 January 2019 in “Elsevier eBooks”
January 2019 in “Elsevier eBooks” Early detection and skin biopsies are crucial for treating skin cancer and diagnosing various skin conditions.
[object Object]  June 2017 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
June 2017 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Teriflunomide often causes mild to moderate hair thinning and loss in MS patients, which usually improves with or without treatment.
 21 citations,
July 2006 in “Veterinary dermatology”
21 citations,
July 2006 in “Veterinary dermatology” CD34 marks potential stem cells in dog hair follicles.
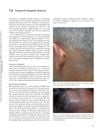 April 2012 in “Informa Healthcare eBooks”
April 2012 in “Informa Healthcare eBooks” Temporal triangular alopecia is a lifelong condition with hairless patches on the side of the head that may be present from birth.
 27 citations,
December 2015 in “Mayo Clinic Proceedings”
27 citations,
December 2015 in “Mayo Clinic Proceedings” The document concludes that lifestyle changes and medical treatments can significantly reduce symptoms of Hidradenitis Suppurativa, a chronic skin condition.
 26 citations,
January 2016 in “Annals of Dermatology”
26 citations,
January 2016 in “Annals of Dermatology” Ecklonia cava polyphenols help increase human hair growth and reduce hair loss.
 1 citations,
September 2023 in “Dermatology and therapy”
1 citations,
September 2023 in “Dermatology and therapy” More research is needed to find the best treatment for dissecting cellulitis of the scalp.
 September 2023 in “Clinical, cosmetic and investigational dermatology”
September 2023 in “Clinical, cosmetic and investigational dermatology” A new surgical method using special sutures significantly reduced wound size and prevented disease return in patients with a scarring scalp condition.
[object Object]  August 2023 in “International journal of experimental research and review”
August 2023 in “International journal of experimental research and review” Ficus racemosa leaf extracts help heal diabetic wounds and lower blood sugar.
 16 citations,
March 2019 in “Experimental dermatology”
16 citations,
March 2019 in “Experimental dermatology” Injury changes how hair follicle stem cells behave, depending on the hair growth stage.
 March 2024 in “Authorea (Authorea)”
March 2024 in “Authorea (Authorea)” Using lyopreserved umbilical tissue allograft may improve healing and reduce recurrence of pilonidal cysts.
 January 2024 in “International journal of pharmaceutical sciences review and research”
January 2024 in “International journal of pharmaceutical sciences review and research” Indian jujube has many medicinal properties and can help treat ailments like diabetes, inflammation, and cancer.
 75 citations,
January 2011 in “Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery”
75 citations,
January 2011 in “Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery” The dermal regeneration template is effective in skin regeneration, reducing scarring, and has potential for future improvements.
 April 2016 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
April 2016 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” M2 macrophages help hair regrowth in wounds by making growth factors.
 17 citations,
October 2002 in “Dermatologic Surgery”
17 citations,
October 2002 in “Dermatologic Surgery” Successful surgical hair restoration requires careful planning, precise execution, and proper aftercare, using techniques like follicular unit transplantation and correct hair angling for best cosmetic results.
 1 citations,
July 2021 in “Aesthetic Plastic Surgery”
1 citations,
July 2021 in “Aesthetic Plastic Surgery” The new triangular flag-shaped design for incisions in hair transplant surgery provides better hair alignment and cosmetic appearance without extra scarring, especially for patients with specific hair directions.
 6 citations,
July 2017 in “Clinics in Plastic Surgery”
6 citations,
July 2017 in “Clinics in Plastic Surgery” The document concludes that individualized reconstruction plans are essential for improving function and appearance after head and neck burns.
 31 citations,
November 2013 in “Dermatologic Clinics”
31 citations,
November 2013 in “Dermatologic Clinics” The ARTAS robotic system for hair restoration is efficient with fewer cuts than manual methods, but it's limited to certain hair types and can still leave scars.
 13 citations,
September 2002 in “Dermatologic Surgery”
13 citations,
September 2002 in “Dermatologic Surgery” Effective repair of bad hair transplants requires skilled techniques and careful use of donor hair, with strategies like reimplantation and camouflage, and new methods to minimize scarring.
 2 citations,
April 2018 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
2 citations,
April 2018 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” The conclusion is that differentiating wound types in RDEB patients is important for clinical trials and understanding the disease.
 April 2005 in “AORN Journal”
April 2005 in “AORN Journal” The book is a detailed guide on dermatologic surgery techniques, recommended for both new and experienced doctors.
 1 citations,
January 2019 in “Springer eBooks”
1 citations,
January 2019 in “Springer eBooks” Hidradenitis Suppurativa is a chronic skin condition best treated early with surgery for better outcomes and less recurrence.
 September 2006 in “Dermatologic Surgery”
September 2006 in “Dermatologic Surgery” Some aggressive scalp cancers are hard to treat and can be deadly, even when removed with specialized surgery.
 18 citations,
September 2006 in “Dermatologic Surgery”
18 citations,
September 2006 in “Dermatologic Surgery” Aggressive scalp squamous cell carcinomas have a high death rate and need early, strong treatment.
 April 2018 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
April 2018 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Watching, not removing, skin growths with moderate atypia and positive edges is okay; patients may get melanoma elsewhere, especially if they've had it before.
 2 citations,
September 2023 in “Scientific reports”
2 citations,
September 2023 in “Scientific reports” The nanocomposite films with vitamins and nanoparticles are promising for fast and effective burn wound healing.

The conclusion is that closing scalp wounds is possible, but restoring hair without donor material is still a major challenge.
January 2025 in “Pharmaceuticals” Peptide-based hydrogels are promising for healing chronic wounds effectively.
 8 citations,
June 2022 in “Frontiers in bioengineering and biotechnology”
8 citations,
June 2022 in “Frontiers in bioengineering and biotechnology” A patch made from human lung fibroblast material helps heal skin wounds effectively, including diabetic ulcers.
January 2024 in “Journal of developmental biology” Abdominal skin heals faster than dorsal skin because it has more stem cells.




























