 10 citations,
June 2000 in “Primary Care”
10 citations,
June 2000 in “Primary Care” The document explains different hair loss types and treatments, emphasizing diagnosis through examination and tests, and specific treatments for each condition.
 329 citations,
January 1997 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
329 citations,
January 1997 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Frontal fibrosing alopecia is a hair loss condition in postmenopausal women, similar to lichen planopilaris, with ineffective treatments.
 89 citations,
February 2002 in “Australasian journal of dermatology”
89 citations,
February 2002 in “Australasian journal of dermatology” A premenopausal woman had hair loss and skin issues, treated with topical steroids.
January 2022 in “Aesthetic surgery journal” Extracellular vesicles may effectively treat hair loss with minimal side effects.
 13 citations,
November 1973 in “Archives of Dermatology”
13 citations,
November 1973 in “Archives of Dermatology” Hair loss may be an early sign of serious illnesses like Hodgkin disease.
 August 2023 in “International Ayurvedic medical journal”
August 2023 in “International Ayurvedic medical journal” Ayurvedic treatment successfully regrew hair in a 7-year-old girl with alopecia areata.
 3 citations,
May 2018 in “Journal of nutritional health & food science”
3 citations,
May 2018 in “Journal of nutritional health & food science” Nutritional supplements can help manage hair loss and promote hair growth by strengthening hair roots and countering harmful effects of pollution, smoking, and deficiencies in vitamins and minerals.
 51 citations,
September 2015 in “Medical Clinics of North America”
51 citations,
September 2015 in “Medical Clinics of North America” The conclusion is that acne, alopecia, and hyperhidrosis are common skin issues with various treatments available, and accurate diagnosis is key for effective management.
 2 citations,
January 2012 in “Hair therapy & transplantation”
2 citations,
January 2012 in “Hair therapy & transplantation” Low serum ferritin levels are not closely linked to telogen effluvium in women.

Researchers found a genetic link for hereditary hair loss but need more analysis to identify the exact gene.
 17 citations,
October 2013 in “F1000Research”
17 citations,
October 2013 in “F1000Research” A 2-year-old boy grew excessive hair after using minoxidil for hair loss, but it improved when the treatment stopped.
 9 citations,
September 2006 in “Clinical Pediatrics”
9 citations,
September 2006 in “Clinical Pediatrics” Pediatricians should treat some hair loss types in children and refer others to a dermatologist.
 September 2003 in “Current Paediatrics”
September 2003 in “Current Paediatrics” The document concludes that accurate diagnosis and understanding the type of hair disorder are crucial for treating hair loss in children.
 12 citations,
August 2000 in “Fertility and Sterility”
12 citations,
August 2000 in “Fertility and Sterility” Topical finasteride doesn't reduce DHT levels, hinting at an endocrine role in hair loss.
 127 citations,
December 2005 in “Experimental Dermatology”
127 citations,
December 2005 in “Experimental Dermatology” Stress can stop hair growth in mice, and treatments can reverse this effect.
 1 citations,
October 2018 in “InTech eBooks”
1 citations,
October 2018 in “InTech eBooks” The document concludes that treatments for cicatricial alopecia are not well-supported by evidence, but hair transplantation shows more predictable and satisfactory results.
 194 citations,
March 2003 in “American Journal of Pathology”
194 citations,
March 2003 in “American Journal of Pathology” Stress stops hair growth in mice by causing early hair growth phase end and harmful inflammation through a specific nerve-related pathway.

Different scalp and hair disorders are more common in certain ethnic groups, with the most common being androgenetic alopecia, which is treated with medications like minoxidil and finasteride.
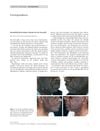 6 citations,
May 2012 in “Clinical and experimental dermatology”
6 citations,
May 2012 in “Clinical and experimental dermatology” Oral minoxidil can cause inflamed, ingrown hairs in the beard area.
 1 citations,
January 2014 in “Elsevier eBooks”
1 citations,
January 2014 in “Elsevier eBooks” Melanocytes produce melanin; their defects cause vitiligo and hair graying, with treatments available for vitiligo.
 11 citations,
May 2003 in “Obstetrics and gynecology (New York. 1953. Online)/Obstetrics and gynecology”
11 citations,
May 2003 in “Obstetrics and gynecology (New York. 1953. Online)/Obstetrics and gynecology” Hirsutism in women often indicates a hormonal imbalance and can be managed with a combination of hormonal treatments and hair removal methods.
 195 citations,
May 2003 in “Obstetrics and gynecology (New York. 1953. Online)/Obstetrics and gynecology”
195 citations,
May 2003 in “Obstetrics and gynecology (New York. 1953. Online)/Obstetrics and gynecology” Most women with excess hair growth have an underlying hormonal issue, often treated with medication and hair removal methods.
 51 citations,
February 2006 in “Clinics in Dermatology”
51 citations,
February 2006 in “Clinics in Dermatology” Pregnant women often experience skin and hair changes, with over half getting stretch marks and pigment changes, and should be cautious with cosmetic procedures due to potential risks.
 1 citations,
January 2006
1 citations,
January 2006 Hirsutism is mainly caused by high androgen levels or sensitivity, with PCOS being the most common cause.
6 citations,
May 2021 in “Aesthetic Surgery Journal” Higher cell number PRP improves hair density and diameter more than lower cell number PRP.
 4 citations,
December 2013 in “The Journal of Dermatology”
4 citations,
December 2013 in “The Journal of Dermatology” A new mutation in the K6b gene caused a girl's late-appearing nail condition.
 November 2024 in “Frontiers in Medicine”
November 2024 in “Frontiers in Medicine” Cirrhosis affects quality of life with various symptoms, requiring a holistic, multidisciplinary approach for management.
 12 citations,
July 2008 in “Facial Plastic Surgery Clinics of North America”
12 citations,
July 2008 in “Facial Plastic Surgery Clinics of North America” The document concludes that careful planning and consideration of male brow anatomy are essential for successful facial rejuvenation with cosmetic surgery.
 May 2023 in “Journal of complementary medicine & alternative healthcare”
May 2023 in “Journal of complementary medicine & alternative healthcare” Ayurveda's descriptions of genetic disorders align with modern genetic understanding.
Diphenyl cresyl phosphate has low toxicity but can harm the liver, kidneys, adrenal glands, and testicles at high doses.



























