31 citations,
May 1960 in “A M A Journal of Diseases of Children” Parathyroid adenoma can cause hyperparathyroidism and hair loss in children.
 30 citations,
April 2007 in “Dermatologic Clinics”
30 citations,
April 2007 in “Dermatologic Clinics” The document concludes that new treatments are needed to better manage acne and reduce side effects related to current therapies.
12 citations,
April 2013 in “Clinical & experimental ophthalmology” Demodex blepharitis can be mistaken for eyelid cancer, so careful diagnosis is crucial.
 3 citations,
December 2020
3 citations,
December 2020 The interdigital gland in crossbred sheep is similar to skin and has specialized structures for secretion.
3 citations,
January 2017 in “Gynecological endocrinology” A postmenopausal woman's excess male hormone symptoms were caused by a rare adrenal gland tissue in her ovary.
 2 citations,
May 2023 in “bioRxiv (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory)”
2 citations,
May 2023 in “bioRxiv (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory)” Sebaceous glands can heal and regenerate after injury using their own stem cells and help from hair follicle cells.
2 citations,
November 2022 in “Veterinary sciences” The interdigital gland of Vembur sheep shows sex-based differences in size and chemical makeup, possibly affecting communication and disease protection.
 2 citations,
January 2015 in “Nihon Rinshō Men'eki Gakkai kaishi”
2 citations,
January 2015 in “Nihon Rinshō Men'eki Gakkai kaishi” Scientists developed a method to regenerate salivary glands using stem cells.
 1 citations,
January 2019 in “Medical principles and practice”
1 citations,
January 2019 in “Medical principles and practice” A boy's hair loss improved after tumor removal and vitamin D treatment, but hair loss returned despite normal vitamin D and no tumor regrowth.
 April 2023 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
April 2023 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” MPZL3 protein helps control the size of oil glands and the growth of oil-producing cells in both mice and humans.
 May 2008 in “The International Conference on Mathematics and Engineering Physics”
May 2008 in “The International Conference on Mathematics and Engineering Physics” Nanoparticles can increase light sensitivity in oil-producing skin glands.
50 citations,
November 2015 in “Journal of pharmacological sciences” α-mangostin nanoparticles improved acne with minimal irritation.
 48 citations,
January 2000 in “Hormone Research in Paediatrics”
48 citations,
January 2000 in “Hormone Research in Paediatrics” Cytokines and neuropeptides are key in controlling androgen levels, affecting skin and hair conditions.
19 citations,
March 2021 in “Experimental dermatology” Stem cells are key for the growth, upkeep, and repair of sebaceous glands and for understanding skin disorders.
 13 citations,
December 2020 in “Dermatologic Therapy”
13 citations,
December 2020 in “Dermatologic Therapy” Sebaceous glands in our skin, developing during pregnancy and active in puberty, produce sebum for skin lubrication, temperature control, and fighting germs, also help in hormone regulation, and their dysfunction can cause conditions like acne and hair loss.
 5 citations,
February 2018 in “Experimental Dermatology”
5 citations,
February 2018 in “Experimental Dermatology” Scientists developed a way to isolate sweat glands from the scalp during hair transplants, keeping them alive for 6 days for research and cosmetic uses.
4 citations,
July 2014 in “The Journal of Dermatology” Plaque-type herpetic folliculitis affects eccrine glands.
 April 2016 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
April 2016 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” The Engrailed-1 gene plays a key role in the development of sweat glands in mice.
 146 citations,
January 2004 in “Hormones”
146 citations,
January 2004 in “Hormones” Human skin acts like a hormone-producing organ, making and managing various hormones important for skin and hair health.
 18 citations,
April 2014 in “Stem cells”
18 citations,
April 2014 in “Stem cells” The study found stem cells in minor salivary glands that can differentiate and are involved in tumor formation when exposed to tobacco.
 8 citations,
February 2010 in “Journal of Dermatology”
8 citations,
February 2010 in “Journal of Dermatology” A topical treatment safely and effectively reduced acne by causing targeted cell death in sebaceous glands without side effects.
4 citations,
March 2016 in “Small ruminant research” Vicuña wool's quality is due to a high density of fine secondary hair follicles, and their skin glands may be used for communication.
 1 citations,
October 2022 in “International journal of endocrinology”
1 citations,
October 2022 in “International journal of endocrinology” Dihydrotestosterone changes some hormone-related gene expressions in rat pituitary glands but doesn't affect the estrous cycle.
 15 citations,
May 2013 in “American Journal of Medical Genetics - Part A”
15 citations,
May 2013 in “American Journal of Medical Genetics - Part A” People with X-linked hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia have no sweat ducts and less, thinner hair.
 April 2018 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
April 2018 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” Researchers found a new way to isolate sweat glands from the scalp for study and culture.
 April 2018 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
April 2018 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” Removing Lrig1-positive stem cells in mice causes temporary loss of sebaceous glands.
 September 2017 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
September 2017 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” The study found that sweat glands normally suppress immune responses, but this is disrupted in certain skin diseases, possibly contributing to their development.
 30 citations,
April 2018 in “Experimental Dermatology”
30 citations,
April 2018 in “Experimental Dermatology” The article concludes that developing in vitro models for human hair structures is important for research and reducing animal testing, but there are challenges like obtaining suitable samples and the models' limitations.
 15 citations,
May 1989 in “PubMed”
15 citations,
May 1989 in “PubMed” Psoriasis on the scalp causes smaller oil glands and thinner hair but doesn't lead to hair loss.
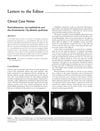 9 citations,
February 2004 in “Clinical and Experimental Ophthalmology”
9 citations,
February 2004 in “Clinical and Experimental Ophthalmology” The document discusses various eye conditions and their treatments, including a rare eye cancer in a baby, vision loss from a cancer drug, cataracts from a baldness treatment, a rare skin disorder, and a specific type of eye disease diagnosed with a special imaging technique.





















