12 citations,
January 2014 in “Dermatology online journal” White hair regrowth in alopecia areata may be more common than thought.
 January 2024 in “The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine ”
January 2024 in “The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine ” Hair loss may indicate a higher risk of heart disease and other health issues related to metabolism.
 August 2014 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
August 2014 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Obesity is linked to more severe hair loss in adult men and to excess hair growth, but its effects on hair conditions are complex and need more research.
 179 citations,
March 2005 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
179 citations,
March 2005 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Oral antiandrogens effectively treat female hair loss, with better results in higher hair loss grades.
 115 citations,
September 2000 in “The Lancet”
115 citations,
September 2000 in “The Lancet” Early hair loss may indicate risk of insulin resistance.
 35 citations,
January 2014 in “BioMed Research International”
35 citations,
January 2014 in “BioMed Research International” Female pattern hair loss involves hormonal factors, genetics, and may be linked to low ferritin levels.
 28 citations,
August 2014 in “Journal of Assisted Reproduction and Genetics”
28 citations,
August 2014 in “Journal of Assisted Reproduction and Genetics” The VEGF +405G allele may increase the risk of PCOS in South Indian women.
 25 citations,
September 2010 in “Journal of Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery”
25 citations,
September 2010 in “Journal of Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery” The study found that Central Centrifugal Cicatricial Alopecia mainly affects middle-aged African descent women, is linked to certain hair care practices and genetics, and often goes undiagnosed for years.
 18 citations,
January 2020 in “Acta dermato-venereologica”
18 citations,
January 2020 in “Acta dermato-venereologica” Over 67 genes linked to ichthyosis help improve diagnosis and treatment.
 15 citations,
April 2003 in “Journal of dermatology”
15 citations,
April 2003 in “Journal of dermatology” Alopecia areata causes hair loss due to an immune attack on hair follicles, influenced by genetics and environment.
14 citations,
March 2017 in “Genes and immunity” Certain microRNAs may help treat alopecia areata by targeting immune pathways.
8 citations,
December 2013 in “The journal of investigative dermatology. Symposium proceedings/The Journal of investigative dermatology symposium proceedings” Mouse models help understand alopecia areata and find treatments.
7 citations,
August 2017 in “Genetic testing and molecular biomarkers” A new mutation in the FLCN gene linked to Birt-Hogg-Dube syndrome was found, suggesting people with certain lung collapse should be tested for this mutation and screened for kidney and colon cancer.
 7 citations,
March 2011 in “Hormone and Metabolic Research”
7 citations,
March 2011 in “Hormone and Metabolic Research” Certain gene variations might help protect against insulin resistance and glucose intolerance in people with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome.
 5 citations,
November 2008 in “Advances in Dermatology”
5 citations,
November 2008 in “Advances in Dermatology” The review highlights the importance of stem cells in hair health and suggests new treatment strategies for hair loss conditions.
 3 citations,
June 2023 in “Frontiers in medicine”
3 citations,
June 2023 in “Frontiers in medicine” Oxidative stress may contribute to hair loss in alopecia areata and antioxidants could potentially help as a treatment.
 3 citations,
December 2014 in “Journal of Clinical Oncology”
3 citations,
December 2014 in “Journal of Clinical Oncology” Men with a certain baldness pattern at age 40-50 may have a higher risk of aggressive prostate cancer.
 1 citations,
April 2016 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
1 citations,
April 2016 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” UV photography can help identify people at higher risk for skin cancer, and male pattern baldness at age 45 is linked to a higher risk of certain skin cancers.

Early-onset baldness is linked to genetics, lifestyle, and can indicate higher risk for heart and metabolic diseases, and affects mental health.
 January 2009 in “Egyptian Journal of Medical Human Genetics”
January 2009 in “Egyptian Journal of Medical Human Genetics” The study suggests that a specific gene variation and higher gene activity are linked to increased baldness in Egyptian men.
234 citations,
November 2009 in “American journal of human genetics” Common variants in the Trichohyalin gene are linked to straight hair in Europeans.
 27 citations,
December 2015 in “Mayo Clinic Proceedings”
27 citations,
December 2015 in “Mayo Clinic Proceedings” The document concludes that lifestyle changes and medical treatments can significantly reduce symptoms of Hidradenitis Suppurativa, a chronic skin condition.
6 citations,
December 2022 in “Journal of Infection” This study examined the association between the ACE1 rs1799752 polymorphism and long-COVID symptoms in 288 previously hospitalized COVID-19 survivors, finding no significant differences in symptoms based on genotypes. The results align with previous research on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 polymorphisms, suggesting that genetic variability might explain the lack of association. The study highlights that COVID-19 severity does not necessarily correlate with long-COVID development and calls for larger, population-based studies to further investigate these findings.
 April 2021 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
April 2021 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” The document corrects an author's affiliation in previous articles about COVID-19 and its links to hair loss and hormones.
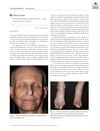 March 2019 in “Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft”
March 2019 in “Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft” Rothmund-Thomson syndrome type 2 can cause chronic, poorly healing wounds.
 January 2018 in “Springer eBooks”
January 2018 in “Springer eBooks” Hidradenitis Suppurativa is likely an autoinflammatory disease, and better understanding its causes could improve treatments.
 144 citations,
March 2013 in “Circulation Research”
144 citations,
March 2013 in “Circulation Research” K_ATP channel gene mutations are linked to heart diseases, but more research is needed to understand the connection and treatment potential.
 40 citations,
June 2013 in “Scientific Reports”
40 citations,
June 2013 in “Scientific Reports” A gene variant in KRT71 causes the curly fur in Selkirk Rex cats.
18 citations,
January 2013 in “PLoS ONE” HLA-DRB5 and other genes may be linked to alopecia universalis.
 9 citations,
September 2015 in “Reproductive Biomedicine Online”
9 citations,
September 2015 in “Reproductive Biomedicine Online” Longer GGN repeats in the androgen receptor gene are linked to polycystic ovary syndrome.






















