 June 2012 in “Springer eBooks”
June 2012 in “Springer eBooks” Eating disorders can cause various hair problems, and while hair loss in these disorders is linked to metabolic syndrome, treatment focuses on specific medications and lifestyle changes for the syndrome.
 21 citations,
March 2006 in “Seminars in Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery”
21 citations,
March 2006 in “Seminars in Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery” Most hair loss disorders can be accurately diagnosed and treated in an outpatient setting.
February 2024 in “Animals” Hair loss peaks in spring and regrowth in late summer, with pregnant females losing the most hair.
 14 citations,
February 2017 in “Anais brasileiros de dermatologia/Anais Brasileiros de Dermatologia”
14 citations,
February 2017 in “Anais brasileiros de dermatologia/Anais Brasileiros de Dermatologia” Trichotillomania is often misdiagnosed as alopecia areata and can be treated effectively with N-acetylcysteine and psychotropic drugs.
 November 2023 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
November 2023 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Trichoscopy helps tell apart other hair loss conditions from common hair loss.
 November 2022 in “IntechOpen eBooks”
November 2022 in “IntechOpen eBooks” Hair loss can significantly impact a person's mental health, causing issues like anxiety and depression, and stress can trigger hair loss.
6 citations,
December 2016 in “Journal of Obsessive-Compulsive and Related Disorders” Adults with trichotillomania do not have different pain sensitivity to cold pressor pain compared to healthy individuals.
 2 citations,
January 2023 in “Journal of Education, Health and Sport”
2 citations,
January 2023 in “Journal of Education, Health and Sport” Cognitive-behavioral therapy with habit reversal training is the most effective treatment for trichotillomania.
 27 citations,
January 1990 in “Child Psychiatry & Human Development”
27 citations,
January 1990 in “Child Psychiatry & Human Development” The document concludes that supportive home environments and addressing parent-child interactions can effectively treat trichotillomania in children.
2 citations,
March 2022 in “Indian Journal of Psychiatry/Indian journal of psychiatry” The conclusion is that careful management of both psychiatric and skin conditions is crucial for HIV patients, using medication and interdisciplinary approaches.
69 citations,
August 2006 in “Behavior Therapy” Group behavior therapy reduces hair-pulling symptoms more than supportive therapy but has limited long-term effectiveness.
52 citations,
October 1997 in “American Journal of Psychiatry” Trichotillomania is a complex condition involving compulsive hair pulling that causes distress and hair loss.
 12 citations,
December 2020 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
12 citations,
December 2020 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” The COVID-19 pandemic increased symptoms in people with skin picking and hair pulling disorders.
August 2021 in “Oxford University Press eBooks” New treatments for hair-pulling disorder focus on personalized approaches and combining therapies for better results.
January 2015 in “The Encyclopedia of Clinical Psychology” Habit reversal training effectively treats hair-pulling disorder in both adults and children.
24 citations,
June 2020 in “Dermatologic Therapy” New drugs like N-acetylcysteine and dronabinol show promise for treating hair-pulling disorder.
17 citations,
August 2018 in “Clinics in Dermatology” Skin and hair-picking disorders are common and need both skin and mental health treatments.
 2 citations,
June 2016 in “PubMed”
2 citations,
June 2016 in “PubMed” An 11-year-old girl with compulsive hair pulling was successfully treated with therapy and medication.
 May 2017 in “InTech eBooks”
May 2017 in “InTech eBooks” Hair pulling disorder is treated with therapy and medication; hair loss from tension can be reversed if caught early.
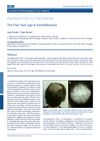 13 citations,
June 2012 in “Journal of Dermatological Case Reports”
13 citations,
June 2012 in “Journal of Dermatological Case Reports” An 8-year-old boy with hair-pulling disorder had a bald patch that was confirmed not to be a fungal infection and was treated with therapy.
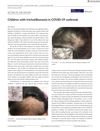 5 citations,
May 2021 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology”
5 citations,
May 2021 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology” More children are showing signs of hair-pulling disorders during the COVID-19 pandemic due to stress and lack of social interaction.
 6 citations,
May 1993 in “Archives of Disease in Childhood”
6 citations,
May 1993 in “Archives of Disease in Childhood” Children's hair loss can be caused by many factors, including autoimmune diseases, emotional stress, genetics, and infections, with treatment and prognosis varying.
 November 2017 in “Pediatrics in Review”
November 2017 in “Pediatrics in Review” A 4-year-old girl with hair loss was diagnosed with early-onset trichotillomania and improved with behavioral interventions.
 15 citations,
September 2015 in “Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft”
15 citations,
September 2015 in “Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft” Skin doctors should recognize and treat conditions like hair-pulling and skin-picking early, often using therapy and medication, to help 50-70% of patients.
 5 citations,
March 2001 in “Journal of biomechanics”
5 citations,
March 2001 in “Journal of biomechanics” Growing hairs are easier to pull out than resting hairs due to different anchorage strengths.
 1 citations,
December 2014 in “Klinik Psikofarmakoloji Bülteni-Bulletin of Clinical Psychopharmacology”
1 citations,
December 2014 in “Klinik Psikofarmakoloji Bülteni-Bulletin of Clinical Psychopharmacology” Adding aripiprazole to the treatment improved hair-pulling symptoms in a teenager.
May 2015 in “UC Merced Undergraduate Research Journal” Behavioral therapies are more effective than drugs for treating trichotillomania.
119 citations,
February 2009 in “Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews” Trichotillomania involves hair pulling and can be treated with therapy and medication.
 4 citations,
October 2018
4 citations,
October 2018 Hair loss in children is often caused by scalp infections, immune disorders, hair pulling, stress, and requires careful treatment due to emotional effects.
 83 citations,
January 2001 in “American journal of clinical dermatology”
83 citations,
January 2001 in “American journal of clinical dermatology” Clomipramine may significantly reduce hair-pulling in Trichotillomania, but more research is needed on treatments and early onset cases.


















