 52 citations,
February 2006 in “Archives of Dermatology”
52 citations,
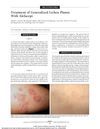
February 2006 in “Archives of Dermatology” Alefacept may effectively treat severe lichen planus, with patients showing significant improvement and no side effects.
 1 citations,
July 2020 in “bioRxiv (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory)”
1 citations,
July 2020 in “bioRxiv (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory)” Removing centrosomes from skin cells leads to thinner skin and stops hair growth, but does not greatly affect skin cell differentiation.
 117 citations,
August 2019 in “Drug Design Development and Therapy”
117 citations,
August 2019 in “Drug Design Development and Therapy” Minoxidil effectively treats hair loss, but use cautiously and monitor side effects.
 January 2014 in “Springer eBooks”
January 2014 in “Springer eBooks” Inflammasome proteins can indicate the severity and treatment response of various diseases and injuries.
 89 citations,
October 1996 in “Dermatologic Clinics”
89 citations,
October 1996 in “Dermatologic Clinics” Alopecia areata is likely caused by a combination of genetic factors and immune system dysfunction, and may represent different diseases with various causes.
 March 2024 in “Dermatology and therapy (Internet)”
March 2024 in “Dermatology and therapy (Internet)” Genetic factors could lead to personalized treatments for hair loss.
 37 citations,
January 2016 in “Drug design, development and therapy”
37 citations,
January 2016 in “Drug design, development and therapy” Tofacitinib citrate is effective for moderate-to-severe chronic plaque psoriasis but has safety concerns at higher doses.
April 2024 in “Molecules/Molecules online/Molecules annual” Paris polyphylla saponins may effectively treat acne due to their antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties.
 April 2018 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
April 2018 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Minoxidil didn't significantly increase hair growth in minipigs.
 3 citations,
March 2023 in “JAAD case reports”
3 citations,
March 2023 in “JAAD case reports” Upadacitinib cleared scalp alopecia areata in three patients and also improved atopic dermatitis with minimal side effects.
 February 2024 in “Sohag Medical Journal”
February 2024 in “Sohag Medical Journal” Various local treatments for alopecia areata show promise, but individualized plans and more research are needed.
 3 citations,
March 2021 in “International journal of pharmaceutical sciences review and research”
3 citations,
March 2021 in “International journal of pharmaceutical sciences review and research” Licorice has many health benefits but more research is needed to fully understand them.
 24 citations,
November 2013 in “Trends in pharmacological sciences”
24 citations,
November 2013 in “Trends in pharmacological sciences” Increasing ABC transporters in hair follicles may prevent chemotherapy-induced hair loss.
 57 citations,
February 2014 in “Experimental Dermatology”
57 citations,
February 2014 in “Experimental Dermatology” Prostaglandin D₂ might be targeted for new male pattern baldness treatments.
 25 citations,
March 2012 in “Journal of oncology pharmacy practice”
25 citations,
March 2012 in “Journal of oncology pharmacy practice” An 81-year-old man's white hair began to regain its original color while he was treated with lenalidomide, suggesting that graying hair might be reversible.
 34 citations,
November 2010 in “Development”
34 citations,
November 2010 in “Development” Activating Notch in adult skin causes T cells and neural crest cells to gather, leading to skin issues.
 July 2023 in “Stem Cells Translational Medicine”
July 2023 in “Stem Cells Translational Medicine” Mesenchymal Stem/Stromal Cells (MSCs) help in wound healing and tissue regeneration, but can also contribute to tumor growth. They show promise in treating chronic wounds and certain burns, but their full healing mechanisms and potential challenges need further exploration.
 1 citations,
January 2015 in “Springer eBooks”
1 citations,
January 2015 in “Springer eBooks” Chemotherapy can cause skin side effects that affect patients' lives, but they can be managed to avoid interrupting cancer treatment.
 May 1991 in “Current problems in dermatology”
May 1991 in “Current problems in dermatology” Skin issues can indicate immune system problems.
14 citations,
January 2019 in “PubMed” Vitamin D might be involved in the development of alopecia areata and could help in its treatment.

Type II spiral ganglion neurites avoid high concentrations of laminin and fibronectin.
81 citations,
January 2000 in “American journal of clinical dermatology” Various treatments can improve post-acne scars, but results vary.
92 citations,
September 2013 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” BMAL1 and Period1 genes can influence human hair growth.
 7 citations,
March 2020 in “PloS one”
7 citations,
March 2020 in “PloS one” α-parvin is necessary for skin and hair growth and for the correct orientation of skin cells.

Recognizing unusual brain and skin symptoms is crucial for diagnosing lupus early.
 86 citations,
July 1990 in “British Journal of Pharmacology”
86 citations,
July 1990 in “British Journal of Pharmacology” Diazoxide, minoxidil sulphate, and cromakalim relax rat blood vessels by opening K+ channels, with some differences in their actions.
 68 citations,
November 2012 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
68 citations,
November 2012 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Prostaglandin D2 blocks new hair growth after skin injury through the Gpr44 receptor.
 January 2023 in “Biomaterials Science”
January 2023 in “Biomaterials Science” Certain genes are more active during wound healing in axolotl and Acomys, which could help develop materials that improve human wound healing and regeneration.
 4 citations,
October 2021 in “Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine”
4 citations,
October 2021 in “Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine” White blood cells and their traps can slow down the process of new hair growth after a wound.

The research found how certain drugs and polymers form stable complexes, which could help develop new pharmaceutical forms.


























