 60 citations,
August 2008 in “Human molecular genetics online/Human molecular genetics”
60 citations,
August 2008 in “Human molecular genetics online/Human molecular genetics” A position effect on the TRPS1 gene causes excessive hair growth in humans and mice.
[object Object]  58 citations,
October 2001 in “Dermatologic Clinics”
58 citations,
October 2001 in “Dermatologic Clinics” Hair loss can indicate underlying systemic diseases and addressing these can sometimes reverse the hair loss.
 26 citations,
December 2011 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
26 citations,
December 2011 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” New gene identification techniques have improved the understanding and classification of inherited hair disorders.
 20 citations,
July 2009 in “Journal of Pediatric and Adolescent Gynecology”
20 citations,
July 2009 in “Journal of Pediatric and Adolescent Gynecology” Quick treatment of hair disorders in teenage girls is important because of the emotional effects.
 17 citations,
November 2012 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
17 citations,
November 2012 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” The document concludes that over 500 genes are linked to hair disorders and this knowledge is important for creating new treatments.
 9 citations,
December 2020 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
9 citations,
December 2020 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Low-dose oral minoxidil increases hair thickness and length in children with a hair disorder called Loose Anagen Hair Syndrome.
 7 citations,
July 2011 in “Survey of Ophthalmology”
7 citations,
July 2011 in “Survey of Ophthalmology” The document concludes that periocular hair disorders have various causes and treatments, and proper evaluation by specialists is important for management and prognosis.
 2 citations,
December 2004 in “Medicine”
2 citations,
December 2004 in “Medicine” Different hair and scalp disorders cause hair loss or excess hair growth, with various treatments available depending on the specific condition.
 November 2019 in “Harper's Textbook of Pediatric Dermatology”
November 2019 in “Harper's Textbook of Pediatric Dermatology” Understanding normal hair growth and loss in children is key to diagnosing and treating hair disorders.

Different scalp and hair disorders are more common in certain ethnic groups, with the most common being androgenetic alopecia, which is treated with medications like minoxidil and finasteride.
 24 citations,
May 2012 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
24 citations,
May 2012 in “International Journal of Dermatology” The document concludes that eyelash trichomegaly, which is the abnormal growth of eyelashes, can be present from birth, caused by diseases, or result from certain medications.
 February 2024 in “Cosmoderma”
February 2024 in “Cosmoderma” Low-dose oral minoxidil can help treat male and female pattern hair loss, especially in those who can't use topical treatments or have heart health issues.
 January 2022 in “Function”
January 2022 in “Function” Studying rare genetic disorders can help us understand and treat common diseases better.
 July 2021 in “Research, Society and Development”
July 2021 in “Research, Society and Development” Minoxidil is effective and safe for hair growth in Androgenetic Alopecia, with manageable side effects.
24 citations,
July 2005 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” A woman's eyelashes grew thicker and longer after taking topiramate, but returned to normal when she stopped the medication.
 138 citations,
August 1985 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
138 citations,
August 1985 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Minoxidil promotes hair growth in male pattern baldness.
 117 citations,
August 2019 in “Drug Design Development and Therapy”
117 citations,
August 2019 in “Drug Design Development and Therapy” Minoxidil effectively treats hair loss, but use cautiously and monitor side effects.
[object Object]  63 citations,
January 1984 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
63 citations,
January 1984 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Minoxidil promotes hair growth by increasing cell division and DNA synthesis.
 19 citations,
May 2020 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
19 citations,
May 2020 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Low-dose oral minoxidil improves hair growth in male hair loss.
 14 citations,
August 2013 in “Facial Plastic Surgery Clinics of North America”
14 citations,
August 2013 in “Facial Plastic Surgery Clinics of North America” Some nonsurgical hair loss treatments are effective, especially if started early.
 10 citations,
August 2012 in “Current Problems in Pediatric and Adolescent Health Care”
10 citations,
August 2012 in “Current Problems in Pediatric and Adolescent Health Care” Hair changes can indicate systemic diseases or medication effects.
 4 citations,
November 2009 in “Medical Clinics of North America”
4 citations,
November 2009 in “Medical Clinics of North America” Stress, nutritional issues, and chronic diseases can cause hair loss, and nail changes may signal internal diseases; treatment focuses on the underlying cause.
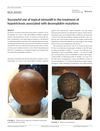 1 citations,
August 2019 in “Pediatric dermatology”
1 citations,
August 2019 in “Pediatric dermatology” Topical minoxidil helped an 8-year-old boy with a genetic hair disorder grow hair.
 November 2019 in “Harper's Textbook of Pediatric Dermatology”
November 2019 in “Harper's Textbook of Pediatric Dermatology” The document is a detailed medical reference on skin and genetic disorders.
 43 citations,
December 2013 in “Seminars in Cell & Developmental Biology”
43 citations,
December 2013 in “Seminars in Cell & Developmental Biology” Genetic mutations can cause hair growth disorders by affecting key genes and signaling pathways.
 32 citations,
January 2019 in “American Journal of Clinical Dermatology”
32 citations,
January 2019 in “American Journal of Clinical Dermatology” Minoxidil helps treat eyebrow thinning, monilethrix, early hair loss, and shortens chemo-related hair loss.
 15 citations,
May 2017 in “Journal of Dermatological Treatment”
15 citations,
May 2017 in “Journal of Dermatological Treatment” Latanoprost works better for hair growth, and combining it with betamethasone valerate is most effective.
 15 citations,
January 1971 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
15 citations,
January 1971 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Hair can indicate early signs of metabolic disorders, with issues like protein deficiency stopping hair growth.
 12 citations,
July 2020 in “Dermatologic Therapy”
12 citations,
July 2020 in “Dermatologic Therapy” Minoxidil, applied on the skin or taken orally, can improve hair growth in kids, but more research is needed due to possible side effects.
 2 citations,
April 2017 in “Asian Journal of Psychiatry”
2 citations,
April 2017 in “Asian Journal of Psychiatry” Valproic acid can cause hair loss when taken orally but may promote hair growth when applied topically.





























