 4 citations,
July 2012 in “Genesis”
4 citations,
July 2012 in “Genesis” The Megsin-Cre transgene is a new tool for genetic manipulation in the skin and upper digestive tract.
 2 citations,
February 2024 in “Nature cell biology”
2 citations,
February 2024 in “Nature cell biology” Mechanical forces are crucial for shaping cells and forming tissues during development.
 1 citations,
December 2021 in “Kathmandu University medical journal”
1 citations,
December 2021 in “Kathmandu University medical journal” Adult earlobe can have a benign cyst that is usually removed by surgery.
 1 citations,
February 2013 in “InTech eBooks”
1 citations,
February 2013 in “InTech eBooks” Genetic mutations cause various hair diseases, and whole genome sequencing may reveal more about these conditions.
 1 citations,
July 2012 in “Nasza Dermatologia Online”
1 citations,
July 2012 in “Nasza Dermatologia Online” CCCA may be caused by both hair traction and an immune response.
 January 2018 in “Elsevier eBooks”
January 2018 in “Elsevier eBooks” The document explains how male reproductive hormones work and affect the body.
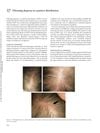 April 2012 in “Informa Healthcare eBooks”
April 2012 in “Informa Healthcare eBooks” Fibrosing alopecia in a pattern distribution is a unique hair loss condition with inflammation and scarring, resembling but distinct from common balding.
 1039 citations,
February 2009 in “Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology”
1039 citations,
February 2009 in “Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology” Skin stem cells are crucial for maintaining and repairing the skin and hair, using a complex mix of signals to do so.
 508 citations,
February 2007 in “Cell”
508 citations,
February 2007 in “Cell” Epithelial stem cells are crucial for tissue renewal and repair, and understanding them could improve treatments for damage and cancer.
 375 citations,
February 2006 in “Journal of Cell Science”
375 citations,
February 2006 in “Journal of Cell Science” The document concludes that the hair cycle is a complex process involving growth, regression, and rest phases, regulated by various molecular signals.
 314 citations,
April 2010 in “Developmental Cell”
314 citations,
April 2010 in “Developmental Cell” β-catenin in the dermal papilla is crucial for normal hair growth and repair.
 299 citations,
January 2018 in “Journal of Clinical Investigation”
299 citations,
January 2018 in “Journal of Clinical Investigation” Different types of fibroblasts play various roles in diseases and healing, and more research on them could improve treatments.
 295 citations,
June 2009 in “Science”
295 citations,
June 2009 in “Science” Stromal stem cells may help heal wounds by becoming structural cells or affecting the immune system, but more research is needed to understand how.
 254 citations,
January 2012 in “Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology”
254 citations,
January 2012 in “Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology” Stem cell offspring help control their parent stem cells, affecting tissue health, healing, and cancer.
 236 citations,
July 2001 in “Trends in Molecular Medicine”
236 citations,
July 2001 in “Trends in Molecular Medicine” Future hair loss treatments should aim to extend hair growth, reactivate resting follicles, reverse shrinkage, and possibly create new follicles, with gene therapy showing promise.
 211 citations,
November 2018 in “Nature Cell Biology”
211 citations,
November 2018 in “Nature Cell Biology” Stem cells help heal skin wounds by moving and changing roles, working with other cells, and needing more research on their activation and behavior.
 129 citations,
May 2015 in “Cell Stem Cell”
129 citations,
May 2015 in “Cell Stem Cell” Different types of stem cells exist within individual skin layers, and they can adapt to damage, transplantation, or tumor growth. These cells are regulated by their environment and genetic factors. Tumor growth is driven by expanding, genetically altered cells, not long-lived mutant stem cells. There's evidence of cancer stem cells in skin tumors. Other cells, bacteria, and genetic factors help maintain balance and contribute to disease progression. A method for growing mini organs from single cells has been developed.
 126 citations,
January 2009 in “International Journal of Trichology”
126 citations,
January 2009 in “International Journal of Trichology” Oxidative stress contributes to hair graying and loss as we age.
 118 citations,
January 2016 in “Current Topics in Developmental Biology”
118 citations,
January 2016 in “Current Topics in Developmental Biology” The document concludes that while significant progress has been made in understanding skin biology and stem cells, more research is needed to fully understand their interactions with their environment.
112 citations,
January 2013 in “Experimental dermatology” Faulty Notch signalling may cause hair follicle changes and inflammation in hidradenitis suppurativa.
 109 citations,
September 2011 in “Human molecular genetics online/Human molecular genetics”
109 citations,
September 2011 in “Human molecular genetics online/Human molecular genetics” New treatments targeting specific genes show promise for treating keratin disorders.
 109 citations,
November 2005 in “The journal of investigative dermatology. Symposium proceedings/The Journal of investigative dermatology symposium proceedings”
109 citations,
November 2005 in “The journal of investigative dermatology. Symposium proceedings/The Journal of investigative dermatology symposium proceedings” Targeting hair follicles can improve skin treatments and reduce side effects.
 103 citations,
January 2006 in “Journal of Cell Science”
103 citations,
January 2006 in “Journal of Cell Science” The document concludes that the hair cycle is a complex process involving growth, regression, and rest phases, regulated by various molecular signals.
 96 citations,
July 2014 in “Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Medicine”
96 citations,
July 2014 in “Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Medicine” The document concludes that adult mammalian skin contains multiple stem cell populations with specific markers, important for understanding skin regeneration and related conditions.
 90 citations,
June 2006 in “The American Journal of Dermatopathology”
90 citations,
June 2006 in “The American Journal of Dermatopathology” The document concludes that accurate diagnosis of different types of hair loss requires careful examination of hair and scalp tissue, considering both clinical and microscopic features.
 89 citations,
September 2010 in “Annual Review of Genomics and Human Genetics”
89 citations,
September 2010 in “Annual Review of Genomics and Human Genetics” The document concludes that understanding the genes and pathways involved in hair growth is crucial for developing treatments for hair diseases.
 83 citations,
May 2013 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences”
83 citations,
May 2013 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences” Skin development in mammals is controlled by key proteins and signals from underlying cells, involving stem cells for maintenance and repair.
 82 citations,
January 2000 in “Hormone Research in Paediatrics”
82 citations,
January 2000 in “Hormone Research in Paediatrics” DHEA stimulates skin oil glands and could help postmenopausal women, with potential for acne and excessive hair growth treatments.
 78 citations,
August 2002 in “Experimental Dermatology”
78 citations,
August 2002 in “Experimental Dermatology” Researchers developed a quick and easy way to get and grow cells from the base of human hair follicles.
 72 citations,
July 2012 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
72 citations,
July 2012 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Mice lacking a key DNA methylation enzyme in skin cells have a lower chance of activating stem cells necessary for hair growth, leading to progressive hair loss.





























