citations,
April 2020 in “Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology” Acyclovir cream may slow down hair growth, suggesting it could be a new treatment for excessive hairiness.
 1 citations,
November 2016 in “Congenital Anomalies”
1 citations,
November 2016 in “Congenital Anomalies” Get head MRI for babies with achondroplasia early, use free immunoglobulin light chains to detect certain neurodevelopmental disorders, and video calls work for speech therapy in patients with facial anomalies.
 June 2021 in “Journal of emerging technologies and innovative research”
June 2021 in “Journal of emerging technologies and innovative research” Onion and Aloe vera can help protect hair from damage caused by hair dyes.
 September 2020 in “Journal of the turkish academy of dermatology”
September 2020 in “Journal of the turkish academy of dermatology” Some dermatology patients in Turkey use traditional medicine, with herbal remedies being most common, but these treatments can have mixed results and risks.
 August 2022 in “Case reports”
August 2022 in “Case reports” Isotretinoin effectively treated a rare scalp condition, but careful drug monitoring and a dairy-free diet were important.
1 citations,
January 2024 in “Microorganisms” Mice with a virus similar to COVID-19 had skin damage, but a special treatment helped repair it.
 August 2023 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences”
August 2023 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences” Human skin xenografting could improve our understanding of skin development, renewal, and healing.
 1 citations,
October 2000 in “Pediatrics in Review”
1 citations,
October 2000 in “Pediatrics in Review” The document says that hookworms are treated with mebendazole and stress-related hair loss usually gets better in 6 months, while other hair loss types have specific treatments.
 January 2023 in “Indian dermatology online journal”
January 2023 in “Indian dermatology online journal” Skin problems after waxing led to a sarcoidosis diagnosis.
 October 2023 in “TURKDERM”
October 2023 in “TURKDERM” COVID-19 reduced dermatology visits by 30.4%, with more male patients and increased cases of psoriasis, bullous diseases, and melanoma.
 2 citations,
November 2015 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
2 citations,
November 2015 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” RANKL improves the immune response against herpes simplex virus by enhancing T cell activation and could help develop better treatments or vaccines.

Dupilumab helped improve skin and prevent new lesions in a child with a rare immune disorder and severe eczema.
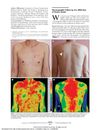 6 citations,
September 2010 in “Archives of Dermatology”
6 citations,
September 2010 in “Archives of Dermatology” Thermography matched the patient's pain levels in a shingles case and might help diagnose shingles without a rash.
 3 citations,
January 2008 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
3 citations,
January 2008 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” A patient's skin rash did not affect the area where a previous viral rash was healing, suggesting a rare immune response.
June 2022 in “Annals of Indian Academy of Neurology” A woman's shingles infection triggered her first episode of a rare neurological disorder and blood vessel inflammation.
January 2009 in “Journal of musculoskeletal pain” A patient got Herpes zoster after a knee injection, possibly due to the injection's trauma, but more evidence is needed.
 November 2022 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
November 2022 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” The study suggests a link between varicella-zoster virus and segmental vitiligo, with evidence of the virus disrupting skin pigment cells.
 3 citations,
June 2022 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
3 citations,
June 2022 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” During the COVID-19 pandemic, more people were diagnosed with stress-related skin conditions like acne and temporary hair loss.
 3 citations,
January 2022 in “Einstein (São Paulo)”
3 citations,
January 2022 in “Einstein (São Paulo)” The pandemic increased stress-related skin conditions and those affected by behavior changes.
2 citations,
January 2012 in “PubMed” Mycophenolate mofetil is effective for treating severe lupus nephritis in children.
 August 2023 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
August 2023 in “International Journal of Dermatology” COVID-19 and its vaccines can cause various skin issues, with urticaria being the most common.


























