 4 citations,
January 2020 in “International Journal of Trichology”
4 citations,
January 2020 in “International Journal of Trichology” Too much epidermal growth factor can cause hair loss.
 12 citations,
February 2010 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
12 citations,
February 2010 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” A cancer drug caused unusual hair growth on a 100-year-old man's scalp and eyelashes.
 September 2021 in “Research Square (Research Square)”
September 2021 in “Research Square (Research Square)” Not having enough or having too much of the protein Grainyhead-like 3 leads to various developmental problems.
 77 citations,
March 2014 in “Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Medicine”
77 citations,
March 2014 in “Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Medicine” Fat cells are important for healthy skin, hair growth, and healing, and changes in these cells can affect skin conditions and aging.
 7 citations,
October 2018 in “BMC genomics”
7 citations,
October 2018 in “BMC genomics” Key genes can rewire networks, changing skin appendage types.

Hair follicle stem cells are crucial for touch sensation and proper nerve structure in mice.
 August 2019 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
August 2019 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Skin may help in getting rid of excess iron through the process of skin cell renewal.
 168 citations,
August 2009 in “EMBO molecular medicine”
168 citations,
August 2009 in “EMBO molecular medicine” Epidermal stem cells are diverse and vary in activity, playing key roles in skin maintenance and repair.
 44 citations,
January 2002 in “American Journal of Clinical Dermatology”
44 citations,
January 2002 in “American Journal of Clinical Dermatology” Skin reactions to antidepressants are common but usually not serious and can be treated.
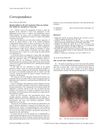 2 citations,
June 2005 in “Clinical Oncology”
2 citations,
June 2005 in “Clinical Oncology” A man's bald spot grew hair after starting cancer treatment with gefitinib.
76 citations,
March 2008 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Videodermoscopy can help diagnose and monitor nail bed psoriasis.
 46 citations,
November 2018 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
46 citations,
November 2018 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” The vitamin D receptor is essential for skin stem cells to grow, move, and become different cell types needed for skin healing.
 37 citations,
July 2016 in “Current Opinion in Cell Biology”
37 citations,
July 2016 in “Current Opinion in Cell Biology” Live imaging has advanced our understanding of stem cell behavior and raised new research questions.
December 2004 in “Differentiation” 6 citations,
July 2015 in “JAAD Case Reports” Doxycycline can effectively treat hair loss caused by EGFR inhibitors.
1 citations,
August 2013 in “The Journal of Cell Biology” Lack of Evi in skin causes psoriasis-like symptoms in mice.
 39 citations,
July 2021 in “Stem Cell Research & Therapy”
39 citations,
July 2021 in “Stem Cell Research & Therapy” Using fat stem cells and blood cell-rich plasma together improves healing in diabetic wounds by affecting cell signaling.
 1 citations,
July 2023 in “Communications biology”
1 citations,
July 2023 in “Communications biology” Removing Mediator 1 from certain mouse cells causes teeth to grow hair instead of enamel.
 23 citations,
August 2018 in “Facial Plastic Surgery Clinics of North America”
23 citations,
August 2018 in “Facial Plastic Surgery Clinics of North America” Using defensins to activate stem cells may improve skin aging signs without causing inflammation.
10 citations,
November 2017 in “Skin Appendage Disorders” Erosive pustular dermatosis in elderly people may be linked to aging immune systems and skin damage.
338 citations,
April 2001 in “Current Biology” c-Myc activation in mouse skin increases sebaceous gland growth and affects hair follicle development.
 4 citations,
January 2012 in “Chemical Immunology”
4 citations,
January 2012 in “Chemical Immunology” Some drugs, especially biologics, can cause skin reactions that look like other skin diseases, and stopping the drug usually helps clear up these reactions.
 81 citations,
April 2009 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
81 citations,
April 2009 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Hair shedding is an active process that could be targeted to treat hair loss.
 57 citations,
March 2018 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences”
57 citations,
March 2018 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences” The extracellular matrix is crucial for controlling skin stem cell behavior and health.
April 2018 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” Esrp1 is important for skin health by helping form and maintain the skin barrier.
39 citations,
November 2005 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” Fatp4 is crucial for healthy skin development and function.
135 citations,
December 2006 in “PLoS Medicine” Hyaluronate fragments can help reverse skin thinning by working with the CD44 receptor.
65 citations,
October 1988 in “Clinics in dermatology” The dermal papilla interacts with the epidermis to control hair growth and development.
 36 citations,
March 2011 in “Nature Communications”
36 citations,
March 2011 in “Nature Communications” Cells from a skin condition can create new hair follicles and similar growths in mice, and a specific treatment can reduce these effects.
 August 2016 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
August 2016 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” The hexosamine pathway helps protect skin cells from stress and may improve skin and hair health.




















