 November 2023 in “Dermatology and Therapy”
November 2023 in “Dermatology and Therapy” Baricitinib treatment helps regrow eyebrow, eyelash, and scalp hair in severe alopecia areata, improving patients' emotional well-being and quality of life.
 339 citations,
February 2014 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
339 citations,
February 2014 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Most patients with frontal fibrosing alopecia are postmenopausal women, and treatments like finasteride and dutasteride can improve or stabilize the condition.
 66 citations,
June 2021 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
66 citations,
June 2021 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Baricitinib is effective and safe for treating severe alopecia areata.
 34 citations,
February 2018 in “Drug Design Development and Therapy”
34 citations,
February 2018 in “Drug Design Development and Therapy” Bimatoprost is safe and effective for improving eyebrow hair.
 9 citations,
April 2017 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
9 citations,
April 2017 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Different areas of the scalp have varying hair thickness, useful for different types of hair transplant needs.
 7 citations,
May 2013 in “Optometry and vision science”
7 citations,
May 2013 in “Optometry and vision science” Bimatoprost can help regrow eyelashes in people with trichotillomania.
 6 citations,
July 2017 in “Clinics in Plastic Surgery”
6 citations,
July 2017 in “Clinics in Plastic Surgery” The document concludes that individualized reconstruction plans are essential for improving function and appearance after head and neck burns.
 5 citations,
March 2014 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
5 citations,
March 2014 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” The study suggests hormonal factors may play a role in Frontal Fibrosing Alopecia and that treatments like oral antiandrogens and steroids could be beneficial.
 3 citations,
May 2019 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology”
3 citations,
May 2019 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology” Miliacin with polar lipids helps hair growth and improves hair loss in women.

The document concludes that the girl's hairlessness is likely inherited from her parents.
 December 2011 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
December 2011 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” The book is a detailed and useful guide for doctors learning about hair transplantation.
 17 citations,
June 2016 in “Croatian Medical Journal”
17 citations,
June 2016 in “Croatian Medical Journal” Patients with chronic graft-versus-host disease often have skin problems like vitiligo and alopecia areata.
 39 citations,
April 2001 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
39 citations,
April 2001 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Latanoprost, a glaucoma medication, caused excessive eyelid hair growth in many patients.
 166 citations,
April 2012 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
166 citations,
April 2012 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Mostly postmenopausal Caucasian women get Frontal Fibrosing Alopecia, which often includes eyebrow loss and has limited treatment success.
 85 citations,
April 2007 in “Dermatologic Clinics”
85 citations,
April 2007 in “Dermatologic Clinics” Some drugs can cause hair loss, change hair color and shape, or increase hair growth, and treatment may involve stopping the drug or using specific hair growth treatments.
 23 citations,
November 2018 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
23 citations,
November 2018 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” The study concluded that severity of Frontal fibrosing alopecia is not linked to how long someone has it, can start before menopause, and eyebrow loss may be an early sign.
 10 citations,
August 2012 in “Current Problems in Pediatric and Adolescent Health Care”
10 citations,
August 2012 in “Current Problems in Pediatric and Adolescent Health Care” Hair changes can indicate systemic diseases or medication effects.
 May 2017 in “InTech eBooks”
May 2017 in “InTech eBooks” Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE) is a popular hair transplant method with minimal scarring that can transplant many grafts quickly and improve appearance and psychological well-being.
 216 citations,
October 1997 in “American Journal of Ophthalmology”
216 citations,
October 1997 in “American Journal of Ophthalmology” Using the eye pressure medication latanoprost can cause excessive hair growth and darker eyelashes on the treated eye.
 72 citations,
July 2014 in “American journal of clinical dermatology”
72 citations,
July 2014 in “American journal of clinical dermatology” Some treatments, like corticosteroids and sensitizing agents, can help with alopecia areata, but more high-quality research is needed.
 41 citations,
December 2015 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
41 citations,
December 2015 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” The conclusion is that a new biopsy technique and humidity chamber help study skin mites better and suggest mite overpopulation may cause skin diseases.
 22 citations,
June 2002 in “Seminars in cutaneous medicine and surgery”
22 citations,
June 2002 in “Seminars in cutaneous medicine and surgery” Laser hair removal works well for people with dark hair and light skin, but it's less effective for light hair or dark skin; improvements are expected.
 11 citations,
March 2008 in “Experimental Dermatology”
11 citations,
March 2008 in “Experimental Dermatology” A substance called compound-1 could help increase hair growth by maintaining prostaglandin levels in hair follicles.
 5 citations,
September 1986 in “Pediatric Dermatology”
5 citations,
September 1986 in “Pediatric Dermatology” A family showed a new condition with inherited hair loss and skin changes, possibly due to one genetic disorder.
 4 citations,
November 2015 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
4 citations,
November 2015 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Testosterone may worsen hair loss by affecting hair growth signals, while different prostaglandins can either hinder or promote hair growth.
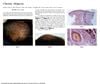 June 1995 in “Archives of Dermatology”
June 1995 in “Archives of Dermatology” A woman's hair loss was due to trichotillomania, which is often misdiagnosed and can require different treatments based on age and underlying conditions.
 180 citations,
November 1991 in “American Journal of Psychiatry”
180 citations,
November 1991 in “American Journal of Psychiatry” Fluoxetine was not effective in treating hair-pulling disorder in the short term.
 75 citations,
January 2009 in “International journal of trichology”
75 citations,
January 2009 in “International journal of trichology” Hair grays due to oxidative stress and fewer functioning melanocytes.
 67 citations,
December 2008 in “Developmental Biology”
67 citations,
December 2008 in “Developmental Biology” Msx2 and Foxn1 are both crucial for hair growth and health.
 44 citations,
February 2015 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
44 citations,
February 2015 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Combining diphenylcyclopropenone with anthralin is more effective for hair regrowth in alopecia areata than using diphenylcyclopropenone alone, but may cause more side effects.






























